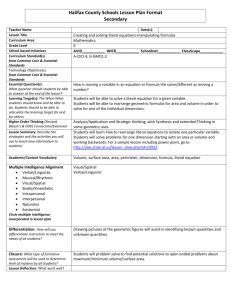
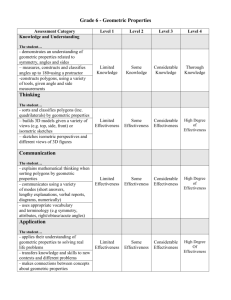
M_MM_5th_6Wks_IPG_0708 - Curriculum
advertisement
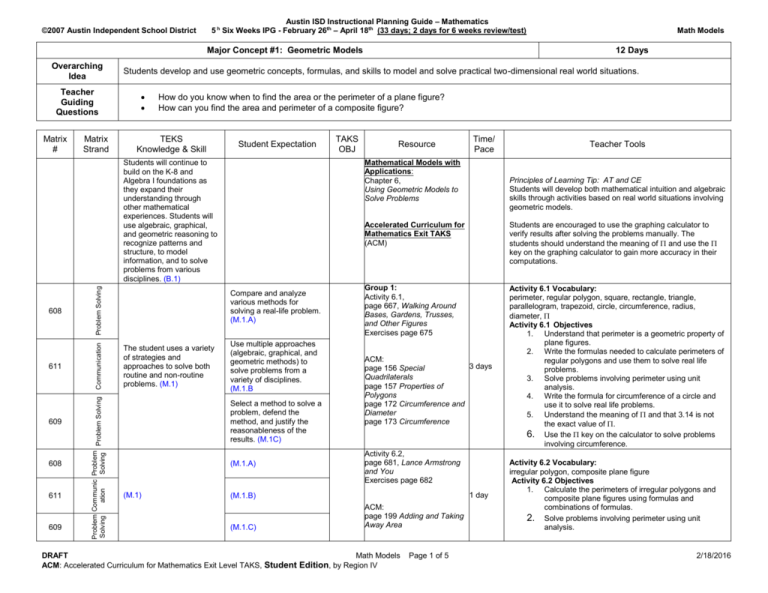
©2007 Austin Independent School District Austin ISD Instructional Planning Guide – Mathematics 5 h Six Weeks IPG - February 26th – April 18th (33 days; 2 days for 6 weeks review/test) Major Concept #1: Geometric Models Overarching Idea Teacher Guiding Questions Matrix # Matrix Strand Problem Solving Communication 609 608 611 609 Problem Communic Problem Problem Solving Solving ation Solving 611 12 Days Students develop and use geometric concepts, formulas, and skills to model and solve practical two-dimensional real world situations. How do you know when to find the area or the perimeter of a plane figure? How can you find the area and perimeter of a composite figure? TEKS Knowledge & Skill Student Expectation Compare and analyze various methods for solving a real-life problem. (M.1.A) The student uses a variety of strategies and approaches to solve both routine and non-routine problems. (M.1) Use multiple approaches (algebraic, graphical, and geometric methods) to solve problems from a variety of disciplines. (M.1.B Select a method to solve a problem, defend the method, and justify the reasonableness of the results. (M.1C) (M.1.A) (M.1) TAKS OBJ Resource Time/ Pace Mathematical Models with Applications: Chapter 6, Using Geometric Models to Solve Problems Students will continue to build on the K-8 and Algebra I foundations as they expand their understanding through other mathematical experiences. Students will use algebraic, graphical, and geometric reasoning to recognize patterns and structure, to model information, and to solve problems from various disciplines. (B.1) 608 Math Models Principles of Learning Tip: AT and CE Students will develop both mathematical intuition and algebraic skills through activities based on real world situations involving geometric models. Accelerated Curriculum for Mathematics Exit TAKS (ACM) Students are encouraged to use the graphing calculator to verify results after solving the problems manually. The students should understand the meaning of and use the key on the graphing calculator to gain more accuracy in their computations. Group 1: Activity 6.1, page 667, Walking Around Bases, Gardens, Trusses, and Other Figures Exercises page 675 Activity 6.1 Vocabulary: perimeter, regular polygon, square, rectangle, triangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, circle, circumference, radius, diameter, Activity 6.1 Objectives 1. Understand that perimeter is a geometric property of plane figures. 2. Write the formulas needed to calculate perimeters of regular polygons and use them to solve real life problems. 3. Solve problems involving perimeter using unit analysis. 4. Write the formula for circumference of a circle and use it to solve real life problems. 5. Understand the meaning of and that 3.14 is not the exact value of . 6. Use the key on the calculator to solve problems involving circumference. ACM: 3 days page 156 Special Quadrilaterals page 157 Properties of Polygons page 172 Circumference and Diameter page 173 Circumference Activity 6.2, page 681, Lance Armstrong and You Exercises page 682 1 day (M.1.B) (M.1.C) Teacher Tools ACM: page 199 Adding and Taking Away Area DRAFT Math Models ACM: Accelerated Curriculum for Mathematics Exit Level TAKS, Student Edition, by Region IV Page 1 of 5 Activity 6.2 Vocabulary: irregular polygon, composite plane figure Activity 6.2 Objectives 1. Calculate the perimeters of irregular polygons and composite plane figures using formulas and combinations of formulas. 2. Solve problems involving perimeter using unit analysis. 2/18/2016 ©2007 Austin Independent School District Austin ISD Instructional Planning Guide – Mathematics 5 h Six Weeks IPG - February 26th – April 18th (33 days; 2 days for 6 weeks review/test) 12 Days (cont’d. from previous page) Major Concept #1: Geometric Models (Continued) Overarching Idea Teacher Guiding Questions 609 611 328 Problem Communi Problem Solving cation Solving 611 Communication 608 Matrix Strand Graphing & Transformations Matrix # Math Models Students develop and use geometric concepts, formulas, and skills to model and solve practical two-dimensional real world situations. How do you know when to find the area or the perimeter of a plane figure? How can you find the area and perimeter of a composite figure? TEKS Knowledge & Skill Student Expectation (M.1.A) (M.1) The student uses algebraic and geometric models to represent patterns and