Lecture 18
advertisement

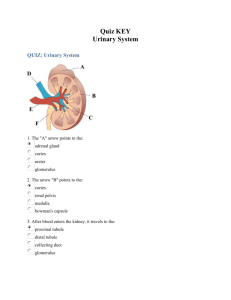
Lecture 18: The Urinary System I. General Anatomy A. Primary Structures 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra B. Primary Functions 1. maintains osmotic balance (salts & water) 2. eliminates nitrogenous wastes (urea) 3. regulates composition and volume of blood 4. help regulate blood pressure (hormone - renin) II. Kidney - between parietal peritoneum and posterior abdom wall A. Location 1. between T12 and L3 2. partially protected by ribs 11-12 3. right slightly lower than left (liver on right) B. External Anatomy 1. 4-5 inches long; 2-3 inches wide. Bean-shaped. 2. concave toward the midline 3. hilus - at concave center, site of ureter departure a. vessels, lymph, nerve enter/exit here 4. renal sinus - cavity where ureter enters 5. 3 layers around kidney a. renal capsule - innnermost fibrous membrane b. adipose capsule - fatty layer, protection c. renal fascia - outermost fibrous membrane C. Internal Anatomy 1. cortex - outer reddish area 2. medulla - inner reddish-brown area a. renal pyramids - triangular, apex to center b. renal papillae - point into renal sinus 3. parenchyma - cortex and pyramids combined a. nephron - microscopic unit of the kidney b. site of filter of the blood c. collecting tubule - gathers filtered urine 4. renal pelvis - major cavity of renal sinus a. major calyces - 2-3 grooves for urine flow b. minor calyces - 8-18 minor grooves for flow D. Nephron - microscopic, functional unit of kidney (1 mil) 1. renal tubule - filter path of filtrate from blood a. glomerulus - bulb where capillaries congregate b. proximal convoluted tubule i. cuboidal epithelium with microvilli c. descending tubule d. Loop of Henle e. ascending tubule f. distal convoluted tubule i. cuboidal epithelium (few microvilli) g. collecting tubule h. papillary ducts - urine from many collecting 2. Histology 1. parietal layer - simple squamous epithelium i. restricts passage of blood cells 2. basement membrane i. restricts passage of large proteins 3. visceral layer - epithelial cells (podocytes) 3. cortical nephron - no tubules into medulla 4. juxtamedullary nephron - tubules into the medulla i. contain "filtration slits" III. Ureters - carries urine from renal pelvis --> bladder A. Direction of Flow nephrons -> collecting tubules -> papillary ducts -> calyces -> renal pelvis -> ureters -> urinary bladder B. Histology 1. mucosa - inner coat; transitional epithelium 2. muscularis - inner/longitudinal; outer/circular 3. fibrous coat - anchors ureters in place IV. Urinary Bladder - just posterior to symphysis pubis A. Histology 1. mucosa - innermost, transitional epithelium a. remember stretching ability! b. rugae - folds that form when empty 2. submucosa - connective tissue 3. detrusor muscle - 3 layers of smooth muscle 4. serous coat - formed by peritoneum B. Valves 1. internal sphincter - circular smooth muscle 2. external sphincter - skeletal muscle (voluntary) V. Urethra - from floor of bladder to body exterior A. Female 1. directly posterior to sym. pubis; ant. to vagina 2. urethral orifice - between clitoris & vag. opening 3. histology a. mucosa - innermost, transitional->stratified b. spongy tissue - intermediate, with veins c. muscularis - circular smooth muscle B. Male 1. directly below bladder, through prostate gland, through urogenital diaphragm, through penis 2. Histology a. mucosa - pseudostratified-> stratified squamous b. submucosa - connective tissue below c. urethral glands - lubrication secretion