Notes on Halogens
advertisement

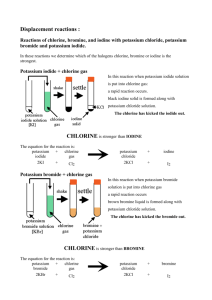
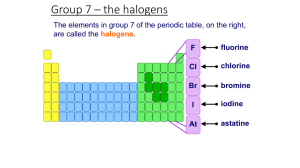
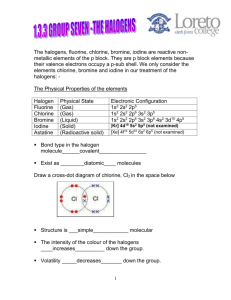
Halogens- Group 7 Objectives: Describe chlorine, bromine and iodine in Group VII (trend in physical properties and displacement reactions. Prior Knowledge: The group number tells you how many electrons there are in the outer shell of the atoms. • The outer-shell electrons are also called valency electronsand their number shows how the elements behave. • All elements in a group have similar properties. • Some of the groups have special names: Group 1 – The alkali metals Group 2 – The alkaline earth metals Group 7 – The halogens Group 0 – The noble gases Physical Properties Form colored gases. Are brittle and crumbly in their solid form, and do not conduct electricity. Form diatomic molecules (means they exist as 2 atoms.) Eg: Cl2, Br2, I2. These are elements which react with most metals to form salts. Have seven outer shell electrons. each molecule in the element is diatomic (contains two atoms, eg F2) Elements become darker and solidify down the group. They have low melting and boiling points which increases down the group. all halogens are poisonous. Page 1 of 5 Trends in their chemical properties Reactivity increases as you go up group 7. Why? Because the smaller the atom, the easier it is to attract the electron – so the more reactive the element will be. Why are they so reactive? Because their atoms are only one electron short of a full shell. Compounds of the Halogens Halogens gives a charge of –1, so they give similar formulae, eg: NaBr, NaI Reactions of the Halogens - reacts vigorously with metals to form ionic salts for the equation: 2K + Br2→2KBr Group 7 elements are coloured, but the compounds they form with group 1 metals are white solids and make colourless solutions. Displacement Reactions More reactive halogen displaces less reactive halogen. Eg: aqueous fluorine was added into sodium bromide solution. State the chemical equation of the reaction. Chemistry Dept/Grade9/First Term/2014 Imaduddin School F2(aq) + 2NaBr(aq)→2NaF(aq) + Br2 (aq) WORKSHEET on HALOGENS When chlorine solution is added to potassium bromide the solution turns orange. The word equation below describes the reaction: 1. The properties of the Group 7 Halogen elements Atomic chlorine + potassium bromide sodium chloride + bromine number a) Write the colour of each chemical under its name in the equation. b) Name the type of reaction taking place: _____________________________________ 9 Element Symbol Fluorine F 17 Cl 35 Br 53 I 85 Astatine At state, colour at Electron room temperature arrangement pale yellow gas black solid Decide whether each of the following pairs will react. If they will, name the products. Otherwise, write no reaction. a. Complete the table above. chlorine + potassium iodide b. What is the colour of the vapour (gas) formed on heating (i) bromine, _______________________________________________ bromine + potassium chloride (ii) iodine? c. Compare the properties of halogens with matals. eg strength of solid, heat and electrical conduction? _____________________________________________ bromine + potassium iodide _______________________________________________ iodine + potassium astatide _______________________________________________ d. What is the group trend in melting and boiling point down the group with increase in atomic number? fluorine + potassium chloride ______________________________________________ Page 2 of 5 Chemistry Dept/Grade9/First Term/2014 Imaduddin School e. How does the trend affect their physical state as you go down the group with increase in atomic number? f. The molecules consist of diatomic molecules. What does this mean? k. g. Describe simple chemical tests for (a) chlorine, (b) iodine Draw dot and cross diagram to show the bonding in chlorine molecule. 2. h. The Reactivity Trend of the Halogens a. Complete the table of results above. b. Which halogens does chlorine displace? c. Which halogens does bromine displace? What sort of compounds do they form when combined with metals? Draw dot and cross diagram to show the bonding in sodium chloride. d. Which halogens does iodine displace? e. What is the reactivity rule for displacement reactions? i. What is the charge on the halide ion? Quote the symbol of the ion from chlorine and explain why it is having that particular charge? f. From your observations what is the reactivity trend for chlorine, bromine and iodine? j. What sort of compounds do they form when combined with non- metals? eg hydrogen chloride HCl and explain how the bond is formed. Page 3 of 5 Chemistry Dept/Grade9/First Term/2014 Imaduddin School halogen\salt Potassium chloride chlorine water (pale green solution) Potassium bromide no change bromine water (orange solution) Convert the particle picture into a symbol equation for the reaction. ______________________________________________________________ no change iodine water (very dark solution of iodine dissolved in potassium iodide solution) g. Potassium iodide c) Chlorine can also displace iodine from potassium iodide. Write a symbol equation for this reaction. ______________________________________________________________ d) Predict which element bromine will displace and write an equation for the reaction. no change ______________________________________________________________ e) Why do the halogens have such similar chemical properties? ______________________________________________________________ How does their reactivity compare to Noble Gases? Explain? 4 Gaining electrons The particles in potassium bromide are ions. h. Write word and symbol equations for the reaction between potassium chloride and astatine. 3. The particle picture shows a displacement reaction. Page 4 of 5 Chemistry Dept/Grade9/First Term/2014 Imaduddin School During the reaction, chlorine atoms gain an electron and become charged ions, so the chlorine atoms are reduced. - END - a) What happens to the bromide ions during the reaction? ______________________________________________________________ A smaller, more reactive halogen can take electrons from a larger halogen. b) Suggest why smaller non-metal atoms gain electrons more easily than larger ones. ______________________________________________________________ Page 5 of 5 Chemistry Dept/Grade9/First Term/2014 Imaduddin School




![[1] - Boswellsgmt](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006603407_1-fadfbce8d94050a9fb3c38a07d86e8ee-300x300.png)