structures. (M.9) Resource (M.1.B) Use geometric transformations, symmetry, and perspective drawings to describe mathematical patterns and structure in art and architecture. (M.9.A) Time/ Pace Activity 6.3, page 685, Walking Around Revisited Exercises page 694 (M.1.B) (M.1.C) (M.1) TAKS OBJ 3 days ACM: page 181 Area of a Circle page 182 Area of a Circle Activity 6.4, page 698, A New Pool and Other Home Improvements Exercises page 701 Group 1: review skills What Have I Learned? page 731, How Can I Practice? page 733 assess mastery Activity 6.3 Vocabulary: area Activity 6.3 Objectives 1. Write the formulas needed to calculate areas of regular polygons and composite plane figures and use them to solve real life problems. 2. Write the formula for area of a circle and use it to solve real life problems. Activity 6.4 Vocabulary: 1 day Activity 6.6, page 717, Moving Up With Math Exercises page 720 ACM: page 149 Similar Polygons page 152 Similar Polygons page 155 Triangles page 157 Properties of Polygons Teacher Tools 2 days 2 days Activity 6.4 Objectives 1. Use geometric models to solve problems in context. 2. Distinguish between problems requiring area formulas and perimeter formulas. Activity 6.6 Vocabulary: equilateral, isosceles, scalene, equiangular, right, acute, obtuse, similarity Activity 6.6 Objectives 1. Recognize the geometric properties of similar triangles. 2. Use similar triangles in indirect measurement. 3. In context, use proportional reasoning to analyze and choose the correct set up to utilize similar triangles to model a real-life situation. Teachers can use the Section 6 Skills Checks worksheets in the Pearson Teacher’s Resource Guide to assess the student’s understanding of the concepts/skills covered in Chapter 6 Group 1 activities as an in-class quiz or as an athome assignment. The Section 7 Assessment of the Teacher’s Resource Guide includes samples of quizzes, tests, and exams that can be used as is or modified as needed. Teachers are encouraged to include TAKS formatted problems from the numerical fluency focus objectives on all formal assessments. Students should be reminded that they have access to tutorials and extra practice problems using the MathXL CD in addition to the Interact Math and MyMathLab websites/software. DRAFT Math Models ACM: Accelerated Curriculum for Mathematics Exit Level TAKS, Student Edition, by Region IV Page 2 of 5 2/18/2016 ©2007 Austin Independent School District Austin ISD Instructional Planning Guide – Mathematics 5 h Six Weeks IPG - February 26th – April 18th (33 days; 2 days for 6 weeks review/test) Major Concept #2: Three Dimensional Figures Overarching Idea Teacher Guiding Questions Communication 609 608 611 609 608 611 609 Problem Communic Problem Problem Commu Problem Solving ation Solving Solving nication Solving 611 Problem Solving 608 Matrix Strand 10 Days Students develop and use geometric concepts, formulas, and skills to model and solve practical three-dimensional real world situations. How do you find the surface area of a three-dimensional object? How do you find the volume of a three-dimensional object? TEKS Knowledge & Skill Problem Solving Matrix # Math Models Student Expectation (M.1.A) (M.1) (M.1.B) (M.1.C) (M.1.A) (M.1) TAKS OBJ Resource Time/ Pace Group 2: Activity 6.8, page 738, Painting Your Way Through the Summer Exercises page 741 ACM: page 189 Cube Towers page 190 Area and Volume page 191 Net of a Cube page 192 Faces, Vertices, and Edges page 194 Visualizing the Net page 196 Visualizing 3 days Activity 6.9, page 743, Truth in Labeling Exercises page 746 (M.1.B) (M.1.C) (M.1.A) (M.1) Activity 6.10, page 748, Analyzing an Ice Cream Cone Exercises page 751 (M.1.B) 3 days Teacher Tools Activity 6.8 Vocabulary: surface area, rectangular prism, right circular cylinder, sphere Activity 6.8 Objectives 1. Recognize the geometric properties of threedimensional figures. 2. Write the formulas for and calculate surface areas of boxes (rectangular prisms), cans (right circular cylinders), and balls (spheres). Activity 6.9 Vocabulary: volume Activity 6.9 Objectives 1. Write the formulas for and calculate volumes of boxes (rectangular prisms) and cans (right circular cylinders). 2. Recognize geometric properties of threedimensional figures. 