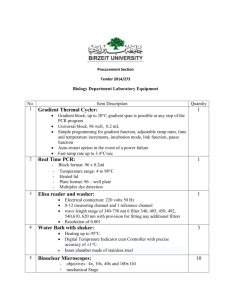
ICA MatLab Code from Appendix D (file: ica_appD_demo.m)
advertisement

%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Demonstration code for "Independent component analysis: A Tutorial
Introduction"
% JV Stone, MIT Press, September 2004.
% Copyright: 2005, JV Stone, Psychology Department, Sheffield University,
Sheffield, England.
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Basic Bell-Sejnowski ICA algorithm demonstrated on 2 speech signals.
% The default value of each parameter is given in [] brackets.
% [0] Set to 1 to hear signals.
listen=0; % set to 1 if have audio.
% [1] Set random number seed.
seed=9; rand('seed',seed);
randn('seed',seed);
%
M
%
N
[2] M = number of source signals and signal mixtures.
= 2;
[1e4] N = number of data points per signal.
= 1e4;
% Load data, each of M=2 columns contains a different source signal.
% Each column has N rows (signal values).
% Load standard matlab
% Set variance of each
load chirp; s1=y(1:N);
load gong; s2=y(1:N);
sounds (from MatLab's datafun directory)
source to unity.
s1=s1/std(s1);
s2=s2/std(s2);
% Combine sources into vector variable s.
s=[s1,s2];
% Make new mixing matrix.
A=randn(M,M);
% Listen to speech signals ...
% [10000] Fs Sample rate of speech.
Fs=10000;
if listen
soundsc(s(:,1),Fs);
soundsc(s(:,2),Fs);end;
% Plot histogram of each source signal -
% this approximates pdf of each source.
figure(1);hist(s(:,1),50); drawnow;
figure(2);hist(s(:,2),50); drawnow;
% Make M mixures x from M source signals s.
x = s*A;
% Listen to signal mixtures signals ...
if listen
soundsc(x(:,1),Fs); soundsc(x(:,2),Fs); end;
% Initialise unmixing matrix W to identity matrix.
W = eye(M,M);
% Initialise y, the estimated source signals.
y = x*W;
% Print out initial correlations between
% each estimated source y and every source signal s.
r=corrcoef([y s]);
fprintf('Initial correlations of source and extracted signals\n');
rinitial=abs(r(M+1:2*M,1:M))
maxiter=100;
eta=1;
% [100] Maximum number of iterations.
% [0.25] Step size for gradient ascent.
% Make array hs to store values of function and gradient magnitude.
hs=zeros(maxiter,1);
gs=zeros(maxiter,1);
% Begin gradient ascent on h ...
for iter=1:maxiter
% Get estimated source signals, y.
y = x*W; % wt vec in col of W.
% Get estimated maximum entropy signals Y=cdf(y).
Y = tanh(y);
% Find value of function h.
% h = log(abs(det(W))) + sum( log(eps+1-Y(:).^2) )/N;
detW = abs(det(W));
h = ( (1/N)*sum(sum(Y)) + 0.5*log(detW) );
% Find matrix of gradients @h/@W_ji ...
g = inv(W') - (2/N)*x'*Y;
% Update W to increase h ...
W = W + eta*g;
% Record h and magnitude of gradient ...
hs(iter)=h; gs(iter)=norm(g(:));
end;
% Plot change in h and gradient magnitude during optimisation.
figure(1);plot(hs);title('Function values - Entropy');
xlabel('Iteration');ylabel('h(Y)');
figure(2);plot(gs);title('Magnitude of Entropy Gradient');
xlabel('Iteration');ylabel('Gradient Magnitude');
% Print out final correlations ...
r=corrcoef([y s]);
fprintf('FInal correlations between source and extracted
signals ...\n');
rfinal=abs(r(M+1:2*M,1:M))
% Listen to extracted signals ...
if listen
soundsc(y(:,1),Fs);
soundsc(y(:,2),Fs);end;
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%