Notes on Stonehenge (Sample notes page for topic #2 of the
advertisement

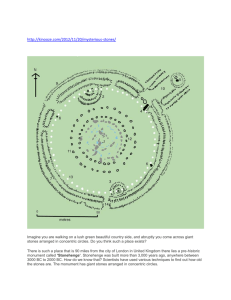
Notes on Stonehenge (Sample notes page for topic #2 of the Odyssey Groups Research Project) UNESCO.org Most famous of the circular megaliths created during Neolithic times in Britain Not built all at once—built in stages over 2,000 years (3100-1100 BC) o The fact that it took so long to build shows their significance to its builders 2 different materials used= sandstone blocks (sarsens) from nearby Salisbury in south + bluestones from Pembroke County, Wales (124 miles away); largest stones are 40 tons Why it’s special= huge megaliths that are shaped (worked on), sophisticated design and layout (uses horizontal lintel stones atop the regular standing stones), exact positioning Called “the most architecturally sophisticated prehistoric stone circle in the world” by the State Party (nearby Avebury is called the largest stone circle in the world”) Chroniclers like Geoffrey of Monmouth saw it as a wonder of the world in the 12thc. Indepenent.co.uk (“Secret History of Stonehenge Revealed”) Stonehenge’s site may’ve been held sacred 500 years before the first stone circle was built based on new investigation involving Universities of Birmingham, Bradford, Vienna New evidence links Stonehenge to sun worship= during a survey of the area nearby (the “Cursus”), teams from the U’s of Birmingham and Vienna discovered 2 large pits near the eastern and western ends of Stonehenge using ground-penetrating radar … these pits align with the sunrise and sunset on the summer solstice when viewed from the “heel stone” … further evidence came when the teams used computers to figure out the location of the midway point between the two pits … If the E pit was sunrise and the W one sunset, the midway point (noon point) of the procession route from one pit to the next would also be significant to sun worshippers … the computers proved that the point would be smack in the center of Stonehenge Walking around monuments was common ritual for ancient peoples around the world How does this prove Stonehenge’s holiness predates the stones? (1) The midway point on the route wouldn’t be significant without the Cursus, so Stonehenge is at least as old as the Cursus (not later, as was believed). Since the pits align based on the heel stone, the stone’s location had to have been sacred before there were ever stones there Smithsonianmag.com (“New Light on Stonehenge”) Possible functions= prehistoric observatory, royal burial ground, sacred healing center Bluestones thought to have healing powers in 13thc= bathing in water used to wash the stones would cure you; place of origin (Wales) known for supposed healing springs 1st phase was simple earthen-work; 2nd phase was wood timbers; 3rd phase was stone, about 200 years after 1st phase … 80 bluestones were first stones erected Remains found nearby suggest people came here to be healed from as far as Swiss Alps First bluestones placed between 2400-2200 B.C.—200-300 years later than the previous estimate of 2600 B.C. according to radiocarbon dating of organic material in postholes … the new date fits in the time period of the burial remains, suggesting it was a healing site First burial there at 3030BC, predating stones= could’ve become healing site later on Hard to say this was a healing site for sure= most remains cremated so can’t see injuries; healing powers of stones based on where they come from so far are unsubstantiated Could’ve been special since 8000BC= charcoal discovered dates from that time Science.nationalgeographic.com (“Scientists Try to Crack Stonehenge's Prehistoric Puzzles”) Creation theories= created by Merlin, erected by invading Danes, created by aliens as landing area for spacecraft, created by Celts (mistaken belief of John Aubrey in 1660s) Notes on Stonehenge (Sample notes page for topic #2 of the Odyssey Groups Research Project) UNESCO.org Most famous of the circular megaliths created during Neolithic times in Britain Not built all at once—built in stages over 2,000 years (3100-1100 BC) o The fact that it took so long to build shows their significance to its builders 2 different materials used= sandstone blocks (sarsens) from nearby Salisbury in south + bluestones from Pembroke County, Wales (124 miles away); largest stones are 40 tons Why it’s special= huge megaliths that are shaped (worked on), sophisticated design and layout (uses horizontal lintel stones atop the regular standing stones), exact positioning Called “the most architecturally sophisticated prehistoric stone circle in the world” by the State Party (nearby Avebury is called the largest stone circle in the world”) Chroniclers like Geoffrey of Monmouth saw it as a wonder of the world in the 12thc. Indepenent.co.uk (“Secret History of Stonehenge Revealed”) Stonehenge’s site may’ve been held sacred 500 years before the first stone circle was built based on new investigation involving Universities of Birmingham, Bradford, Vienna New evidence links Stonehenge to sun worship= during a survey of the area nearby (the “Cursus”), teams from the U’s of Birmingham and Vienna discovered 2 large pits near the eastern and western ends of Stonehenge using ground-penetrating radar … these pits align with the sunrise and sunset on the summer solstice when viewed from the “heel stone” … further evidence came when the teams used computers to figure out the location of the midway point between the two pits … If the E pit was sunrise and the W one sunset, the midway point (noon point) of the procession route from one pit to the next would also be significant to sun worshippers … the computers proved that the point would be smack in the center of Stonehenge Walking around monuments was common ritual for ancient peoples around the world How does this prove Stonehenge’s holiness predates the stones? (1) The midway point on the route wouldn’t be significant without the Cursus, so Stonehenge is at least as old as the Cursus (not later, as was believed). Since the pits align based on the heel stone, the stone’s location had to have been sacred before there were ever stones there Smithsonianmag.com (“New Light on Stonehenge”) Possible functions= prehistoric observatory, royal burial ground, sacred healing center Bluestones thought to have healing powers in 13thc= bathing in water used to wash the stones would cure you; place of origin (Wales) known for supposed healing springs 1st phase was simple earthen-work; 2nd phase was wood timbers; 3rd phase was stone, about 200 years after 1st phase … 80 bluestones were first stones erected Remains found nearby suggest people came here to be healed from as far as Swiss Alps First bluestones placed between 2400-2200 B.C.—200-300 years later than the previous estimate of 2600 B.C. according to radiocarbon dating of organic material in postholes … the new date fits in the time period of the burial remains, suggesting it was a healing site First burial there at 3030BC, predating stones= could’ve become healing site later on Hard to say this was a healing site for sure= most remains cremated so can’t see injuries; healing powers of stones based on where they come from so far are unsubstantiated Could’ve been special since 8000BC= charcoal discovered dates from that time Science.nationalgeographic.com (“Scientists Try to Crack Stonehenge's Prehistoric Puzzles”) Creation theories= created by Merlin, erected by invading Danes, created by aliens as landing area for spacecraft, created by Celts (mistaken belief of John Aubrey in 1660s)