Notes – Chapter 24 Phylogeny and Systematics
advertisement

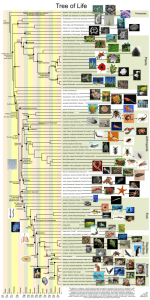
Notes – Chapter 25 Phylogeny and Systematics •_______________________________________– evolutionary history of a species or group of related species •_______________________________________ – study of biological diversity in an environmental context (tracing phylogeny) •_______________________________________ - science of naming, identifying, and describing diverse forms of life •_______________________________________ – supercontinent of land masses (present 250 mya) Geologic Time Scale •Major Events in Evolution ♦4.6 bya – formation of the __________________________ (Precambrian) ♦3.5 bya – prokaryotic cells ♦2.2 bya – eukaryotic cells ♦600 mya – soft-bodied ______________________________ ♦500 mya – colonization of land plants (Paleozoic) ♦420 mya – jawless fish ♦375 mya – bony fish, amphibians, insects ♦325 mya – first seed plants, reptiles ♦220 mya – cone-bearing plants (Mesozoic) ♦175 mya – ____________________________________ abundant ♦80 mya – angiosperms ♦60 mya – mammals, birds, pollinating insects (Cenozoic) ♦30 mya – primate groups ♦2.5 mya – apelike ancestors ♦0.5 mya – _____________________________________ appear Radiometric Dating •The measurement of certain radioactive ___________________________________ in fossils or rocks. •____________________________________ ___ – the number of years it takes for ____________% of the original sample to decay; it is unaffected by temperature, pressure, and other environmental variables •Carbon-14 to Nitrogen-14 → 5,730 years •Potassium-40 to Argon-40 → 1.3 billion years •Uranium-238 to Lead-206 → 4.5 billion years –Found in Volcanic Rock The Fossil Record •The fossil record is far from being complete, it is slanted in favor of species that existed for a long time, were abundant and widespread, and had shells or hard skeletons. •A substantial fraction of species that have lived probably left no fossils, most fossils that formed have been destroyed, and only a fraction of the existing fossils have been discovered. Major Mass Extinctions •__________________________________ Period – 250 mya •________% of marine animal went extinct •8 out of 27 orders of Permian insects did not survive •The extinction occurred in less than 5 million years •Reasons •Occurred about the same time the continents merged to form ____________________________ – Marine and terrestrial habitats disturbed •Massive volcanic eruptions in what is now Siberia – increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide = ____________________________________ •Global warming = reduced temp. differences between the poles and equator. Could lead to uneven mixing of the oceans which decrease amount of dissolved oxygen Major Mass Extinctions •__________________________________ Period – 65 mya •Extinction of dinosaurs •Killed more than half of the marine species •Exterminated many families of terrestrial plants and animals •Reasons •The climate became cooler, and shallow seas receded from continental lowlands •Large volcanic eruption in what is now India •“____________________________________ Hypothesis” – a large comet (dirt and ice) or small asteroid (rock and metal) collided with Earth Taxonomy •_____________________________– Binomial; based on a 2-part Latin name; genus and species. •Ex. Pseudacris nigrita, Homo sapiens •Hierarchical Classification – way for us to structure and view of our world Phylogenetic Systematics •Phylogenetic ____________________– reflect the hierarchical classification of taxonomic groups •______________________________ ___ – a “tree” constructed from a series of dichotomies, or 2-way branch points that represent divergence of an animal from a common ancestor; the “deeper” the branch to greater the divergence •The sequence symbolizes historical chronology •_______________________________ – each branch in a cladogram; ancestral species and all of its decendents How Do We Construct a Cladogram? •_________________________________ – likeness attributed to shared ancestry; all forelimbs of mammals are homologous •Not all likeness qualifies as homology •________________________________ Evolution – Species from different evolutionary branches may come to resemble one another if they have similar ecologocial roles and natural selection has shaped analogous adaptation. Similarity due to convergence is called analogy. •Example – the wings of a bird, bat, and bee. •As a general rule – the greater the number of homologous parts between two species, the more closely the species are related. •The more complex two similar structures are, the less likely it is they evolved independently –Example – the human skull and chimpanzee skull match almost perfectly bone for bone, the only difference is the way they fuse together. Most likely, the genes required to build these skulls were inherited from a common ancestor. Phylogeny Can Be Inferred From Molecular Data •Anatomical characteristics and homology alone cannot account for all evolutionary relationships •Systematists compare genes (____________) and gene products (_______________________) to determine evolutionary relationships