Australo, Homo habilis, homo erectus notes
advertisement

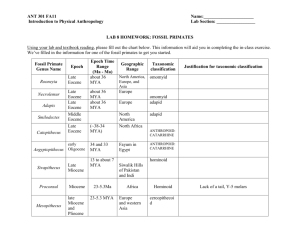
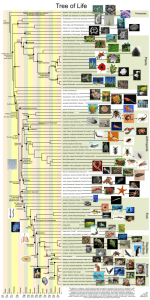
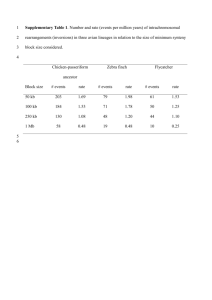
WHO WAS AUSTRALOPITHECINE? ■ Identified by Raymond Dart in South Africa – TAUNG CHILD Dart learned of a partial cranium in 1924 Australopithecus africanus (gracile) Determined it was biped due to placement of foramen magnum Had ape-sized Brain Human-like jaws Today we know of seven species of Australopithecus Found in a variety of locations in Africa From the Pliocene epoch (5 million to 1.6 million years ago) Louis & Mary Leakey Searched for fossils in Olduvai Gorge, Lake Victoria & Kenya Expanded knowledge of human origins Gave Jane Goodall her start “Lucy” Australopithecus afarensis found in 1974 in Ethiopia Sexually dimorphic Brain size ~ 420 ccs. “First Family” found in Ethiopia also Afar Region – dated about 3.6 million years ago ■ Gracile - 4 – 2.3 mya - Lucy (3.3-2.6 mya) - found in E & S Africa - ape from waist up - human from waist down - males 1.5 x larger than females - cranial capacity 310-510 ccs - bipedal, tree climbing + ■ Robustus - 2.5 – 1.0 mya - thick bones for size - markings where bones attached - skull thicker - up to 530 cc cranial capacity - sagittal crest - really powerful jaws - Broom & M. Leakey WHY BIPEDALISM? Advantages - adapt to changing climate - Needed strong selective pressure to develop - heat stress theory - transport foods safely - holding infants - gather food twice as fast - travel far w/o tiring - spot predators far away - see sources of food & water Disadvantages - more visible to predators - exposes soft underbelly - cannot change running direction instantly - not very fast at running - lower back problems - hernias, hemorrhoids - circulatory problems - serious consequences if foot/leg injury WHAT WERE THE CHARACTERISTICS OF HOMO HABILIS? ■ ■ ■ ■ Discovered by Leakeys at Olduvai Gorge in Kenya Found with identifiable stone tools dated approx 2 mya - Oldowan Habilis lived during Lower Paloeolithic or first part of Old Stone Age Nicknamed “Handy man” ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ 650-750 ccs cranial capacity, better information-processing capability Almost modern looking hands & feet, handedness suggested Brain asymmetry moving towards modern human Tooth size reduced, body similar to gracile Australopithecine Scavenged for meat since had tools Probably planned ahead, cooperation, ?language Growth of manual dexterity and fine manipulation WHAT WERE THE CHARACTERISTICS OF HOMO ERECTUS? ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Found in Africa, Asia, Europe, Java Discovered by Eugene DuBois First time physical differences seen ~12 y/o male skeleton most complete find, dated to ~ 1.6 mya 600-1225 ccs cranial capacity, low vault cranium, near-modern development of the brain, particularly in speech area Brain asymmetrical, handedness, massive brow ridges Sloping forehead, receding chin, face, teeth, jaws smaller than Habilis Sexual dimorphism decreased from earlier bipeds Erectus in Europe about 800,000 yrs ago, China 700-800,000 ya Tool finds in Indonesia in 800,000 ya indicate water travel Height closer to 5’ 3” Heavily muscled, but had Human-like body proportions WHAT KIND OF CULTURE DID HOMO ERECTUS HAVE? ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ Acheulean Tools – sharper points, HAND AXE Acheulian, ca. 450,000 BP More cutting edge surface, England Site was apparently a hunting More standardized or trapping camp. found deer, bison, Diverse tools elephant, horse and rhinoceros remains, Used fire ~ 1.3-1 mya – protection, chopping tools, including the pearwarmth, cooking shaped hand-axe above Improved planning ability, greater use of natural resources Evidence of hearths, shelter, can infer clothing Ability to organize hunts ~ 400,000 ya Oldest rock carvings found in a cave in India Used red ochre . Acheulian hand axe Rock art in one of the shelters, cattle and other animals. Note the elephant with human figure (dancing or in ritual motion) over its head. India