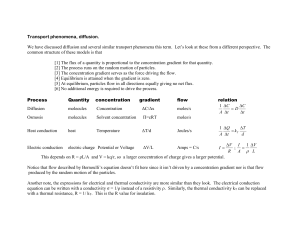
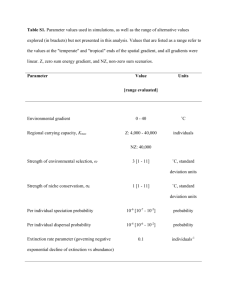
Maths answers (MS Word , 206kb)
advertisement

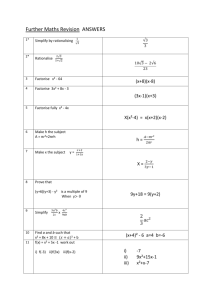
Maths Questions Answers 19 1. 30 83 2.252 3. 1 12 7 4.10 3 5. 8= 0.375 6. 7. 23 𝑥 6 −31 𝑦 18 8. 25% 9. 33.33% 10. 85% 11. y5 12. a-4 13. z1 = z 14. 1 15. a24 16. 2.576 x 102 17. 2.82 x 103 18. 2 19. 3 20. 9 21. N = m kg s-2. 22. Pa = N m-2 = m-1 kg s-2. 23. a. True b. False c. False d. True e. False f. False 24. 0.109 nm 25. 74 pm 26. 1.21 Å 27. 1.54 Å 28. divide by 103 (1000), or multiply by 10-3. 29. divide by 103 which is the same as multiplying by 10-3. 30. To collect the necessary data, we should vary the concentration of the solution and measuring the absorbance. Independent variable is the concentration and dependent variable is the absorbance. (Doesn’t matter if you don’t have independent/dependent). To find the molar absorption coefficient, we plot a graph of absorbance vs concentration, where the gradient is ε x path length (and we know the path length). So ε is the gradient of the graph ÷ path length. This means that ε has the units of mol-1 dm3 cm-1 or mol-1 dm2. 31. Independent variable is heat required and dependent variable is the change in temperature. We could find the specific heat capacity of water by plotting a graph of heat required vs change in temperature, where the gradient is specific heat capacity x mass. We know the mass of water so we can work out the specific heat capacity by gradient ÷ mass of water. 32. The equation given in the question can be rearranged to 𝑘 ln 𝑇 = −𝛥𝐻 1 𝑅 . 𝑇 + ln 𝑘 𝑘𝐵 ℎ + 𝛥𝑆 𝑅 . 1 The plot of ln 𝑇 vs 𝑇 gives a straight line with gradient of −𝛥𝐻 𝑅 rearranged and solved for enthalpy, and an intercept of ln , which can be 𝑘𝐵 ℎ rearranged to solve for entropy. So 𝛥𝐻 = −𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑡 × 𝑅 and 𝛥𝑆 = (𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡 − ln 𝑘𝐵 ℎ ) × 𝑅. + 𝛥𝑆 𝑅 which can be