MATH136_Feb2013 - Heartland Community College
advertisement

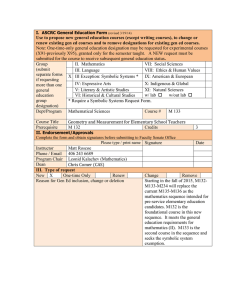
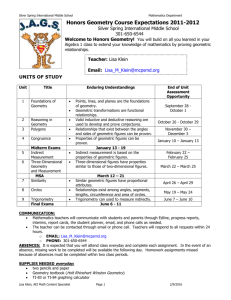
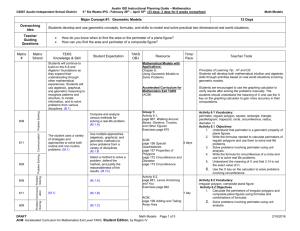
Heartland Community College Master Course Syllabus Division: Math, Science Course Prefix and number MATH 136 Course Title Mathematics for Elementary Teachers II COURSE PREFIX & NUMBER: MATH 136 COURSE TITLE: Mathematics for Elementary Teachers II DATE PREPARED: March 13, 1997 DATE REVISED: December 7, 2012 PCS/CIP/ID NO: 11 131202 IAI NO. (if available) : M1 903 EFFECTIVE DATE OF FIRST CLASS: January, 2012 CREDIT HOURS: 3 CONTACT HOURS: LECTURE HOURS: 3 3 LABORATORY HOURS: 0 CATALOG DESCRIPTION (Include specific prerequisites): Prerequisite: Math 135 (with a grade C or better), or equivalent, or permission of the instructor. This course focuses on mathematical reasoning and problem solving; and provides instruction in teaching mathematics at the elementary grade level. Topics include algebra, probability, statistics, geometry, measurement, and the use of technology in the elementary school classroom. Note, a scientific calculator is required for this course (a graphing calculator is also acceptable). TEXTBOOKS: Mathematics for Elementary School Teachers,5th Edition, Brassarear, Brroks/Cole. RELATIONSHIP TO ACADEMIC DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMS AND TRANSFERABILITY: MATH 136 fulfills 3.0 of the semester hours of credit in Mathematics required for the A.A. or A.S. degree. This course should transfer as part of the General Education Core Curriculum described in the Illinois Articulation Initiative to other Illinois colleges and universities participating in the IAI. However, students should consult an academic advisor for transfer information regarding particular institutions. Refer to the IAI web page for information as well at www.itransfer.org. COURSE OBJECTIVES (Learning Outcomes) 1. Apply probability concepts and techniques (e.g., tree diagrams, geometric shapes, etc.) and counting techniques to solve problems. 2. Apply the concepts of statistics by gathering, organizing, representing, analyzing interpreting and presenting the results of the data. 3. Understand the basic concepts of Euclidean geometry (e.g., terminology, properties of one, two and three dimensional objects, metric system, etc.). 4. Understand the concepts of congruence and similarity to solve geometric problems and develop geometric constructions 5. Understand how distance, area and volume formulas are developed, and apply the formulas to make: measurement estimates and compute accurate measurements of distance, area, volume, time, and other measurable quantities 6. Understand the concepts of geometric transformations, translations, reflections and rotations 7. Discern which methods of problem solving are appropriate and most effective, explain why various methods work, and apply those methods to new situations. 8. Demonstrate that mathematics is useful and enjoyable; and develop a positive and enthusiastic attitude towards mathematics. Due to the nature of this course the problem solving skills developed will be C1, PS2. COURSE OUTLINE: 1. Probability (counting techniques, multistage experiments, expected value, probabilities using geometric shapes, tree diagrams, and simulations, etc.) 2. Statistics (measures of central tendency and variation, graphs, normal distribution, etc.) 3. Geometry (notation, polygonal curves, linear measure, properties of angles, etc.) 4. Constructions and Similarity (congruence properties, constructing geometric figures, transforming figures into similar triangles, etc.) 5. Measurement (areas and volumes of geometric figures, etc.) 6. Motion Geometry ( e.g., transformations, translations, symmetries, etc.) METHOD OF EVALUATION (Tests/Exams, Grading System): Methods of evaluation may consist of, but are not limited to test(s), quiz(zes), homework, project(s), and a final exam. REQUIRED WRITING AND READING: Required writing will be part of most assignments and tests. Students will be expected to explain how they found the solution, describe the solution graphically, and interpret the answer in the context of the problem. Students are expected to read the material in the textbook for each section studied. Revised by CAS 6/98