Density Lab
advertisement

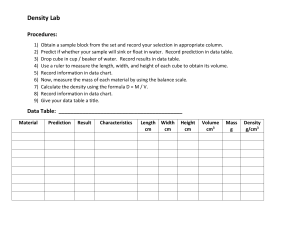
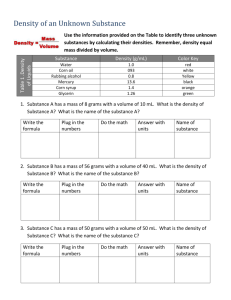
Lab: Density Purpose: to calculate the density of various substances and determine whether the objects will sink or float in water. Materials: Part 1 10 ml graduated cylinder triple beam balance 50 ml graduated cylinder various objects Part 2 Container of water Calculator Part 1 A. Take the mass of a 50 beaker and record it in Table 1. B. Measure 10 mL of water in the graduated cylinder marked “water” and pour the water into the beaker. Record the volume of the water in Table 1. C. Take the mass of the beaker and water and record the mass in Table 1. D. Dump the water into the sink and use a paper towel to dry out the beaker. E. Repeat steps A-D for the oil (but pour the oil back into the beaker of oil, not down the drain). F. Choose 1 of the cubes from your tray and record the number of the block in Table 2. G. Measure the mass of the cube and record it in Table 2. H. Measure the length, width and height of the block and record these measurements (in cm) in Table 2. I. Record the identity of the last object in your tray in table in Table 3. J. Determine the mass of the object and record this measurement in Table 3. K. Use the 50 ml graduated cylinder (and the liquid displacement method) to determine the volume of this object. Record this measurement in Table 3. Part 2 L. Record the number of the blocks you measured in steps F-H in Table 4. M. Record the identity of the last object you measured in Table 4. N. Use the formula D = m/V to calculate the density of the all substances. Record these densities in Table 4. O. Carefully place each object in the container of water. Record whether each object sinks or floats. Name _____________________________________ Lab Worksheet: Density Table 1: Water Measurements Substance Measured Mass (g) Volume (mL) Water Oil Table 2: Block Measurements Mass (g) Length (cm) Width (cm) Block # Identity of object Substance Water Oil Block # ______ Block # ______ Substance: Table 3: Object Mass (g) Height (cm) Volume (mL) Table 4: Densities of Substances Density Sink or float? g/mL g/mL g/cm3 g/cm3 g/mL Questions: 1. Which substances floated? 2. Which substances sunk? 3. In general, did the substances that floated have a density greater than or less than 1? 4. Predict whether the following substances will float or sink. Hydrogen (0.00009 g/cm3) - ________________________ Aluminum (2.7 g/cm3) - _____________________ Gold (19.3 g/cm3) - _____________________ 5. Use the information in lab to explain why a helium-filled balloon floats in air.