AnVil Informatics – Application Systems – 6-14-01
advertisement

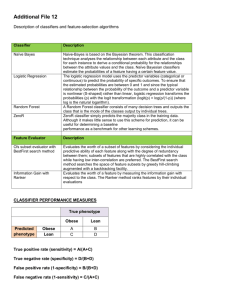
AnVil Informatics – Application Systems – 6-14-01 This document briefly outlines some specific applications, which could be implemented currently using techniques developed with AnVil technologies. These applications are to be applied to specific problems in the bioinformatic or cheminformatic arenas. For the most part the techniques have been tried or implemented using various tools including AnVil’s Java platform, the new DS and other commercial or public domain packages. Outline of Specific Application Systems 1. Specific applied Classifiers - AnVil can evaluate and produce the best possible classifier from 100 hundreds of possible models or classifiers. For example we can generate most possible “state of the Art classifiers” such as “Support Vector machines” , Random Forests or standard back-prop Neural Networks. The key points are that to get the best possible classifier “data enhancement” is usually necessary. In many cases a standard back-propogation NN may be the best or unfortunately it may be impossible to get the accuracy desired. 2. A Radviz Gradual Visual Classifier – Training, Validation and testing any kind of data can be made much more “user friendly” with interaction and the “graduated classification” Radviz system. 3. Clustering and Specific Cluster Comparison – which clustering technique best clusters your data for example to some known functional description. AnVil’s proprietary cluster comparison methods will tell you which is best. A myriad of clustering techniques can be applied such as Kohonen, K-means, Hiarchical, PCA and variations. 4. Micro Array Gene Expression Disease Classifier– filtering, selection, MultiDisease Classifier. – This system can find the optimum gene set to diagnose two or more disease states using various gene selection mechanisms such as AbsentPresent user selectiont (dendrogrammatic?) and RadViz differential selection, PURS (Principle Uncorrelated Record Selection) and 3-way differential clustering. 5. Quality Control MetaData Analysis System – Using a full statistical analysis, multi-correlation and Multi-class analysis quality control data is analyzed and visualized to get a high level overview of your data. 6. Data Cleaning, Impute Missings, Extraction and Organizing System - This system is used to take a customers unformatted, dirty, and unorganized data and produce a coherent database system which can be easily data mined. 7. Partial Subset Visual Classifier – On systems where classification accuracy is not high enough, or a “black box” classifier is not satisfactory this system uses “association rules” and RadViz to find “subset” areas in a dataset that can be classified with a high accuracy. 8. Gene Correlation Searching/Analysis – based on our threee correlation methods (Pearson , Jacknife and Cosine) we could build a database of gene correlation over different experiments. For example in one experiment we have looked at the two genes U11863(1713) and. U39400(2011) and found a very high negative correlation(-0.976). A database query system could be built for customers with different correlation values for different experiments. Most of the above “systems” are “virtual” meaning that currently they can only be implemented with a lot of “manual” work, but some or all of them could be implemented (in varying degrees) into a “turnkey” system. How much software development is necessary to implement some of these systems? Each system would take at least a week to come up with a realistic estimate of the effort involved. Patrick Hoffman