Word
advertisement

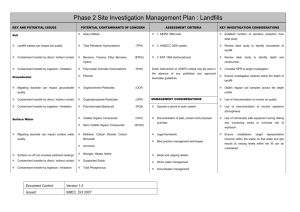
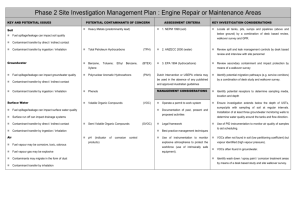
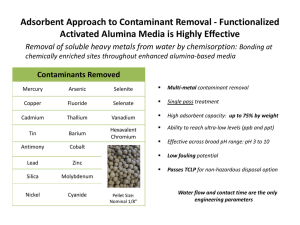
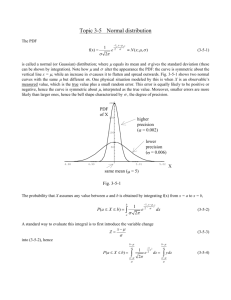
CE 499: Applied Contaminant Transport Modeling Instructor Felipe de Barros, Assistant Professor, Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Office: KAP 224B E-mail: fbarros@usc.edu Telephone: 213-740-6130 Topics Introduction to contaminant transport in the environment (surface and subsurface flows); Mass balance equations; Basic transport phenomena (advection, molecular diffusion, dispersion); Chemical reactions & radioactive decay; Transport in rivers and streams; Transport in aquifers; Fundamentals of groundwater hydrology (soil properties, Darcy’s Law, governing equations); human health risk assessment; uncertainty quantification and probabilistic risk analysis; flow heterogeneity and mixing. Objectives 1) Learn fundamentals of contaminant transport modeling in surface water and groundwater. Understand the consequences of pollutants in the environment and human health. 2) Understand basic physical and chemical transport processes affecting contaminants in surface and subsurface water environments 3) To become familiar with the use of statistical and probability analysis for risk assessment 4) To become experienced with modeling techniques commonly used in hydrological and hydrogeological applications 5) Develop basic coding skills to perform simulations and predict the magnitude, extension and impact of contaminants in the environment 6) Develop a systematic modeling approach to solve environmental, health and sustainability issues. Textbook Chemical Fate and Transport in the Environment, Hemond & Fechner-Levy, Academic Press; 2 edition (September 21, 1999) Other references Mixing in inland and coastal waters. Fischer et al., Elsevier, 1979. Hydraulics of Groundwater, Jacob Bear, 1979 (Dover books on Engineering). Suggested Preparation CE 309 – Fluid Mechanics, or equivalent. Some coding experience (you are free to use any computational software that you are familiar with, e.g., Matlab, Mathematica, Maple, Fortran, C++, etc.) Grading Midterm Exam (25%), Homework (25%), Final Project (50%) 1 CE 499 Applied Contaminant Transport Modeling Week 1: Introduction to contaminant transport and its importance in the environment; Practical problems. Week 8: Contaminant transport in groundwater; sources of contaminants in the subsurface; soil properties Week 2: Week 9: Chemical concentration; mass balance (conservation law) Connectivity, anisotropy, homogeneity; Groundwater flow equation; Introduction to contaminant transport in groundwater (con’t) Week 3: Basic fluid mechanics Week 10: Contaminant transport in groundwater; Aquifer Week 4: remediation (con’t); Diffusion, advection and dispersion Week 5: Diffusion, advection and dispersion (con’t). Exam Review. Week 6: Contaminant transport in surface water (rivers). Week 7: Contaminant transport in surface water (rivers) (con’t) Week 11: Exam Review. Midterm Exam. Week 12: Uncertainty quantification (review of statistics). Week 13: Probabilistic human health risk analysis; Monte Carlo simulations Week 14: Mixing and heterogeneity. Week 15: Interactions between surface water and groundwater Week 16: Project Presentations 2