Test Review: Unit II Cells and microscopes What is a prokaryote? A
advertisement

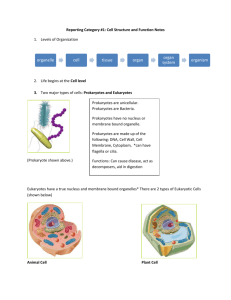
Test Review: Unit II Cells and microscopes 1. What is a prokaryote? A prokaryote is a single celled organism that does not have a nucleus. 2. What is an example of an organism that has prokaryotic cells? An example of a prokaryotic organism is bacteria. 3. What is a eukaryote? Can be a single celled organism or a multicelled organism. Eukaryotes have a distinct nucleus in their cells. 4. What is an example of an organism that has eukaryotic cells? Human, pig, dog, yeast. 5. What is an organelle? An organelle is a specialized compartment within a cell that has a particular function. Organelle means “little organs” because they are like organs in that they have a distinct job. 6. List 4 ways that prokaryotes are different from eukaryotes. 1) Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus and eukaryotes do. 2) Prokaryotes are single celled and eukaryotes can be multicelled or single celled. 3) Prokaryotes have a flagella to help them move and eukaryotes do not. 4) Prokaryotes do not have membrane bound organelles in their cell and eukaryotes do. 5) Prokaryotes are a lot smaller than eukaryotic cells. 7. Draw and label a bacteria, an animal and a plant cell 8. What 4 things do all cells have? a. Cell Membrane b. DNA c. Cytoplasm d. Ribosomes 9. What organelles are found in plant cells but not animal cells? Cell Wall, Cloroplasts, and Central Vacuoles 10. What are the functions of the following organelles? a. Cell membrane: To protect the cell and to only allow substances to enter and leave the cell. b. Cell wall: Organelle that provides structure and protection to the cell. (only in plants and some bacteria) c. Cytoplasm: Semi-liquid material between nucleus and cell membrane d. Ribosomes: Organelle that manufactures (build) proteins. e. Nucleus: Organelle that controls cellular processes and contains/protects the genetic information. (DNA) f. Endoplasmic reticulum: i. Smooth E.R.: Site where lipids for the cell membrane are put together. Does not contain ribosomes and therefore is “smooth”. ii. Rough E.R.: Site where proteins are manufactured prior to being exported from the cell. Contains ribosomes and is there for considered “rough”. g. Golgi body (apparatus): Organelle that modifies, packages, sorts, and ships proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum and other materals to be stored in cell or secreted from the cell. (This of a post office) h. Central vacuole: Organelle found in plants that stores water, salts, ions, and minerals. i. Chloroplast: Photosynthesis takes place here. Captures light energy and converts it into chemical energy in sugar. Found in plants and some photosynthetic bacteria. j. Mitochondria: Cellular respiration takes place here. Converts chemical energy into useable energy (ATP) for the cell. This is the organelle that produces energy for our cells. k. Lysosome: Organelle that contains enzymes for the digestion of biomolecules and breaking down worn out cellular parts. 11. Which organelle is comparable to the human excretory system? Lysomsomes 12. Which organelle would you expect to find a lot of in cells that need a lot of energy? Mitochondria 13. What is cell differentiation? Cell differentiation is when cells become specialiezed for a specific function. For example, we have skin cells, muscle cells, and neurons. These are all specialized cells. 14. What is the function of: a. Epithelial cells: Also known as skin cells. Are specialized for protection. b. Bone cells: Specialized cells that are important for providing support and for movement. c. Nerve cells: Carry messages throughout our body. 15. What determines the function of a cell? DNA determines the function of the cell. 16. Where are the instructions found that build these cells (#14)? Why aren’t they all the same? In our genetic information (DNA) is where the instructions are found. The cells are not the same because the DNA code that builds the cells is not the same. 17. What allowed scientists to come up with the cell theory? Microscope Development. 18. While using a microscope, you are asked for the total magnification of a specimen. How do you find the total magnification? Multiply the objective lens times the magnification power that you are using. 19. Label parts of the microscope: 20. When preparing a wet mount of a specimen, why are stains like methylene blue used? Stains are used to dye cells so that they are easily seen under a microscope. 21. Which direction would you move this slide to center the cell in the field of view? To the Left and Down. 22. What is the diameter of this cell? 0.5 mm 23. Why do you use low power to find a specimen instead of high power? You want to get a larger field of view to focus the specimen.