acid precipitation
advertisement

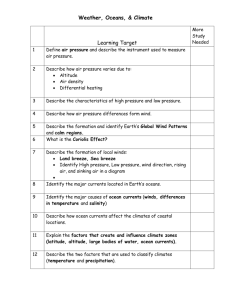
Science 8 Water Systems Test Review Vocabulary You must be able to give a definition, match the terms to a definition or fill in blanks. adaptation aquifer aquitard basin capillary action chlorination condensation Continental Divide continental shelf convection current current diversity dredging erosion estuary evaporation flocculation flood plain fresh water glacier ground water guyot gyre habitat heat capacity irrigation percolation plankton precipitation productivity runoff salinity saturated zone seamount sediment system thermohaline tide trench tributaries tsunami turnover watershed water table wavelength Multiple Choice, True/False or Short Answer Questions 1. Explain four reasons why the water cycle is important. 2. Describe the steps in the water cycle (evaporation and transpiration, condensation, precipitation, runoff and percolation). 3. Explain why estuaries are very important. 4. Explain how marshes are different from swamps. 5. Explain how water vapour is different from the water from which it evaporated 6. Explain how erosion is controlled during logging (strip or selective logging) and farming (contour ploughing). 7. Explain why erosion and deposition are opposite geological processes. 8. Describe two ways that people protect homes or towns from flooding. 9. What is one problem with levees? 10. What is freeze-thaw erosion and what human structures are most affected by it? 11. Describe some forms of water in condensation and precipitation. 12. Explain why rain often falls more on one side of a mountain range than the other. 13. Describe two ways that chemicals other than water end up in surface water and groundwater. 14. How are capillary action and percolation opposites? What causes each? 15. How and why do people make use of groundwater? 16. Explain how differences in temperature and salinity create ocean currents. 17. List three things ocean currents provide for living things. 18. List three factors that change the direction of ocean currents. 19. List some problems and benefits of waves. 20. Why are dams useful? 21. What problems can be caused by dams? 22. Explain similarities and differences in waves and tsunamis. 23. Explain how oxygen becomes dissolved in the ocean. 24. What are turnovers and why are they important in lakes? 25. Explain why there is more diversity in tropical climates such as rain forests. 26. Explain the effects of latitude on climate. 27. Explain the effects on climate of being near a large body of water. 28. Explain the effects of warm ocean currents on climate. 29. Describe differences in ocean habitats (dark zone, light zone, shoreline and reef). 30. Describe adaptations of living things in the light zone, dark zone, shores or reef. 31. Describe three technologies that allow safe exploration of the ocean. 32. Who was Jacques Cousteau and why is he famous? Science 8 Water Systems Test Review Diagrams Label parts of a wave A) Trough B) Wavelength C) Crest Label a diagram of underground water (percolation, precipitation, wells, water table, aquifer or saturated zone, aquitard) Label parts of a watershed (divides, lakes, ponds, tributaries, rivers, water table, precipitation) Label a diagram of underwater geological features (seamount, guyot, volcanic island, trench, continental shelf, continental slope, sea canyon, trench) Science 8 Water Systems Test Review Graphs Given climate data, create a climate graph. Compare climate graphs of two cities to identify the effects of latitude or nearby bodies of water. (Which is probably farther north? Which is probably on a coast or the interior of a continent? City A Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec -4.8 -5.4 -2.5 1.6 6.2 10.9 15.4 15.5 11.8 6.9 2.6 -2.2 Monthly precipitation (mm) 150 125 131 122 101 102 89 108 131 162 144 149 Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec 0.8 5.2 21 20.3 13.1 7.8 -0.8 -13.5 17 5 13 50 Average Temperature Jul City B Average Temperature -15.3 -7.2 18 - 61 182 136 250 25 200 20 150 15 100 10 50 5 0 0 -50 -5 -100 -10 -150 -15 -200 -20 J Precipitation (mm) 95 F M A M J J A S O N D 250 25 200 20 150 15 100 10 50 5 0 0 -50 -5 -100 -10 -150 -15 -200 -20 J F M A M J J A S O N D Mean Temp. (ºC) Precipitation (mm) Monthly precipitation (mm) 12.7 15.7 Mean Temp. (ºC) Jan 60 28