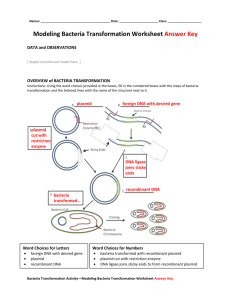
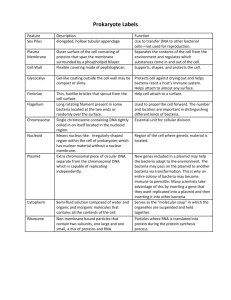
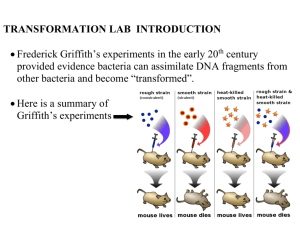
pGLO
advertisement

MIRAMAR COLLEGE Intro to Molecular & Cellular Biology Laboratory (Bio210A) Instructor: Elmar Schmid, Ph.D. Data Collection & Analysis Data Collection Observe the results on your four agar plates you obtained from the previous transformation lab under normal room lighting Then turn off the room light and observe the colonies under ultraviolet (UV) light by holding the UV lamp over it Carefully observe and draw what you see on each of the four plates. Put your drawings as well as your written report in the corresponding rows and columns of the data table below Data Table: _______________________ (Student Name) Plate Image Colonies Color Size (under UV) (Ø mm) Count LB-amp + pGLO LB-amp/ara LB-amp pGLO (Control) LB 1 MIRAMAR COLLEGE Intro to Molecular & Cellular Biology Laboratory (Bio210A) Instructor: Elmar Schmid, Ph.D. Result Analysis & Calculation of Transformation Efficiency The goal of data analysis for this part of the lab is to determine if and to which extent genetic transformation of the bacteria occurred Before going to the part where you will calculate the transformation efficiency of your transformation experiment, let’s first ask a couple of more general questions 1. Which of the traits listed below and that you originally observed for E.coli did NOT seem to become altered after transformation? (Circle your answer(s) a. the colony shape b. the colony color under normal light c. the size (diameter) of the colony d. bacterial motility e. metabolic rate 2. Of the E.coli traits you originally noted, which seem now to be significantly different or altered after performing the transformation procedure? List those traits below and describe the changes you observed. New trait Observed change 3. If the genetically transformed cells have acquired the ability to live in the presence of the antibiotic ampicillin, then what might be inferred about the other genes, e.g. for GFP, on the plasmid pGLO you used in your transformation experiment? 4. From the results that you obtained, how could you prove that the changes with E.coli you observed were due to the transformation procedure? 5. Look again at your four agar plates. Do you observe E.coli colonies on the LB plate (= Plate #4) without ampicillin (amp) or arabinose (ara)? Why? 6. From your results, can you tell if these bacteria growing on plate #4 are ampicillin-resistant by simply looking at them (different shape? Color? etc.)? 2 MIRAMAR COLLEGE Intro to Molecular & Cellular Biology Laboratory (Bio210A) Instructor: Elmar Schmid, Ph.D. 7. How would you change the environment of the bacteria, i.e. the plate they grow on, to best tell IF they are ampicillin resistant? 8. Very often in biology, an organisms traits are caused by a combination of its genes and its environment. Think about the fluorescent green color you in the genetically transformed bacteria (which gained a new trait). 8.1. What two factors must be present in the bacteria’s environment for you to see the new trait “green fluorescent color”? (Hint: one factor is in the agar plate; the other factor is how you looked at the bacteria after transformation) Factor 1: Factor 2: ________________________ ________________________ 8.2. What do you think each of the two environmental factors you listed above are doing to trigger the expression of the new genetic trait “green fluorescent color” 8.3. What advantage would there be for an organism to be able to turn on or off particular genes in response to certain conditions? 8.4. What do you think might be the advantage of the phenotype “green fluorescent body color” in the (natural) marine environment of the jellyfish “Aequorea victoria”, form which the GFP gene was originally isolated? 3 MIRAMAR COLLEGE Intro to Molecular & Cellular Biology Laboratory (Bio210A) Instructor: Elmar Schmid, Ph.D. Lab Summary Questions ________________________ (Student Name) (mandatory part of your weekly lab report; answer the questions below and turn sheet back to your instructor at the beginning of the next lab session) Q. 1: The ori region on plasmids A) is the site where the antibiotic gene is located B) is the site where a foreign gene has been inserted C) is the site where DNA replication begins D) is the site where the plasmid is anchored with the cell membrane Q. 2: Many biotechnology-modified and commercially available plasmids have socalled MCS sequences? What does “MCS” stand for? ________________________________________________ Q. 3: Which of the following statements about a MCS is/are correct? A) it serves as site for the easy deletion of antibiotic genes B) it serves as site for the easy identification of positive bacterial clones after transformation C) it serves as the site for the easy and predictable insertion of foreign DNA sequences or genes D) it serves as a site enabling the later isolation of the plasmid from the bacteria E) it is a bacterial evolutionary “left-over sequence” which has no function Q. 4: The transformation technique which relays on strong electrical discharges to insert DNA, e.g. a plasmid, into bacteria is referred to as: A) electrophoresis B) electroporation C) electrolysis D) electroshocking E) sonication Q. 5: The heat-shock method of bacterial transformation relays on the presence of cations, such as calcium (Ca2+) for optimum efficiency. Explain why. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Q. 6: Which of the following temperatures do molecular biologist commonly use to “heat-shock” the bacteria during the heat-shock transformation method? A) 25oC B) 37oC C) 42oC D) 56oC E) 95oC 4 MIRAMAR COLLEGE Intro to Molecular & Cellular Biology Laboratory (Bio210A) Instructor: Elmar Schmid, Ph.D. Q. 7: What was the source of the green fluorescent light you observed in the successfully transformed E.coli bacteria on agar plate #2 after UV irradiation? A) the pGLO plasmid B) the GFP gene C) GFP D) bacterio chlorophyll become excited E) the autofluorescence of certain bacterial proteins under UV Q. 8: Why is the marine jellyfish Aequorea victoria, which naturally expresses GFP, capable to glow with a green fluorescent light without UV irradiation? Q. 9: After transformation with an antibiotic resistance gene-carrying plasmid, which bacteria die during the following selection step using the antibiotic -containing LBagar plates? A) the bacteria which did not take up the resistance gene-containing plasmid B) the bacteria which took up the resistance gene-containing plasmid 5 SOUTHWESTERN COLLEGE School of Mathematics, Science & Engineering Intro Molecular & Cellular Biology Lab (BIO 211): Instructor: Elmar Schmid, Ph.D. 6