storyboard
advertisement

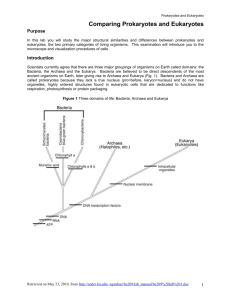
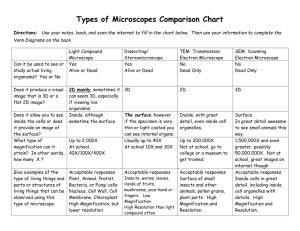
Presentation Details: Slides: 9 Duration: 00:03:46 Filename: C:\Users\jpage\Documents\NCVPS Learning Objects\Biology Cell Types Navigation to PPT W\Module 1 Lesson 2 Notes.ppt Presenter Details: Module 1 Lesson 2 Notes Cells are so small, How do we know about cell structure? You will learn about the compound light microscope and different types of cells in this lesson. Published by Articulate® Presenter www.articulate.com Slide 1 Module 1 Lesson 2 Notes The Microscope and Cell Types Duration: 00:00:10 Advance mode: By user Cells are so small, How do we know about cell structure? Notes: Module 1 Lesson 2 Notes. Cells are so small, how do we know about cell structure? You will learn about the compound light microscope and different types of cells in this lesson. You will learn about the compound light microscope and different types of cells in this lesson. Slide 2 Major Parts of the Microscope Duration: 00:01:06 Advance mode: By user Notes: These are the major parts of a compound light microscope. These are the major parts of a compound light microscope. You will need to learn all of these parts. You will need to learn all of these parts. Slide 3 Microscope Functions Duration: 00:00:21 Advance mode: Auto A microscope can be used to see objects at different magnifications. The higher the magnification the closer the detail of the object. To calculate the power of magnification, multiply the power of the eyepiece by the power of the objective. Eyepiece Published by Articulate® Presenter Notes: A microscope can be used to see objects at different magnifications. The higher the magnification the closer the detail of the object. To calculate the power of magnification, multiply the power of the eyepiece lens by the power of the objective. Objectives www.articulate.com Slide 4 Magnification Duration: 00:00:36 Advance mode: Auto Slide 5 Cell Types Duration: 00:00:11 Advance mode: Auto Slide 6 Two Basic Cell Types Duration: 00:00:09 Advance mode: Auto Published by Articulate® Presenter As you increase the magnification of an object you can see better details of the object, but you cannot see as much of the object because you are closer to it. This is a table to show sample magnifications on a standard light microscope. Eyepiece Magnification 10x 10x 10x Objective Magnification 4x 10x 40x Total Magnification 40x 100x 400x Cells come in all shapes and sizes. Below you can see a muscle cell, a nerve cell and red blood cells. Not all cells have the exact same components or make up. Notes: As you increase the magnification of an object you can see better details of the object, but you cannot see as much of the object because you are closer to it. This is a table to show sample magnifications on a standard light microscope. Notes: Cells come in all shapes and sizes. Below you can see a muscle cell, a nerve cell and red blood cells. Not all cells have the exact same components or make up. Notes: The two basic types of cells are: Eukaryote and Prokaryote www.articulate.com Slide 7 Prokaryotes Traits of Prokaryotes Traits of Prokaryotes Duration: 00:00:28 Advance mode: Auto 1-No nucleus, and their genetic material is stored on DNA called plasmids. 2-No membrane-bound organelles 3-Have ribosomes (like eukaryotes) 4-Smaller than eukaryotes 5-Bacteria are all prokaryotes 6-Much more simple than eukaryotes Slide 8 Eukaryotes Duration: 00:00:25 Advance mode: Auto Slide 9 Plant and Animal Cells Duration: 00:00:19 Advance mode: Auto Published by Articulate® Presenter Notes: 1-No nucleus, and their genetic material is stored on DNA called plasmids. 2-No membrane-bound organelles 3-Have ribosomes (like eukaryotes) 4-Smaller than eukaryotes 5-Bacteria are all prokaryotes 6-Much more simple than eukaryotes Traits of Eukaryotes Notes: 1-Genetic material (DNA) is stored in a nucleus. 2-Have membranebound organelles (mitochondria, vacuole, chloroplasts) 3-Have ribosomes 4-Larger and more complex than prokaryotes 5-All plants, animals, fungi and protists are composed of eukaryotic cells. Traits of Eukaryotes 1-Genetic material (DNA) is stored in a nucleus. 2-Have membranebound organelles (mitochondria, vacuole, chloroplasts) 3-Have ribosomes 4-Larger and more complex than prokaryotes 5-All plants, animals, fungi and protists are composed of eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes: Plant and Animal Cells Plant Animal -Cell Wall -No Cell Wall -Chloroplasts -No Chloroplasts -One Large Vacuole -One or more small -Typically rectangular vacuoles in shape -Spherical in shape Notes: Eukaryotes: Plant and Animal Cells Plant Animal -Cell Wall -No Cell Wall -Chloroplasts -No Chloroplasts -One Large Vacuole -One or more small -Typically rectangular vacuoles in shape -Spherical in shape www.articulate.com Published by Articulate® Presenter www.articulate.com