Grade 9 Biology Term 2 Test 2 Memo
advertisement

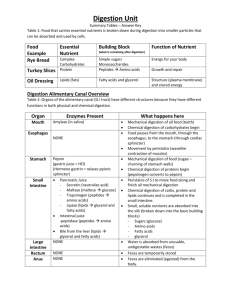
Grade 9 Biology Term 2 Test 2 21st May 2015 Nutrition and Digestion Total Marks: 42 NAME Multiple Choice (circle correct letter) [Total: 5] 1. The diagram shows part of the digestive system What is a function of the liquid produced by part 1 and released into part 2? A to digest proteins to amino acids B to increase the surface area of fat droplets C to acidify the contents of part 2 D to prevent further digestion of starch 2. Why does chewing food speed up digestion? A Bacteria in the food are killed. B Food is mixed with protease. C The surface area of the food is increased. D The taste of food is improved. 3. Which chemical reaction takes place in the stomach? A Proteins are digested by protease. B Proteins are digested into fatty acids. C Starch is digested into amino acids. D Starch is digested by lipase. 4. The small intestines of cows are similar in general structure and function to the small intestines of humans. A disease in cows reduces the number of villi in their small intestines. The cows lose weight and become weak. What explains this? A less amylase produced B less peristalsis C slower absorption of nutrients D slower digestion of proteins 5. In which part of the body do drugs break down? A brain B heart C kidneys D liver 6. The diagram shows the human alimentary canal, with a string marked in metres beside it. How long is the small intestine? A2m B6m C8m D9m Structured Questions 1. The alimentary canal is adapted for chemical and mechanical digestion. (a) Explain how chemical digestion differs from mechanical digestion. chemical digestion (max 2) ref to breakdown of molecules ; breaking bonds ; using enzymes ; insoluble to soluble ; mechanical digestion (max 2) ref to breakdown of, particle / molecule ; ref to increase surface area (for chemical digestion) ; to, mix /churn ;3] Fig. 1.1 is a diagram of the human alimentary canal. Fig 1.1 (b) Table 2.1 shows four functions of the alimentary canal. Complete the table by: • naming the part of the system that carries out each of the functions; • using the letters from Fig. 5.1 to identify the part of the system named. One row has been completed for you. (c) Some people develop gallstones, made of cholesterol, that accumulate in the gall bladder and the bile duct. Gallstones block the flow of bile. Explain how gallstones can affect the digestion of fat. less / no bile, secreted / released ; (so) no / less, bile salts ; enter small intestine / duodenum ; no / less, emulsification of fat ; less / no, increased surface area of fat (globules / AW) for lipase ; slower / harder, digestion ;3] R no digestion [Total: 10] 2. Fig. 2.1 shows three different types of teeth from a human. Fig 2.1 (a) (i) Name the types of teeth labelled A and B. (ii) State where in the jaw tooth type C is found...........................................................................................[1] (b) Explain how regular brushing helps to prevent tooth decay. (c) Explain the roles of chewing and of enzymes in the process of digestion. [Total: 10] 3. (a) Describe how food is moved along the small intestine. 1 peristalsis ; 2 circular muscles contract (to push to food) ; 3 muscle contraction above food pushes it forward ; 4 circular and longitudinal muscles work antagonistically / AW ; [2] (b) The small intestine is lined by many villi. Fig. 3.1 shows a longitudinal section of a villus. Fig. 3.2 shows a cross-section of the same villus at V – W. The diagrams are not drawn to the same scale. Fig 3.1 Fig 3.2 (i) Name structures P, Q, and R. P – epithelium / epithelial cell ; Reject ciliated epithelium, epidermis, goblet cell Accept epithelium with brush border Q – (blood) capillary ; R – lacteal / lymphatic vessel ; [3] (ii) The blood that flows from S enters a vein. Name the vein that transports blood away from the small intestine. hepatic portal (vein) ; [1] (iii) Cell T is an example of the cells that form the surface of the villi. Explain why there are many microvilli on cell T. give a large surface area (of membrane) ; to increase / maximise, absorption ; by diffusion / by active transport ; [2] (iv) Some of the cells on the surface of the villi secrete mucus for protection. Suggest what the villi need to be protected against. enzymes / proteases / lipases ; (stomach) acid ; physical damage / AW ; parasites / (named) pathogens / toxins ;2] [Total: 10] 4. The liver is an organ with a large number of different functions. Fig. 4.1 shows the liver, its blood supply and some other organs. The blood vessels are labelled P to R. Fig 4.1 (a) A person eats a meal containing protein and carbohydrate. Complete Table 4.1 to show the blood vessel that has the highest concentration of glucose, oxygen and urea as this meal is absorbed. Use the letter, P, Q or R to identify each blood vessel. Table 4.1 glucose – R ; oxygen – Q ; urea – P ; Write the letters for the blood vessels with the highest concentration of each substance in the spaces on Table 4.1. [3] (b) Amino acids are absorbed from the small intestine and transported to the liver. Describe how the liver is involved in the metabolism of amino acids. amino acids used to make proteins ; R the liver produces amino acids deamination ; removal of, nitrogen-containing group / amino group / amine group / AW ; formation of urea ; rest of molecule / carbohydrate, is, respired / stored as glycogen / converted to fat / used for energy ;3] [Total: 6]