Chest Physiotherapy: Physio in-service:
advertisement

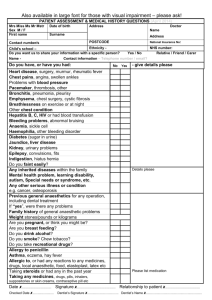
Treatment protocol for cardiopulmonary conditions Condition: Pulmonary TB: Chronic, infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis Signs and Symptoms: Persistent cough Loss of weight and appetite Night sweats Haemoptysis Chest pain: sharp pleuritic pain, or dull ache SOB Lethargy Low-grade fever Associated pneumonia Management: Drug regime: NB to educate patients to continue RX for 6 months!!! First line (2 months): Pyrazinamide, Isoniazid and Rifampicin Continuation phase (4 months): Isoniazid and Rifampicin Isoniazid: kills majority of bacilli rapidly, so that pt is non-infectious Rifampicin: kills persisting bacteria Aim of Physiotherapy Treatment: Objectives: Loosen and assist the removal of secretions Improve respiratory function Prevent chest deformities due to calcifications and thickening of pleura Assist in strengthening and mobility Precautions and contra indications: Chest physio is contra-indicated in presence of cavities, haemoptysis, severe respiratory distress or within the first 2 weeks of anti-TB drug therapy Precautions: Avoid percussion techniques due to risk of haemoptysis and pneumothorax Do not suction in pt with active TB IPPB should not be given if signs of cavitation Treatment Guidelines: Physiotherapy: Chest physio not indicated for TB as the condition is due to granulomas, not secretions! But patients can be treated for associated conditions: Collapsed lobe: Re-expansion ex’s Thoracic mobility ex’s Diaphragmatic breathing ex’s. In the presence of a secondary chest infection when ,on clinical examination secretions are present, the following can be used in therapy: Postural drainage Deep breathing Coughing The use of saline nebulisation preceding treatment Compiled by: Samantha Martin Date: 31/05/07 Reviewed: M Bez, Jan 2010