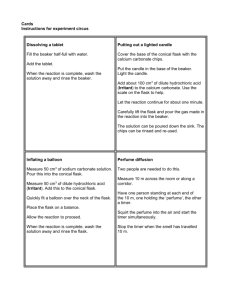
Topic 18 Dissociation constant of weak acids
advertisement

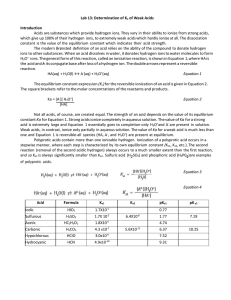
IB CHEMISTRY Determination of the dissociation constant of weak acids Introduction When a weak acid dissolves in water, it breaks apart or dissociates to a slight extent. A proton from the acid is donated to a water molecule. The equation for the dissociation and the equilibrium constant expression are as follows: HA + H2O H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq) Ka = [H+(aq)] [A- (aq)] [HA] where A represents the anion of the weak acid and the square brackets indicate molar concentrations of the species. For most acids the percent of acid that dissociates is less than 5 %. The value of the equilibrium constant, Ka, indicates to what extent this reaction occurs. The greater the value of Ka , the stronger the acid, and the greater the amount of dissociation. This experiment is designed to determine the Ka and pKa values of a number of weak acids. Ethanoic acid, CH3COOH, will be used as an example for the experimental procedure. When ethanoic acid is in water solution, an equilibrium exists in which a mixture of ethanoic acid, hydrogen ions and ethanoate ions will all be present: CH3COOH (l) + H2O (l) H3O+ (aq) + CH3COO- (aq) Ethanoic acid and ethanoate ions are conjugate acid-base pairs. A conjugate acid is a substance that has one more proton in its structure that its corresponding conjugate base. This combination also results from a mixture of a weak acid, ethanoic acid, and its salt, sodium ethanoate. The equilibrium expression is : [ H+ (aq) ] [CH3COO- (aq)] = 1.8 x 10-5 Ka = [CH3COOH] If a solution contains equal concentrations of CH3COOH and CH3COO- , these concentration terms cancel out in the above equation so that Ka = [ H+ (aq) ] = 1.8 x 10-5 , and pH = pKa = 4.74. We will prepare solutions in which the concentrations of acid and its anion are equal. The value of the pH of the solution will then equal the pKa for the acid. Aim: To determine experimentally the dissociation constant of a selection of weak acids. Chemicals unknown acids phenolphthalein solution ethanoic acid solution NaOH (aq), 0.1 mol dm-3 conical flask pH meter electronic balance weighing boats Apparatus beaker, 100 cm3 graduated cylinder, 50 cm3 dropping pipette glass rod conical flask, 100 cm3 Safety alert Acids and bases are harmful to skin and eyes. Wash spills off skin with lots of water. Neutralise acid spills on the table with baking soda; neutralise base spills with vinegar. Phenolphthalein is dissolved in alcohol, so it is flammable. Keep the solution away from flames. Wear goggles. Procedure (if the acid is already in solution, start at step 3 1. Measure out a small quantity of the acid to be tested, about 0.2 g. It is not necessary to know the exact amount. However, if you know the exact amount you can also calculate the molar mass to provide further evidence of the identity of the weak acid. 2. Measure precisely 50.0 cm3 of distilled water into a beaker, add the acid, stir to dissolve and mix well. 3. Pour 25.0 cm3 of the acid solution into a conical flask. You should have 25.0 cm3 of acid left in the beaker. Add 3 drops of phenolphthalein solution to the acid solution in the comical flask, and then using the dropping pipette, add NaOH solution dropwise while swirling the flask. 4. Stop adding the NaOH when the first pink colour persists throughout the solution for at least 5 seconds. 5. At this point the beaker contains exactly one-half of the original acid, essentially all of which is in the undissociated form, HA. The conical flask now contains an equal amount of the conjugate base/salt of the acid as all the acid in the flask has been neutralized: OH- + HA H2O + A- 6. Pour the contents of the conical flask into the beaker of the left over weak acid and mix the solution. 7. Using a pH meter or probe, measure the pH of this solution, which contains equal concentrations of undissociated weak acids and conjugate base/salt. The measured pH is the pKa of the weak acid. Calculate the value of Ka of the acid. Data Collection Show your data in an appropriate results table Conclusion and evaluation Draw your conclusion and carry out an evaluation of both procedure and result.