Chapter 24: Feudal Society
advertisement

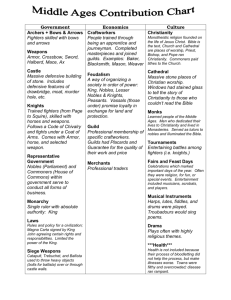
Feudal Society Study Guide – Accommodated After the Viking raids, the people of western Europe wanted security and protection. To protect their property (which included people), the nobles raised their own armies. One of the social groups under feudalism – the government by landowning nobles – was the clergy, or religious leaders. Their duty was to teach Christianity and help the poor and the sick. Land and Government During feudal times, power was based on the ownership of land. Kings began giving soldiers fiefs, or estates, as a reward for their service and loyalty. Nobles grew powerful and gained the right to collect taxes and to enforce law in the area they owned. Around 900, the nobles took on the duty of protecting their lands and people from the Vikings In return, the peasants gave them their lands and promised to work for them in the fields. Feudalism was based on ties of loyalty and duty among nobles. In the ceremony known as the act of homage, vassals promised to serve the lord and help him in battle. Their most important duty was to help the lord in battle by bringing their own army. Vassals agreed to pay a ransom for the lord in exchange for his release if he was captured in battle. The Nobility From the 800sto the 1000s, nobles and their families lived in wooden houses surrounded by palisades, or high wooden fences built for protection. By the 1100s, nobles were living in huge stone houses called castles. In the middle of the castle was located the keep. The great hall and the living quarters of the noble’s household were found here. Noblewomen were known as ladies. They help their husbands run the estate, defended the castle when the men were away, raised children , train young girls in household duties and care for the poor and sick on her husband’s fief. Knighthood Knights were expected to follow certain rules known as the code of chivalry. These rules stated that the knight was to obey his lord, show bravery, respect women, honor the Church, help the poor, be honest and fight fairly. Pages helped the knights of the castle care for their war horses. A squire’s duty was to go into battle with his knight. A squire became a knight in a special ceremony known as dubbing. Knights trained for war by fighting each other in tournaments. The most popular event was the joust. Two armored knights on horseback carrying dull lances charged at each other trying to knock the opponent to the ground. The Manor The land was divided into farming communities called manors. They were found on fiefs and owned by nobles. The seneschal looked after the noble’s fiefs by visiting them regularly. The bailiff made sure the peasants worked hard in the fields. Serfs were a noble’s property. They could not own their own property or marry without the noble’s permission. They could only gain their freedom by running from the fief and escaping to the towns. They did not have to serve in the lord’s army.