Worksheet 18 Key - Iowa State University
advertisement

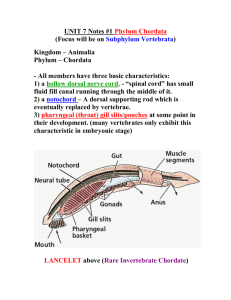
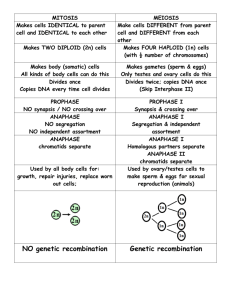
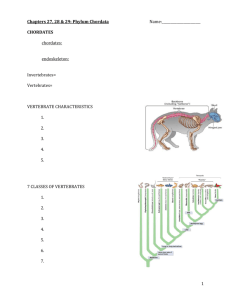
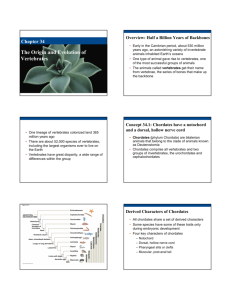
Leader: Kirsten Karkow Course: Biol 211 - Wilsey Date: 3/5/2012 Worksheet 18 – Review for Exam 3 Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Characteristics of Chordates Notochord Dorsal, hollow nerve chord Pharyngeal slits Postanal tail Additional Characteristics of Vertebrates Pronounced cephalization Vertebral column Closed circulatory system Separate males and females Which of the following gives the correct order of development of vertebrates? a. b. c. d. Vertebrates, gnathostomes, lungfish, reptiles, eutherians, monotremes Craniates, vertebrates, chondrichthyes, lobe fins, amniotes, mammals Vertebrates, gnathostomes, amniotes, amphibians, mammals, humans Craniates, vertebrates, lobe fins, bony fishes, reptiles, monotremes Match each group with an appropriate organism from the right column. Craniate Vertebrate Chondrichthyan Amphibian Reptile Monotreme Marsupial Eutherian Platypus Lamprey Monkey Ray Bird Hagfish Caecilian Opossum First organisms to have jaws? Sharks First organisms to live on land? Amphibians Cephalochordata Urochordata “Tunicates”/“Sea Squirts” Lose chordate characteristics “Lancelets” Keep chordate characteristics Ray-finned Fish Ray fins (bones) Monotremes Lay eggs Coelocanths Lobed fins (bone + muscle) Lungfish Lobed fins + lungs (+ gills) Marsupials Develop young in marsupium Eutherians Placental animals Humans are most closely related to apes. They share 99% of their DNA. Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu Define: Genome – all of the DNA within a cell Chromatin – loose DNA. Chromatid – condensed DNA molecule. Chromosome – individual condensed mass of DNA. 1 or 2 chromatids. Somatic Cells – asexual cells. Diploid. Gametes – sexual cells. Haploid. Centromere – attachment point of sister chromatids. Kinetochore – attachment point for mitotic spindle. G1 Checkpoint During G1 Size? Big enough? Favorable environment? G2 Checkpoint During G2 Synthesis went okay? Favorable environment? M Checkpoint During (any) metaphase All lined up/connected? What organisms perform binary fission? Prokaryotes What organisms perform mitosis? When/why? Eukaryotes – growth, cloning, etc. Benign Tumor Mass of cancer cells that hasn’t spread. Malignant Tumor Tumor that has metastasized ⇛ cancer. Define: Gene – hereditary unit. Codes for a protein. Allele – specific version of a gene. Locus – location of the gene on the chromosome. Synapsis – close association of homologous chromosomes. PROPHASE 1! Crossing Over – gene trading between homologous chromosomes. PROPHASE 1! Chiasmata – location of crossing over on homologs. Stay attached until anaphase 1. Euploidy 2n Aneuploidy 2n ± 1/few Polyploidy 2n + n When do homologous chromosomes separate? Anaphase I When do sister chromatids separate? Anaphase II and Anaphase (of mitosis) What processes contribute to genetic variability? Crossing over. Independent assortment. Random fertilization. BE AN SI LEADER!!! Doooooooooooo iiiiiiiiiiiiiit…