Phase 2 Site Investigation Management Plan : Sewage Treatment
advertisement
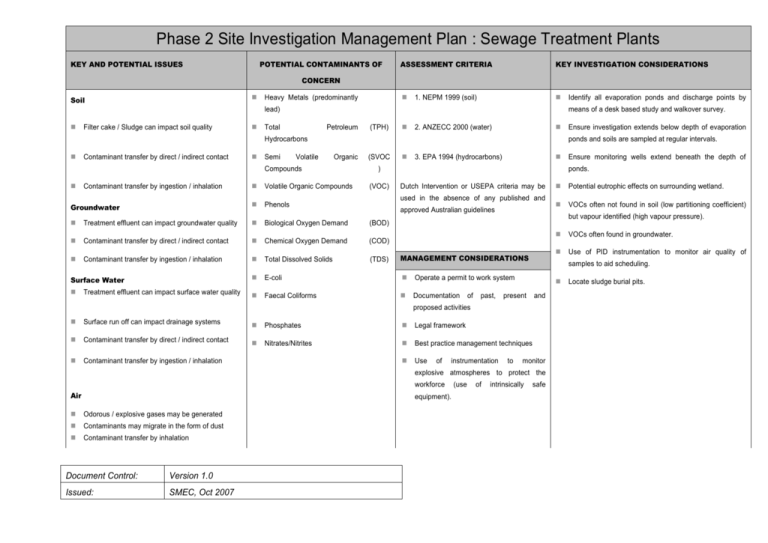
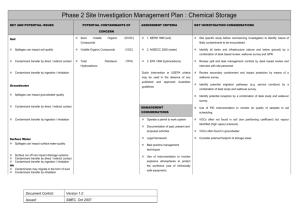
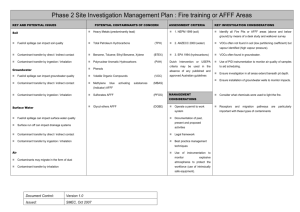
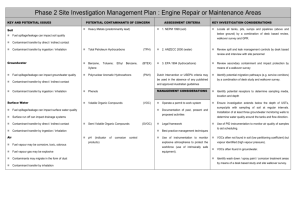
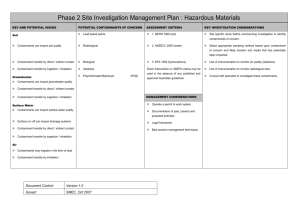
Phase 2 Site Investigation Management Plan : Sewage Treatment Plants KEY AND POTENTIAL ISSUES POTENTIAL CONTAMINANTS OF ASSESSMENT CRITERIA KEY INVESTIGATION CONSIDERATIONS CONCERN Soil Heavy Metals (predominantly 1. NEPM 1999 (soil) lead) Filter cake / Sludge can impact soil quality means of a desk based study and walkover survey. Total Petroleum (TPH) 2. ANZECC 2000 (water) Hydrocarbons Contaminant transfer by direct / indirect contact Semi Volatile Organic (SVOC 3. EPA 1994 (hydrocarbons) ) Volatile Organic Compounds Groundwater Phenols Treatment effluent can impact groundwater quality Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) Contaminant transfer by direct / indirect contact Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Contaminant transfer by ingestion / inhalation Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) Surface Water E-coli Operate a permit to work system Treatment effluent can impact surface water quality Faecal Coliforms Documentation Surface run off can impact drainage systems Phosphates Legal framework Contaminant transfer by direct / indirect contact Nitrates/Nitrites Best practice management techniques Contaminant transfer by ingestion / inhalation Use (VOC) Dutch Intervention or USEPA criteria may be used in the absence of any published and approved Australian guidelines MANAGEMENT CONSIDERATIONS of past, of instrumentation equipment). Odorous / explosive gases may be generated Contaminants may migrate in the form of dust Contaminant transfer by inhalation Document Control: Version 1.0 Issued: SMEC, Oct 2007 (use of Potential eutrophic effects on surrounding wetland. VOCs often not found in soil (low partitioning coefficient) VOCs often found in groundwater. Use of PID instrumentation to monitor air quality of present to samples to aid scheduling. and monitor explosive atmospheres to protect the workforce but vapour identified (high vapour pressure). proposed activities Air Ensure monitoring wells extend beneath the depth of ponds. Contaminant transfer by ingestion / inhalation Ensure investigation extends below depth of evaporation ponds and soils are sampled at regular intervals. Compounds Identify all evaporation ponds and discharge points by intrinsically safe Locate sludge burial pits.