GI DRUGS 1. EMETICS -Drugs that produce vomiting with the intent
advertisement
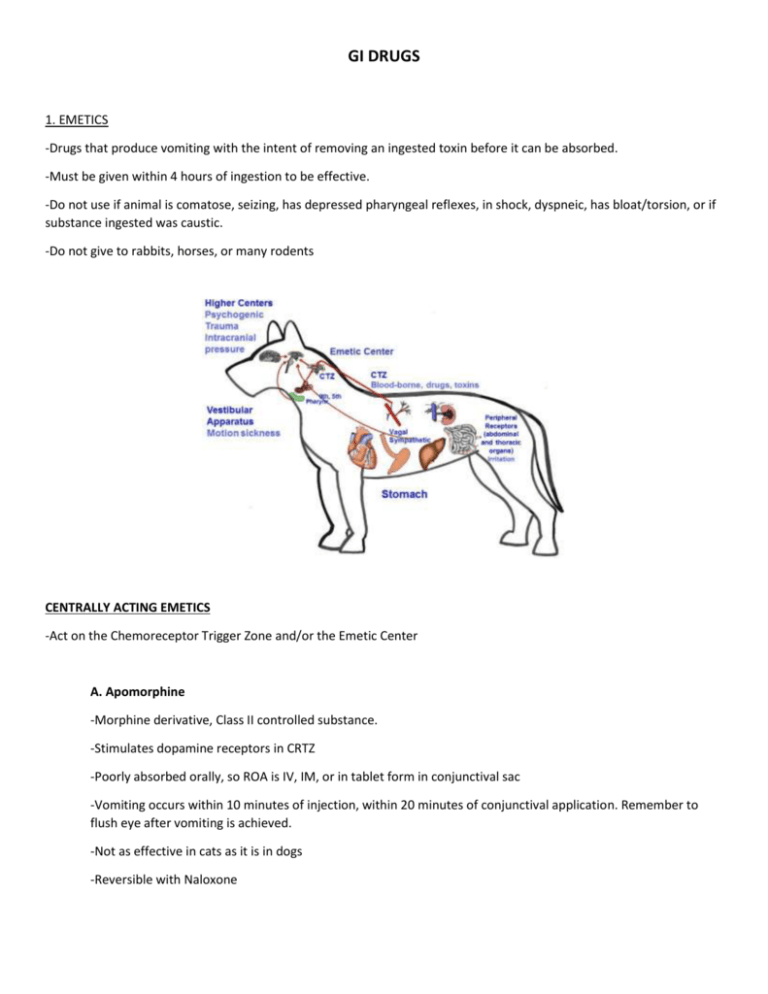
GI DRUGS 1. EMETICS -Drugs that produce vomiting with the intent of removing an ingested toxin before it can be absorbed. -Must be given within 4 hours of ingestion to be effective. -Do not use if animal is comatose, seizing, has depressed pharyngeal reflexes, in shock, dyspneic, has bloat/torsion, or if substance ingested was caustic. -Do not give to rabbits, horses, or many rodents CENTRALLY ACTING EMETICS -Act on the Chemoreceptor Trigger Zone and/or the Emetic Center A. Apomorphine -Morphine derivative, Class II controlled substance. -Stimulates dopamine receptors in CRTZ -Poorly absorbed orally, so ROA is IV, IM, or in tablet form in conjunctival sac -Vomiting occurs within 10 minutes of injection, within 20 minutes of conjunctival application. Remember to flush eye after vomiting is achieved. -Not as effective in cats as it is in dogs -Reversible with Naloxone B. Xylazine (aka Rompun, Anased) -Sedative (non-controlled) and anesthetic that stimulates alpha two receptors in the CRTZ and Emetic center. -Very effective as an emetic in cats, not as effective in dogs -IM injection that produces vomiting within 5 minutes -Emetic dose is lower than sedative dose -Reversible with Yohimbine LOCALLY ACTING EMETIC -Cause irritation of the GI mucosa Hydrogen Peroxide -Used as an emetic in dogs, cats, pigs, ferrets -3% solution that can cause vomiting within 10 minutes when given orally. -Can result in gastritis, aspiration -Should fresh as it loses fizz after a few months -1 tsp per 5 pounds. No more than 45 mL. May be repeated once after 15 minutes. 2. ANTIEMETICS -Prevent or control vomiting -Usually do not treat the underlying cause of vomiting. -Given parenterally A. Phenothiazine derivatives (Chlorpromazine- Thorazine) -Blocks dopamine receptors in the CRTZ that may also directly inhibit the Emetic center. -Tranquilizer, but antiemetic dose should not cause pronounced sedation. -Lowers the seizure threshold. B. Procainamide Derivatives (Metoclopramide- Reglan) -Blocks dopamine receptors in the CRTZ. - Prokinetic drug: increases gastric contractions and speeds emptying, strengthens cardiac sphincter tone. -DO NOT GIVE WITH GI OBSTRUCTION -More effective in dogs than cats. C. Antihistamines (H1 blockers: Diphenhydramine- Benadryl, Dimenhydrinate- Dramamine) -To be used as antiemetics when vomiting is caused by motion sickness or inner ear abnormalities. -Inhibit vomiting by decreasing impulses sent from the vestibular apparatus by blocking H1 receptors at the CRTZ. -More effective in dogs than cats. -May cause sedation. -Although injectables are available, oral dose can be given prophylactically. D. Serotonin Receptor Antagonists (Ondansetron- Zofran, Dolasetron (Anzemet) -Also called 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, these drugs block serotonin (a neurotransmitter) receptors on the vagus nerve and in the CRTZ. -Pricey, but may be worth it for short-term treatment. E. NK-1 Receptor Antagonists (Maropitant citrate- Cerenia) -Inhibit the binding of Substance P (a neuropeptide) to neurokinin receptors in the Emetic center. -Injectable form is approved for use in both dogs and cats. Oral form is for dogs. -Injection may be painful. -Can be given prophylactically to prevent motion sickness (without causing drowsiness), but also used to treat vomiting from other causes.