The Atom & Periodic Table
advertisement
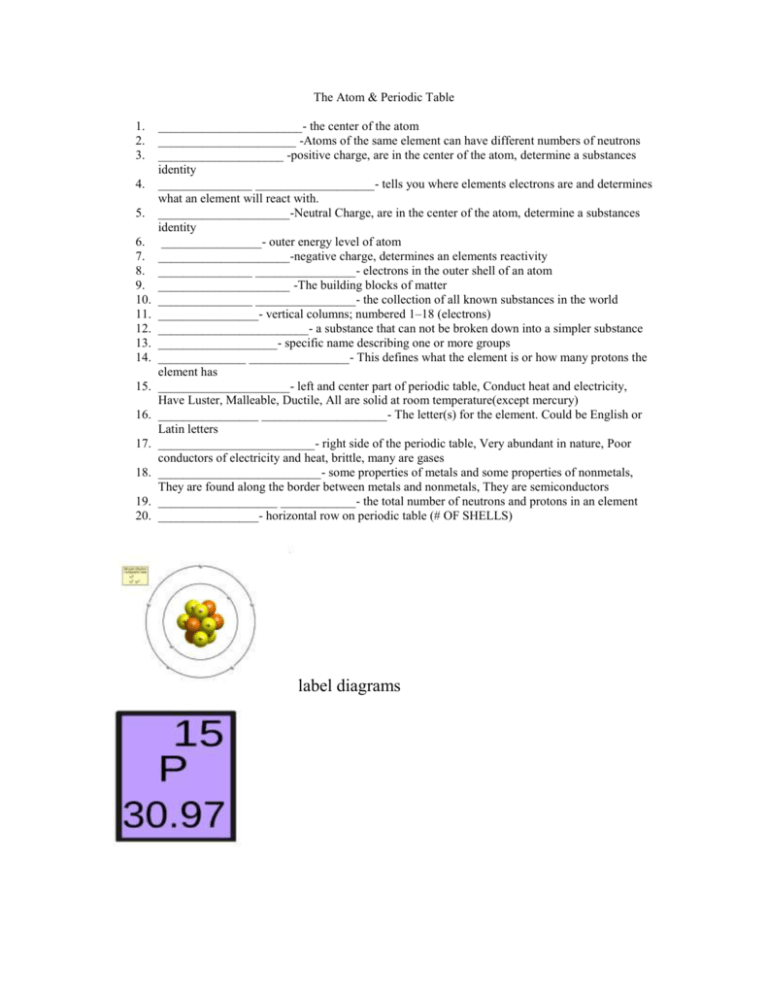
The Atom & Periodic Table 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. _______________________- the center of the atom ______________________ -Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons ____________________ -positive charge, are in the center of the atom, determine a substances identity _______________ ___________________- tells you where elements electrons are and determines what an element will react with. _____________________-Neutral Charge, are in the center of the atom, determine a substances identity ________________- outer energy level of atom _____________________-negative charge, determines an elements reactivity _______________ ________________- electrons in the outer shell of an atom _____________________ -The building blocks of matter _______________ ________________- the collection of all known substances in the world ________________- vertical columns; numbered 1–18 (electrons) ________________________- a substance that can not be broken down into a simpler substance ___________________- specific name describing one or more groups ______________ ________________- This defines what the element is or how many protons the element has _____________________- left and center part of periodic table, Conduct heat and electricity, Have Luster, Malleable, Ductile, All are solid at room temperature(except mercury) ________________ ____________________- The letter(s) for the element. Could be English or Latin letters _________________________- right side of the periodic table, Very abundant in nature, Poor conductors of electricity and heat, brittle, many are gases __________________________- some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals, They are found along the border between metals and nonmetals, They are semiconductors ___________________ ____________- the total number of neutrons and protons in an element ________________- horizontal row on periodic table (# OF SHELLS) label diagrams ANSWERS-The Atom & Periodic Table 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. nucleus_______________________- the center of the atom isotopes___________ -Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons protons________ -positive charge, are in the center of the atom, determine a substances identity electron configuration___- tells you where elements electrons are and determines what an element will react with. neutrons__-Neutral Charge, are in the center of the atom, determine a substances identity shell________- outer energy level of atom electrons__________-negative charge, determines an elements reactivity valence______________- electrons in the outer shell of an atom atoms_____________ -The building blocks of matter periodic table_______________- the collection of all known substances in the world groups/families_______- vertical columns; numbered 1–18 (electrons) element____________- a substance that can not be broken down into a simpler substance family_____- specific name describing one or more groups atomic number________- This defines what the element is or how many protons the element has metals_________- left and center part of periodic table, Conduct heat and electricity, Have Luster, Malleable, Ductile, All are solid at room temperature(except mercury) symbol_________________- The letter(s) for the element. Could be English or Latin letters nonmetals_______- right side of the periodic table, Very abundant in nature, Poor conductors of electricity and heat, brittle, many are gases metalloids _______- some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals, They are found along the border between metals and nonmetals, They are semiconductors atomic mass ______- the total number of neutrons and protons in an element periods_______- horizontal row on periodic table (# OF SHELLS)









