Molecular Compounds-student - Varga
advertisement

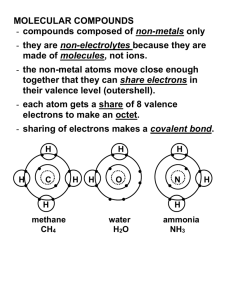
Chem 20 Molecular Compounds Ionic compounds form with an exchange of electrons between a metal and a non-metal. Molecular compounds form by the SHARING of electrons between two __________________. If a chlorine atom is seeking an electron it will find another ______________ atom and each atom will _________ one of its electrons with the other. This means that each atom keeps all of its own electrons but one of its electrons is shared with the other atom. Molecular compounds are normally __________ or __________ at room temperature. A bond formed by the sharing of electrons is also called a _______________ _______. Examples are CO2 and ammonia (NH3). Draw a diagram of a chlorine molecule (Cl2), showing how each chlorine atom shares an electron to form a complete outer shell of electrons: You try it: Draw a diagram of a methane (CH4) molecule. How do you think the atoms come together so that each has a stable (full) valence shell? Chem 20 Combining Capacity: The number of _____________ that a non-metal needs to share to become stable is a clue to the number of ________________ bonds it can form. The number of covalent bonds that a non-metal will have to form to create a __________ molecule is referred to as the atom’s ________________ ______________. For example, carbon has _____ electrons in its valence shell. Carbon therefore “gains” 4 electrons by ____________; carbon has a combining capacity of 4. The following table contains combining capacities of several common non-metals: 4 3 2 1 H C N O You try it: Predict the combining capacities of the following non-metals: F S P Si Cl Diatomic Elements: Recall the first example in this set of notes where we looked at Cl2, a chlorine molecule. Several elements actually exist like this in __________ as _____________ ______________. Chlorine is one example, but there are ____ others as well. The following table will tell you which elements are diatomic, but there is an easier way to remember: Look at the periodic table and notice that the diatomic elements basically form a __________ gun with a hydrogen bullet and they will be easier to remember! Hydrogen H2 Gas Oxygen O2 Gas Nitrogen N2 Gas Fluorine F2 Gas Chlorine Cl2 Gas Chem 20 Bromine Br2 Liquid Iodine I2 Solid Naming and Formulas for Molecular Compounds Rules for Naming: Write the name of the first element of the formula in full Change the ending of the second element’s name to “ide” (same as ionic binary compounds) Use prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element in the molecular formula Note: If the number of atoms in the first element is one, the prefix “mono” is not necessary Ex - Write the name of the molecular compound P2Cl5 Rules for Formulas: Molecular compounds are pretty easy: Just read the name of the compound and use the prefixes to determine the number of atoms of each element. Ex - Write the formulas of the following molecular compounds: Carbon monoxide, Dinitrogen Tetraoxide Chem 20 Here are prefixes that will be helpful to you: mono- 1 di- 2 tri- 3 tetra- 4 penta- 5 hexa- 6 hepta- 7 octa- 8 nona- 9 deca- 10