11 Programme Structure, Levels, Modules and
advertisement
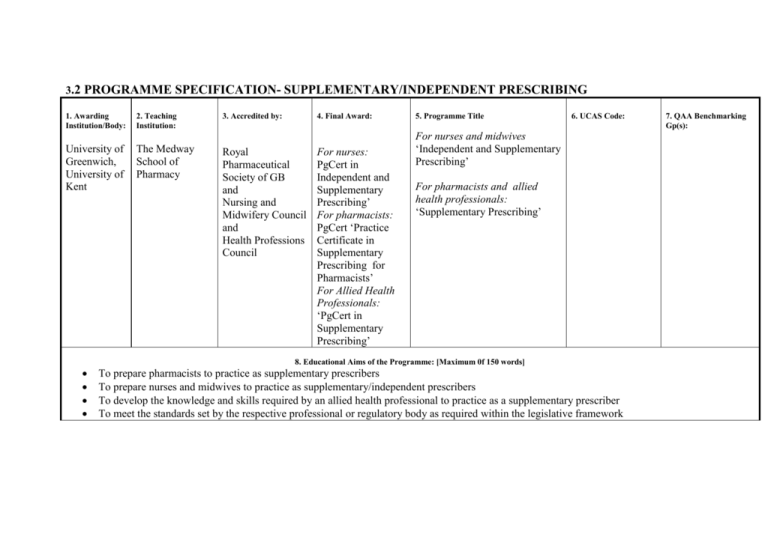
3.2 PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION- SUPPLEMENTARY/INDEPENDENT PRESCRIBING 1. Awarding Institution/Body: 2. Teaching Institution: University of Greenwich, University of Kent The Medway School of Pharmacy 3. Accredited by: 4. Final Award: Royal Pharmaceutical Society of GB and Nursing and Midwifery Council and Health Professions Council For nurses: PgCert in Independent and Supplementary Prescribing’ For pharmacists: PgCert ‘Practice Certificate in Supplementary Prescribing for Pharmacists’ For Allied Health Professionals: ‘PgCert in Supplementary Prescribing’ 5. Programme Title 6. UCAS Code: For nurses and midwives ‘Independent and Supplementary Prescribing’ For pharmacists and allied health professionals: ‘Supplementary Prescribing’ 8. Educational Aims of the Programme: [Maximum 0f 150 words] To prepare pharmacists to practice as supplementary prescribers To prepare nurses and midwives to practice as supplementary/independent prescribers To develop the knowledge and skills required by an allied health professional to practice as a supplementary prescriber To meet the standards set by the respective professional or regulatory body as required within the legislative framework 7. QAA Benchmarking Gp(s): 9. The programme provides opportunities for learners to achieve the following outcomes: [where relevant, provide reference to subject benchmarking statements] 10. The following teaching, learning and assessment methods are used to enable learners to achieve and demonstrate these outcomes: A Knowledge and understanding of: The legal and professional framework for non-medical prescribing Local health service provision and systems National and local frameworks for medicines use National and local budgetary constraints on prescribing Models of consultation Principles of diagnosis Applied advanced physiology Pathophysiology, natural history and progression of defined conditions Changes to pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in certain patient groups Principles of monitoring A Teaching and learning: Print based distance learning to incorporate work-based assignments. Students are required to develop a reflective portfolio of practice activities which are discussed with their peer group during the 5 contact days. These study days also include tutorials, seminars and workshops and involve the students in problem solving exercises, individual and group presentations. A Assessment Methods: The assessment methods associated with each course are detailed in the individual course specifications. Assessments include a combination of problem solving exercises, reflective assignments and an Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE). The nature of the assignments is appropriate to the subject areas and learning outcomes. B Intellectual skills: Review and critically evaluate best available evidence relevant to a specified area of prescribing practice, synthesising information from key sources and databases. Integrate previous learning with professional skills and expertise to synthesise innovative approaches to implementing extended independent/supplementary prescribing in practice Further develop the skills to review and critically analyse own learning and apply this to enhance role as a non-medical prescriber Make sound judgements about prescribing issues in the absence of complete data and communicate conclusions clearly to specialist and non-specialist audiences B Teaching and learning Intellectual skills are developed through reflective practice and learning activities and are supported by workshops and objective structured clinicalstyle practice situations during study days C Subject Practical skills: Consultation skills and medical history taking Physical examination of patients to aid diagnosis and monitoring Interpretation of medical documentation with an understanding of risks and benefits of incomplete data Monitoring patient response against objectives set within clinical management plans Recording prescribing actions and outcomes and the evidence base behind them contemporaneously in patient records C Teaching and learning Practical skills are developed in a co-ordinated manner throughout the programme. These skills are further developed during the 5 day contact time and through work-based learning. B Assessment Methods: Methods used to assess intellectual skills include case studies analysis and short written assignments. Intellectual skills are also assessed as part of the OSCE. C Assessment Methods: Practical skills are assessed through a variety of assessment methods such as short written assignments, case study analysis, problem solving exercises and an OSCE. D Transferable/ key skills: Show evidence of critical self-reflection and the ability to enhance professional competence on the basis of feedback from self and others. Communicate with clarity in both the academic and professional setting to a range of audiences and using a variety of approaches. Show ability to effectively manage and present complex information using a comprehensive range of learning resources Show a capacity for autonomous learning and ability to access professional resources including others as appropriate D Teaching and learning Problem solving, teamwork, communication skills, presentation skills and reflective practice are developed in a contextualized manner throughout the programme. These skills are enhanced during the study days and through work-based learning. D Assessment Methods: A variety of assessment methods are used to assess transferable skills. These include problem solving exercises, reflection upon work-based practice and the OSCE. These assignments are contextualised in A, B and C above. 11 Programme Structure, Levels, Modules and Credits 12 Awards, Credits and Progression The PgCert is offered as part-time structured distance learning with 12 days supervised practice, supported by 5 of Learning Outcomes compulsory contact days at the University. The PgCert consists of four 15 credit courses at Masters level. Students must be suitably qualified pharmacists, nurses, physiotherapists, podiatrists or radiographers and must register for the full PgCert in prescribing. Students completing the Post Graduate Certificate in Supplementary/ Independent Prescribing pathway may progress towards an MSc in Medicines Management providing the 45 compulsory credits within the Medicines Management Programme are completed as part of the credits obtained towards the diploma. Students will be supported by the School with their learning as outlined in the student handbook. Core Courses Non-medical Prescribing in Context (15 credits) Safe and Effective Prescribing (15 credits) Consultation and Decision Making (15 credits) Putting Prescribing Into Practice (15 credits) PgCert 60 credits at M level Pass: Minimum of 40% overall on each course for marked assignments and a pass on competency based assignments. Distinction: not available on this pathway.









