Lecture Manuscript
advertisement

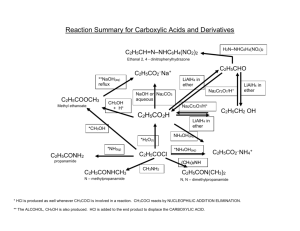
Lecture Manuscript Lecture #5-Thursday January 14th, 1998 – 9:00 AM -I / -M Effects of Substituents on Acidity H X C H H -replace with 1 different substituent Substituents H-CC-R, -Hal, -Br2, -Ph -OR, -NR2, SiR3 Weak Very Weak Strong Bases n-BuLi, SecBuLi, Li-TMP n-BuLi, Sec-BuLi, TertBuLi, T-MEDA Note: T-MEDA is a superbase, meaning you use this as a method of polarizing a carbon metal bond -T-MEDA stands for N,N,N’,N’-tetramethyl ethylene diamine N result: increase charges, compound becomes more basic C(-) - Li (+) electron flow N What do you do with super bases? -can make carbon metal bonds directly and faster e.g. CH C-M C-Hal Another superbase-the strongest! Schossler Reagent- BuLi/KOtBu -advantage: for polymerization reactions (Scheffold, 1992) -so powerful, can deprotinate anything! e.g. C3H6 ----------- C3Li6 -can play with electrophiles result: multiple characteristics, but, very unreactive, therefore this field of chemistry was abandoned. -alkanes are the solvents used for these two above mentioned very strong bases Solvents for Organometallic Chemistry Structure Name B. pt (degree Celsius) +34 Ether M. pt (degree Celsius) -116 O solvents hazards Distillation overLiAlH4, Ph2CO/K ------ Note: Benzophenone Potassium- it’s role is to purify the solution Used for reactions with: I) hydrocarbons II) ethers III) aminer (R3N) Ph Ph C' O C' O- K+ Ph Ph Take neutral diamagnetic compound and dump this molecule: -you produce a radical anion advantages: i) extremely reactive (pick up O2, H2O quickly-very efficient to get rid of bad impurities) ii) used as an indicator (violet or blue colour, when you see colour, sign to tell you that O2 and H2O are gone THF +66 -108 -LiAlH4 -Ketyl 1,4-Dioxane +100 +12 - LiAlH4 - Ketyl O O O -high toxicity -perhaps carcinogen N/A O O Et3N O O O O 1,2dimethyloxy ethane “GLYME” DIGLYME note:adding more O’s -can also be referred to as polyethers ------ +85 -58 - LiAlH4 - Ketyl N/A +162 -64 - LiAlH4 - Ketyl N/A ------- ------- - LiAlH4 - Ketyl -smells like fish Important characteristic to note for above mentioned solvents: Miscibility in water- THF, 1,4-dioxane, and GLYME Non-miscibility in water- ether Note on GLYME: -within kinetic examination of organometallic reactions, it was discovered butyllithium to be more reactive in “GLYME” than in THF! -reason being: the chelating of the bis-ether allows the surrounding metal to have a solvation shell with a lower entropy value -therefore, the reactivity of organometallic species increases by twice as much by the breaking up of oligomers or monomers and also by increasing the polarity between the carbon-metal bond (Scheffold, 1992) Advantages of GLYME and DIGLYME: i) high boiling solvent ii) don’t need autoclave iii) can use over the other solvents for a higher boiling point Disadvantages of ether: -can pick up water and oxygen too easily! Not good because it will cause the formation of peroxides! How do you protect yourself from peroxide formation? -add in KOH , NaOH or CaH2 (great safety method because it will tell you it is active by bubbling) -by adding in base, the peroxides will form salts, which are insoluble and ends the peroxides existence O O2 O H H O O Reactions with Ethers are dangerous-especially chlorinating and brominating -listed below are all the reagents which you cannot work with ethers because they are highly dangerous, chlorinated ethers are carcinogens Cl Br2, Cl2 O O VCL4, NbCl5, MoCl5, TaCl5, NCl6, NCl5, ReCl5 Note: iodine does not react, therefore, it is the only safe halogen -Fluorine and ether mixture is also dangerous, catch fire, explosive, death! Note: only two reagents which can react with ether to form anything of use are: i) NbCl5 ii) TaCl5 eg. The Best Method To Make NbOCl3 O Cl NbCl5 + NbOCl3 Cl Base Solvents for Organometallic Reactions: 1) NaH2- will deprotinate anything with pKa < 25 e.g. alkynes advantage: cheap 2) NaNH2- pKa < 33 Precautions: -use up soon, or store under argon -oxidized easily to yellow solution -looks innocent but is not! How to generate NaNH2: FeII Na + NH3 blue solution -H2 NaNH2 3) Ph3-Na- pKa < 30 Precautions: -safe, crystalline structure is air stable, therefore when you work with it, you do not need to use a glove box -*very useful base* Ph How to generate Ph3-Na: Ph-Hal Ph-MgHal PhCOOMe HCl Ph C Ph---C----Cl + Na OMgX Ph Ph3Na Superbases -can transform a vinyl compound into a vinyl metallic compound -can transform a polycompound into a metallic polycompound H M H M H M M=Li Reagent: BuLi/TMEDA M=K Reagent: BuLi/KotBu Note on Superbases: -compared with the more polar reagents, pentylsodium, butylpotassium and trimethylsilylpotassium, they have the reaction speed of a snail in comparison to superbases such as N,N,N’,N’-tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA) -superbases are so extraordinary in organometallic chemistry because it offers the best performance in terms of yield, rate and selectivity (Scheffold, 1992) Reference Scheffold, R. (1992) Modern Synthetic Methods . Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Basel. Pgs 227-250