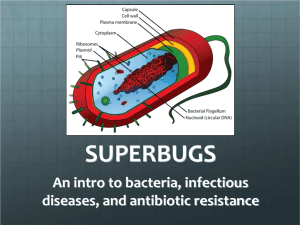
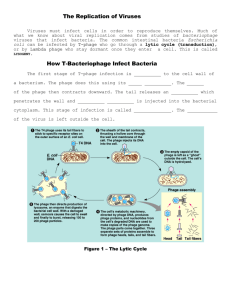
объявление о докладе Зета
advertisement

Понедельник, 7 февраля, 15-00 Зал совещаний, БОН, 5-й этаж Kornelius Zeth Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology Department of Protein Evolution Tuebingen, Germany How to kill a bacterium – structures and mechanisms Bacteria are the target of different anti-microbial molecules derived from the variety of surrounding combatants. These molecules can be produced by neighboring bacteria of the same local niche or from eukaryotic hosts which suppress the uncontrolled bacterial spread by the secretion of anti-microbial peptides. Bacteriocins are the most well known class of proteins which are secreted by many bacterial strains to kill closely related bacteria in solution. Strategies of higher eukaryotes are different in that anti-microbial peptides are secreted to suppress the bacterial growth and possible infections. New protein structures of both classes of molecules provide hints into the specific underlying mechanisms of uptake and action. Приглашаются все желающие!