Heat – Mini Test Review Grade 7
advertisement

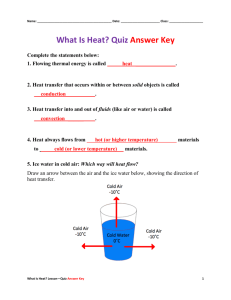
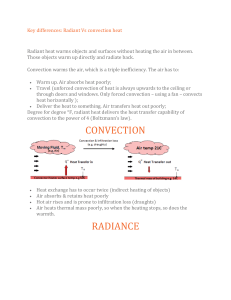
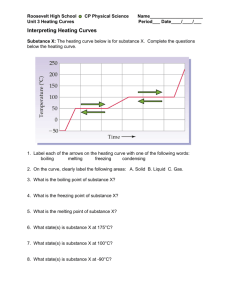
Heat – Test Review Heat – is energy, which transfers from hotter substances to colder ones Temperature – measure of the average energy of motion of particles of a substance Temperature Scales – freezing and boiling points o Kelvin o Celsius – temp of human = 37 C o Fahrenheit Thermometer Expansion Contraction Thermostat Thermocouple Particle Theory and Heat – what happens when heat is applied to objects in different states Melting Point Boiling Point Freezing Point Condensation Heating Curve Cooling Curve Sublimation Changes of State Organizer – chart with name of change, what the state is at the start and finish, and if heat is removed or added Ice to Water to Steam Lab Heat and Convection o What is convection o Convection demonstration – peppercorns/food coloring in water o Diagram of air warming and rising (less dense). Cool air falls (more dense). Cool air replaces warming air. o Thermal Conduction o Conduction demonstration – water and balloon o Definition of conduction o What makes a good conductor Radiation o Definition of radiation o House example –raising temp through the heat of the sun Water Cycle – be able to label the water cycle and know the terms – infiltration, precipitation, condensation, transpiration, accumulation, evaporation, runoff. Heating a Single room using a hot-water and forced-air system Wasted heat – where do people lose heat and how can they prevent this? Why do people not add energy-efficient features to their homes? Thermograph R-values- What is it? Define: Heat Capacity High and low heat capacities: what does this mean? Water and heat capacity – takes a long time to heat up and cool down Energy Sources Renewable and Non-renewable energy Mechanical, Electrical, Chemical and Nuclear Energy (fusion and fission) Heat Pollution Lubricant Cogeneration Solar Heat – why is it important Passive solar heating Active solar heating Greenhouse effect
![Applied Heat Transfer [Opens in New Window]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008526779_1-b12564ed87263f3384d65f395321d919-300x300.png)