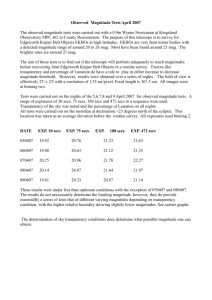
RRD3 - Leek High School
advertisement
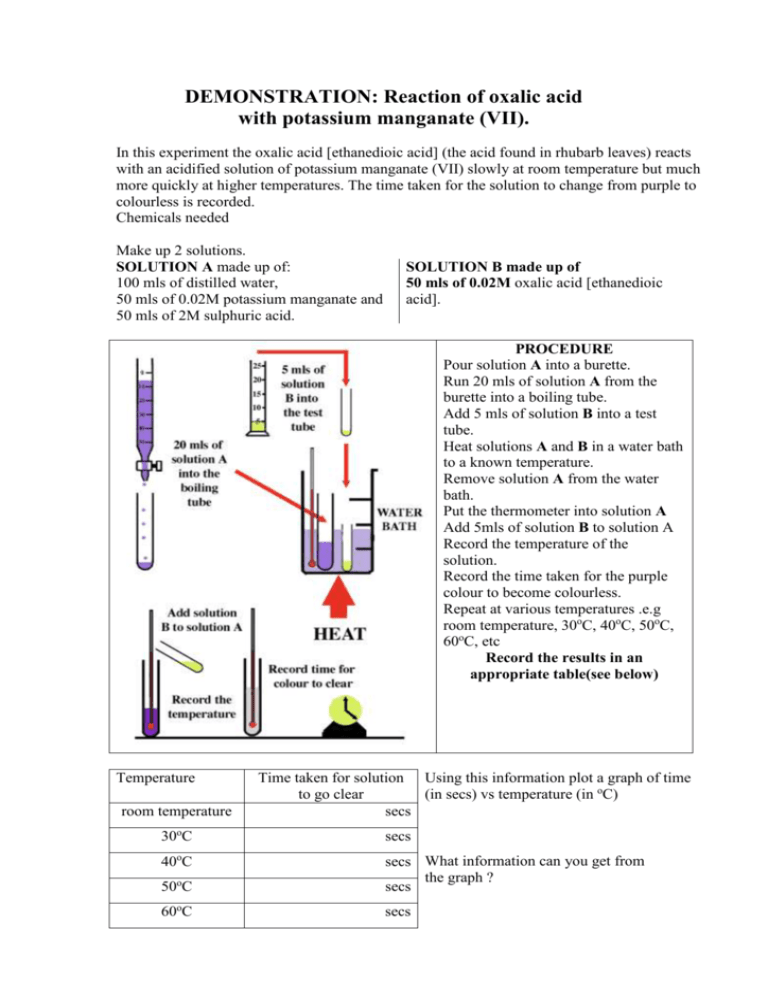
DEMONSTRATION: Reaction of oxalic acid with potassium manganate (VII). In this experiment the oxalic acid [ethanedioic acid] (the acid found in rhubarb leaves) reacts with an acidified solution of potassium manganate (VII) slowly at room temperature but much more quickly at higher temperatures. The time taken for the solution to change from purple to colourless is recorded. Chemicals needed Make up 2 solutions. SOLUTION A made up of: 100 mls of distilled water, 50 mls of 0.02M potassium manganate and 50 mls of 2M sulphuric acid. SOLUTION B made up of 50 mls of 0.02M oxalic acid [ethanedioic acid]. PROCEDURE Pour solution A into a burette. Run 20 mls of solution A from the burette into a boiling tube. Add 5 mls of solution B into a test tube. Heat solutions A and B in a water bath to a known temperature. Remove solution A from the water bath. Put the thermometer into solution A Add 5mls of solution B to solution A Record the temperature of the solution. Record the time taken for the purple colour to become colourless. Repeat at various temperatures .e.g room temperature, 30oC, 40oC, 50oC, 60oC, etc Record the results in an appropriate table(see below) Temperature room temperature Time taken for solution Using this information plot a graph of time to go clear (in secs) vs temperature (in oC) secs 30oC secs 40oC 50oC secs What information can you get from the graph ? secs 60oC secs FOR THE TECHNICIAN measuring cylinder boiling tube water bath bunsen burner stop clock 0.02M potassium manganate (VII) 0.02M ethanedioic acid burette -10 – 110 oC thermometer test tube triopod and gauze bunsen mat Dilute sulphuric acid HAZARD WARNINGS Dilute sulphuric acid Corrosive Causes severe burns 0.02M potassium manganate (VII) An oxidising agent Avoid contact with combustible material. Harmful if swallowed. Ethanedioic acid (oxalic acid) Harmful when swallowed