12-2 What are food chains and food webs?
12-2 What are food chains and food webs?
Food Chains
Organisms in a community are related by how they get their food. A food chain is a way of showing how the energy from food moves through populations of organisms. Every organism is part of a food chain.
Figure 12-4 shows a food chain. The arrows in the food chain show the direction that food and energy move along the chain. A producer, or part of a producer, is always the first link of a food chain. This food chain starts with a phytoplankton.
Most food chains have no more than five links. There is less energy available at the last link than at the first. That is because every time the energy passes from one organism to another, a portion of the energy is lost. Each consumer loses energy through activities, such as searching for food or escaping from predators.
Food Webs
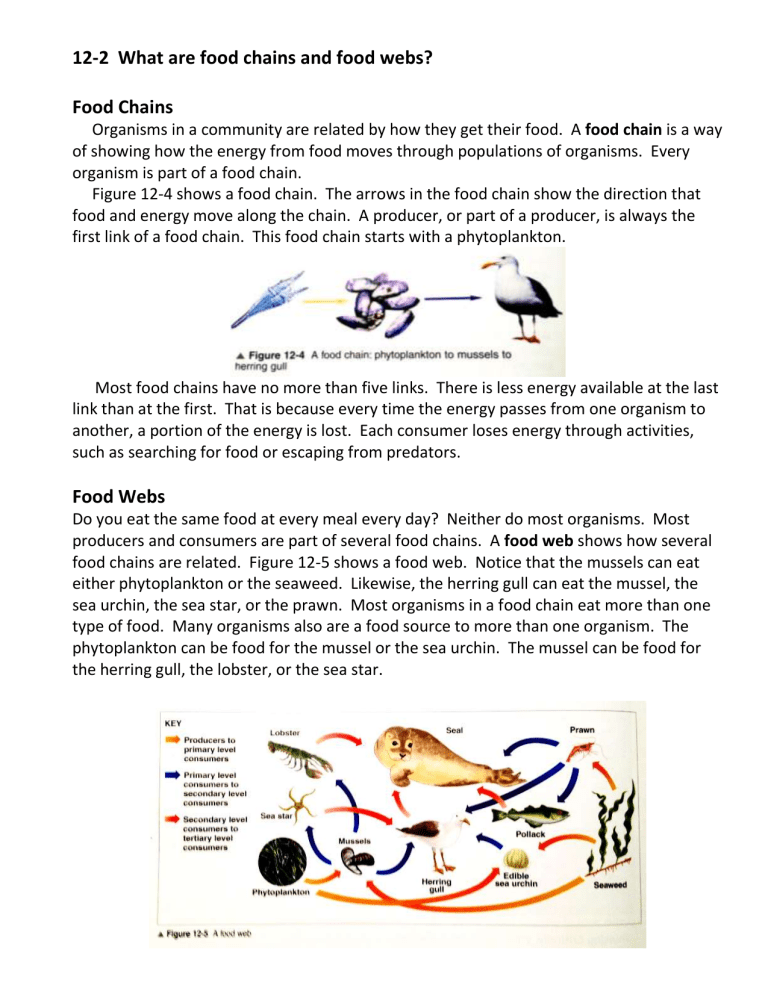
Do you eat the same food at every meal every day? Neither do most organisms. Most producers and consumers are part of several food chains. A food web shows how several food chains are related. Figure 12-5 shows a food web. Notice that the mussels can eat either phytoplankton or the seaweed. Likewise, the herring gull can eat the mussel, the sea urchin, the sea star, or the prawn. Most organisms in a food chain eat more than one type of food. Many organisms also are a food source to more than one organism. The phytoplankton can be food for the mussel or the sea urchin. The mussel can be food for the herring gull, the lobster, or the sea star.
12-2 What are food chains and food webs?
Lesson Review
PART A Answer the following questions about the diagram.
1. What is the diagram called? ________________________
_________________________________________________
2. What does the diagram show? ______________________
_________________________________________________
3. Which organisms in the diagram are primary consumers?
_________________________________________________
4. Which organisms in the diagram are tertiary consumers?
_________________________________________________
5. Which organism is the producer? ___________________
_________________________________________________
PART B Complete the following.
1. What is always the first link in a food chain? _______________________________________________
2. What is the limit of links that most food chains have? ________________________________________
3. Why is there less energy available at the last link than at the first link in a food chain? ___________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
4. What do the arrows in a food chain show? _________________________________________________
Skill Challenge
Skills: diagramming, applying concepts, classifying
In the space provided, draw a food web containing at least four organisms.
CHECKING CONCEPTS
1. What type of organism is always the first link in a food chain?
2. What do arrows show in a food chain?
3. Why is there less energy at the end of a food chain?
4. What is a food web?
.
.
.
.