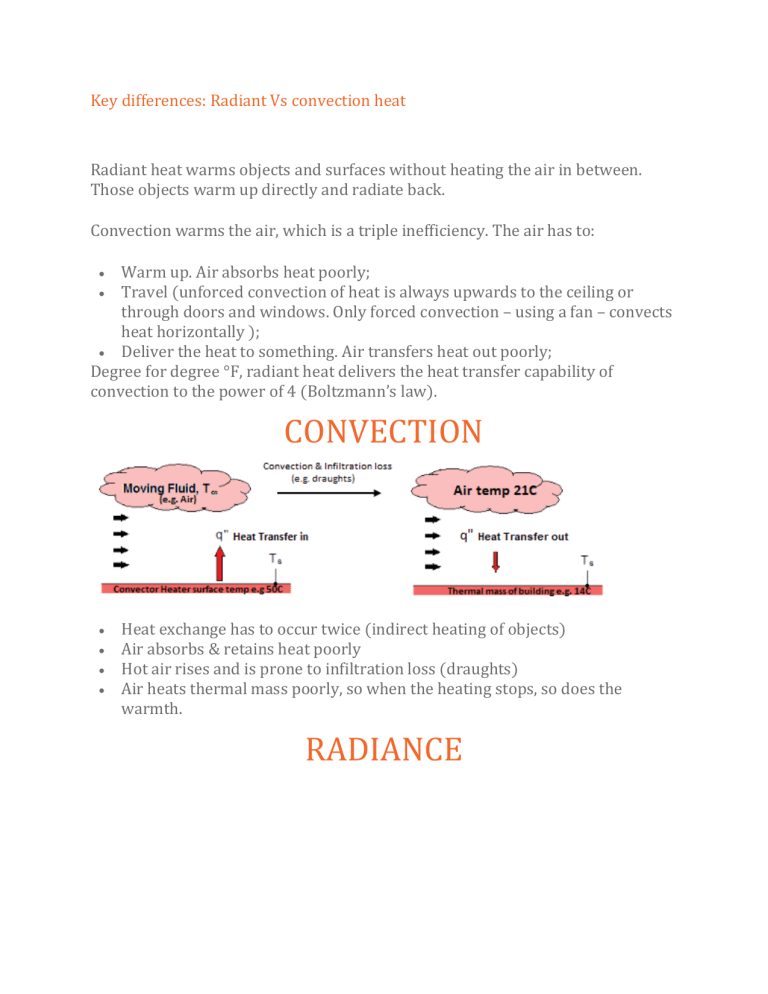
Key differences: Radiant Vs convection heat Radiant heat warms objects and surfaces without heating the air in between. Those objects warm up directly and radiate back. Convection warms the air, which is a triple inefficiency. The air has to: Warm up. Air absorbs heat poorly; Travel (unforced convection of heat is always upwards to the ceiling or through doors and windows. Only forced convection – using a fan – convects heat horizontally ); Deliver the heat to something. Air transfers heat out poorly; Degree for degree °F, radiant heat delivers the heat transfer capability of convection to the power of 4 (Boltzmann’s law). CONVECTION Heat exchange has to occur twice (indirect heating of objects) Air absorbs & retains heat poorly Hot air rises and is prone to infiltration loss (draughts) Air heats thermal mass poorly, so when the heating stops, so does the warmth. RADIANCE Heat exchange occurs once (direct heating of objects) Most domestic materials absorb & retain heat well Less prone to infiltration loss in an enclosed space Excellent priming of thermal mass = when heating stops, residual heat is left in the building. Advantages for heaters The advantages of radiant heating over convection: Heat transferred (watts / foot / second) grows exponentially with temperature rise. Convection heat transfer grows only linearly with temperature. You require less installed capacity in a radiant heating system You don’t need to run it as long You can apply heat only where you need it – you don’t need to heat the whole room You can control it more precisely Types of radiant heaters from Herschel Herschel Infrared supplies Far Infrared Panels – these are mostly used in residential and office applications. Far Infrared Space Heaters – for heating larger enclosed or sheltered outdoor spaces Medium Infrared Space Heaters – for heating unsheltered areas (e.g. patios) or colder indoor areas.



