Chem Ch 6—Periodic Table Activity

Chem Ch 6—Assignments
Ch 6-1 pg 160
5) b
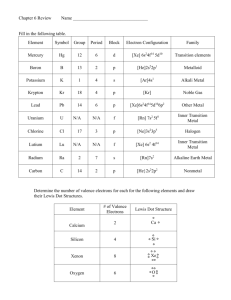
6) a) metal b) metalloid c) nonmetal
7) lithium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, or francium
Ch 6-2 pg 167 d) metal
12) They are in the same group and have the same number of electrons in the highest occupied energy level.
13) a) noble gas
14) Cu, Cd, Au, Co b) transition metal c) representative element
15) 5
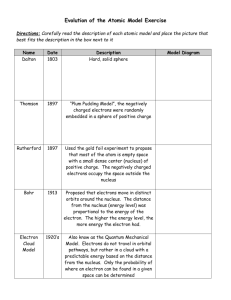
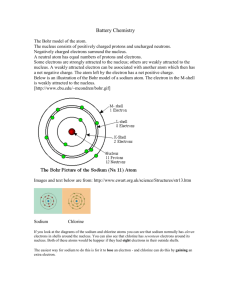
Elements Handbook: When atoms of a noble gas are energized, electrons move into higher energy levels. When the electrons return to lower energy levels, they emit light of specific frequencies. Each noble gas has a unique emission spectrum based on its unique electron configuration.
Ch 6-3 pg 178
22) sodium, aluminum, sulfur, chlorine: periodic trend
23) a) sodium b) phosphorus
WS 5-3 Practice
1) a) Cl b) Cl
2) a) Se
3) a) La
4) a) Cr
5) a) N
6) Rb atom b) S b) La b) Cr b) As
7) Br atom
8) Li +1 ion
9) Te -2 ion
10) Al b) P
WS 5-3 Apply
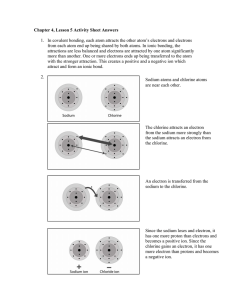
1) Chlorine has a greater/stronger positive charge in the nucleus due to the addition of protons that is able to pull the electrons that are added to the same energy level close to the nucleus decreasing the atomic radius.
2) Sodium would have a +1 charge. It would loose an electron to obtain an octet in its outer energy level. Chlorine would have a -1 charge. it would gain an electron to obtain an octet in its outer energy level.
3) Sodium has an ionization energy of 496 kj/mol and chlorine has an ionization energy of
1256 kj/mol. It is more difficult to remove an electron from a chlorine atom as its electrons are closer to the positively charged nucleus.
4) not in our content
5)
6) The sodium ion (Na +1 ) is larger than the sodium atom (Na). The lose of an electron pulls the remaining electrons closer to the nucleus that now has a greater charge.
The chlorine ion (Cl -1 ) is smaller than the chlorine atom (Cl). The gain of an electron pulls the remaining electrons farther away from the nucleus that now has a lesser charge.