3. Distinguish between problems requiring area formulas and volume formulas. Activity 6.10 Vocabulary: cone Activity 6.10 Objectives 1. Write the formulas for and calculate volumes of balls (spheres) and cones. (M.1.C) DRAFT Math Models ACM: Accelerated Curriculum for Mathematics Exit Level TAKS, Student Edition, by Region IV Page 3 of 5 2/18/2016 ©2007 Austin Independent School District Austin ISD Instructional Planning Guide – Mathematics 5 h Six Weeks IPG - February 26th – April 18th (33 days; 2 days for 6 weeks review/test) 10 Days (cont’d. from previous page) Major Concept #2: Three Dimensional Figures (Continued) Overarching Idea Teacher Guiding Questions Matrix # Matrix Strand Math Models Students develop and use geometric concepts, formulas, and skills to model and solve practical three-dimensional real world situations. How do you find the surface area of a three-dimensional object? How do you find the volume of a three-dimensional object? TEKS Knowledge & Skill Student Expectation TAKS OBJ Resource Time/ Pace Teacher Tools 611 Communication Activity 6.11, page 754, Summertime (M.1) (M.1.B) ACM: page 200 Calculating Area and Volume page 204 Changing Dimensions page 215 Calculating Area and Volume Group 2: review skills What Have I Learned? page 757, How Can I Practice? page 760 Gateway Review page 771 assess mastery DRAFT Math Models ACM: Accelerated Curriculum for Mathematics Exit Level TAKS, Student Edition, by Region IV Page 4 of 5 2 days Activity 6.11 Vocabulary: scale drawing Activity 6.11 Objectives 1. Solve real life problems using geometry formulas. 2. Use scale drawings in the problem-solving process. Teachers should assess the student’s ability to use the concepts/skills covered in the Chapter 6 Group 2 activities. The Gateway sections of the text can be used as the review for a chapter test. 2 days Students should be reminded that they have access to online tutorials and extra practice problems using the MathXL CD in addition to the Interact Math and MyMathLab websites/software. 2/18/2016 ©2007 Austin Independent School District Austin ISD Instructional Planning Guide – Mathematics 5 h Six Weeks IPG - February 26th – April 18th (33 days; 2 days for 6 weeks review/test) Math Models Major Concept #3: Transformations and Math in Art Overarching Idea Teacher Guiding Questions Matrix # Matrix Strand 9 Days Students develop an understanding of transformational geometry and the mathematics involved in nature and the visual arts. Where are some examples of the use of tessellations in the real world? How can you differentiate among the movements of transformational geometry? How has the golden ratio been utilized in nature and the artistic world? TEKS Knowledge & Skill Student Expectation TAKS OBJ Resource Time/ Pace 512 Displaying & Interpreting Data Activity 6.5, page 703, Tessellations Exercises page 713 (M.9) (M.9.A) ACM: page 123 Translations, Rotations, and Reflections page 126 Tessellations page 128 Changes and More Changes page 130 Dilations 4 days 504 Proportional Reasoning in Probability M. C. Escher website: www.mcescher.com Activity 6.7, page 722, Math in Art Exercises page 729 (M.9) (M.9.A) 3 days assess mastery 2 days Teacher Tools Activity 6.5 Vocabulary: transformation, rigid motion, translation, rotation, reflection, glide reflection, axis of reflection, vertex, center of rotation, angle of rotation, symmetry, line of symmetry, reflective symmetry, rotational symmetry Activity 6.5 Objectives 1. Identify a tessellation. 2. Perform a transformation on a given figure. 3. Perform a reflection on a given figure. 4. Perform a rotation on a given figure. 5. Perform a translation on a given figure. 6. Perform a glide reflection on a given figure. 7. Identify reflective and translational symmetry. Activity 6.7 Vocabulary: golden ratio, golden rectangle, perspective, one-point perspective, two-point perspective, illusion, Fibonacci number Activity 6.7 Objectives 1. Recognize a golden rectangle by finding the golden ratio. 2. Recognize Fibonacci numbers and the limit of the ratio of successive Fibonacci numbers. 3. Distinguish between one- and two-point perspectives. 4. Demonstrate an understanding of Desargue’s Theorem. Teachers should assess the student’s ability to use the concepts/skills covered in these two Chapter 6 application activities. A project or report could be used as an assessment tool. The topics covered in these two sections provide an excellent opportunity for students to mine the internet for more information relating art and nature to mathematics and the use of tessellations in ancient and modern cultures. Students should be reminded that they have access to online tutorials and extra practice problems using the MathXL CD in addition to the Interact Math and MyMathLab websites/software. DRAFT Math Models ACM: Accelerated Curriculum for Mathematics Exit Level TAKS, Student Edition, by Region IV Page 5 of 5 2/18/2016