Chapter 1 – Matter Matter and Its Properties
advertisement

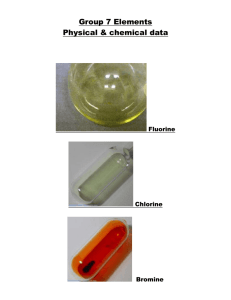
Chapter 1 – Matter Matter and Its Properties - Definitions o Mass – the amount of _________________ o Matter – anything that has __________ and _______________ (takes up space) o Atom – smallest unit of an _______________ that will retain the properties of that element o Element – _______ substance made of only one kind of __________ o Compound – two or more _________________ chemically bonded together Matter and Its Properties – Extensive vs. Intensive & Physical vs. Chemical o Every substance has properties that can be used to _______________ it from other substances. o Extensive Properties – depends on amount of _______________ present o Examples: Volume, ____________, and Amount of energy in a substance Intensive Properties – _______ ______ depend on the amount of matter present Examples: Melting point, _______________ __________, Density, and Ability to conduct __________________ and __________ o Physical Properties – _________ be observed or measured without permanently changing the substance Examples: Weight, ________________, Color, ________________, and Temperature o Chemical Properties – _____________ be observed or measured without permanently changing the substance Examples: Flammability, _________________, and energy in bonds o Whenever a physical or chemical change occurs, ______________ is involved. o Although energy can be absorbed or released in a change, it is not ________________ or ________________. Matter and Its Properties - Changes of State _______________ – definite volume and definite shape _______________ – definite volume, indefinite shape _______________ – indefinite volume, indefinite shape _______________ – high temperature state where atoms lose electrons Matter and Its Properties - Two Classes of Matter o o __________ substances – CANNOT be separated by ordinary physical means Same chemical properties Same ____________________ in every sample Element or compound Examples: Water and _______________ ________________ – CAN be separated by ordinary physical means Each component retains its own unique __________________ Homogeneous – same throughout, also called _______________ Heterogeneous – not same throughout Example: _________________________ Example: _________________________ Let’s Practice: o Q: Consider the air around you. It is a mixture of several gases, mainly nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. Air is considered… homogeneous heterogeneous Periodic Table o Compounds can be broken down by _________________ means to elements. __________________ cannot be broken down. o Elements are organized in the periodic table according to their ___________________. Groups or families – _________________ columns that share similar chemical properties Period – ____________________ rows with gradually changing chemical properties Let’s Practice: o o o Q: Which of the following elements are in the same group? Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine Nitrogen, Sulfur, Bromine Q: Which of the following elements are in the same period? Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine Nitrogen, Sulfur, Bromine Q: Which of the following elements are chemically most similar? Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine Nitrogen, Sulfur, Bromine Metals vs. Non-metals o Metals – elements that are good ____________________ of electricity and heat Found on the __________ side of the periodic table Common properties of metals: o Malleable, _____________, and Luster Most are _______________ at room temperature Have varying degrees of traits Example: _____________________________ Nonmetals – poor _______________________ of electricity and heat Found on the _________________ side of the periodic table. o Brittle Many are ______________ at room temperature Example: _____________________________ Metalloids – have characteristics of both _______________ and ______________________ Example: ____________________________ Groups You Should Know: o Alkali Metals (Group ____) o Alkali Earth Metals (Group _____) o Halogens (Group ____) o Nobel Gases (Group ____) o Hydrogen and Helium are unique. Hydrogen can act as a metal or nonmetal (depending on what it is bonded to). Helium is the most stable and least reactive element on the periodic chart.






![[1] - Boswellsgmt](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006603407_1-fadfbce8d94050a9fb3c38a07d86e8ee-300x300.png)