Print Version

CHE 230 STUDY GUIDE FOR EXAM 1 G.Lind
NOTE : Some end of chapter problems (from Chapters 10, 11, 12, 13) may be included in the exam.
CHAPTER 10
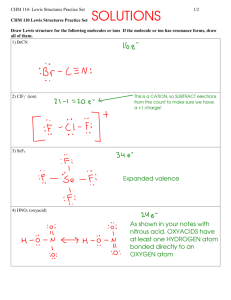
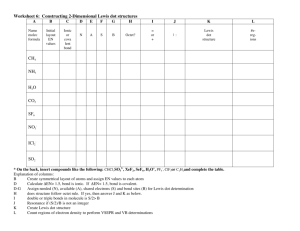
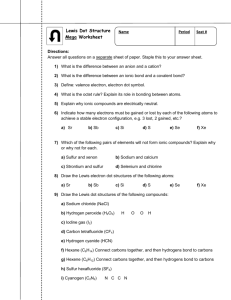
Drawing Lewis structures (including all lone pairs) observing the octet rule (except hydrogen) and using the correct number of valence electrons for a molecule or an ion.
Drawing Lewis structures for exceptions to the octet rule (atoms which don’t have enough and atoms which have too many valence electrons).
Drawing all resonance structures for a molecule or an ion.
Determining formal charges and selecting the “best” Lewis structure.
Determining whether a bond is polar or not.
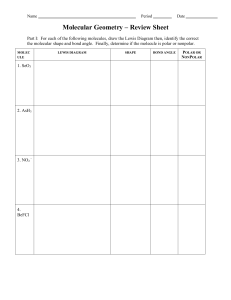
Using the VSEPR theory to determine the electron pair geometry and the molecular geometry.
Determining whether a molecule or ion is polar or not.
CHAPTER 11
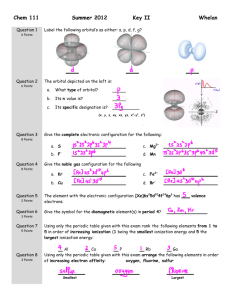
Determine the hybridization (sp, sp 2 , etc) and the electron pair and molecular geometry at each atom in a given Lewis structure. (You don't need to do the orbital diagram). This includes double and triple bonds.
Determine which bond is a - bond and which is a - bond.
CHAPTER 12
heats of formation and vice versa.
Know how to use phase diagrams : solid, liquid, gas, melting, sublimation, boiling etc, critical point, triple point, equilibrium lines, isothermal change, isobaric change, slope of the solid – liquid equilibrium line, boiling point, normal boiling point, etc.
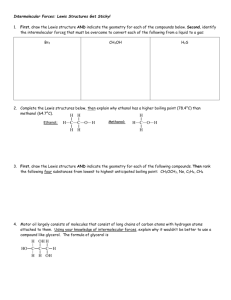
Determine which intermolecular forces are present based on the Lewis structure of a molecule or ion.
Determine which compound has the higher vapor pressure, higher boiling point etc. based on the Lewis structure and the intermolecular forces present.
Know what makes water so unique and what is the uniqueness.
CHAPTER 13
Know what a solution is, a solvent, a solute.
Know which solute will dissolve in which solvent based on the intermolecular forces.
Know how to calculate the different concentrations of a solution (molarity, molalitiy, etc.) and related problems (how many grams of mercury(I) perbromate are needed to make a 0.768 molal aqueous solution, etc.)
Covert between concentration terms (sample problem 13.5)
Other things to know : significant figures scientific notation unit conversions naming of inorganic compounds and ions density molar mass the mole concept always work with units (points will be taken off for any calculation without all the units) don't round until the very end (points will be taken off for rounding before the final result) no units are wrong units