Properties of Hazrdous Chemicals
advertisement
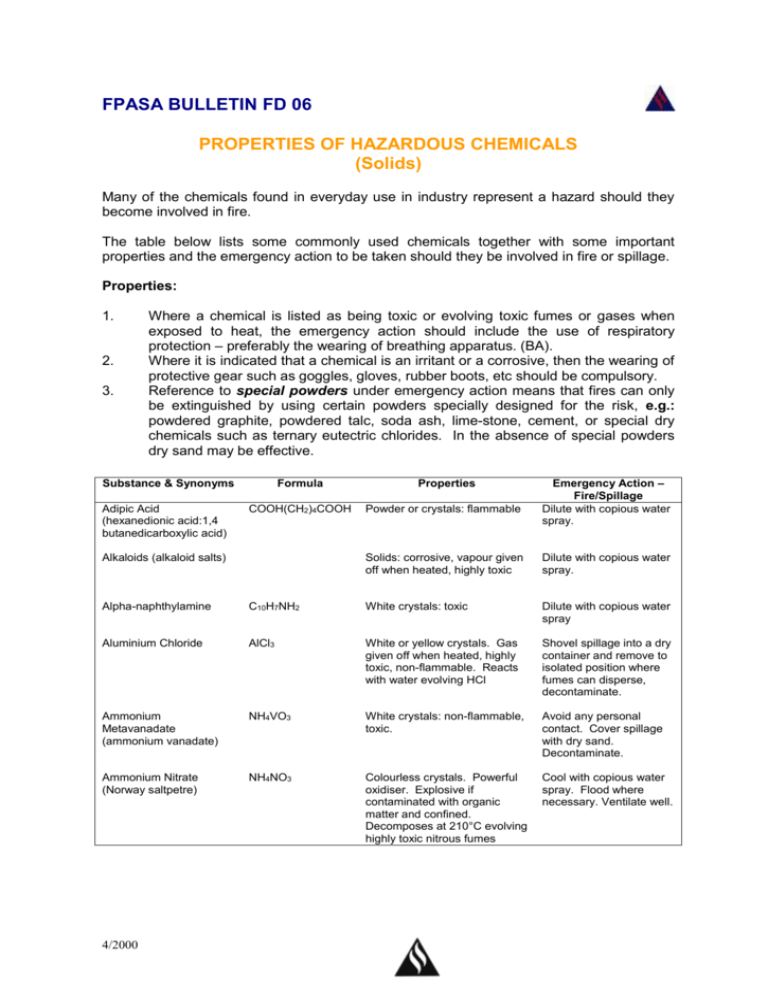
FPASA BULLETIN FD 06 PROPERTIES OF HAZARDOUS CHEMICALS (Solids) Many of the chemicals found in everyday use in industry represent a hazard should they become involved in fire. The table below lists some commonly used chemicals together with some important properties and the emergency action to be taken should they be involved in fire or spillage. Properties: 1. 2. 3. Where a chemical is listed as being toxic or evolving toxic fumes or gases when exposed to heat, the emergency action should include the use of respiratory protection – preferably the wearing of breathing apparatus. (BA). Where it is indicated that a chemical is an irritant or a corrosive, then the wearing of protective gear such as goggles, gloves, rubber boots, etc should be compulsory. Reference to special powders under emergency action means that fires can only be extinguished by using certain powders specially designed for the risk, e.g.: powdered graphite, powdered talc, soda ash, lime-stone, cement, or special dry chemicals such as ternary eutectric chlorides. In the absence of special powders dry sand may be effective. Substance & Synonyms Adipic Acid (hexanedionic acid:1,4 butanedicarboxylic acid) Formula COOH(CH2)4COOH Alkaloids (alkaloid salts) Properties Powder or crystals: flammable Emergency Action – Fire/Spillage Dilute with copious water spray. Solids: corrosive, vapour given off when heated, highly toxic Dilute with copious water spray. Alpha-naphthylamine C10H7NH2 White crystals: toxic Dilute with copious water spray Aluminium Chloride AlCl3 White or yellow crystals. Gas given off when heated, highly toxic, non-flammable. Reacts with water evolving HCl Shovel spillage into a dry container and remove to isolated position where fumes can disperse, decontaminate. Ammonium Metavanadate (ammonium vanadate) NH4VO3 White crystals: non-flammable, toxic. Avoid any personal contact. Cover spillage with dry sand. Decontaminate. Ammonium Nitrate (Norway saltpetre) NH4NO3 Colourless crystals. Powerful oxidiser. Explosive if contaminated with organic matter and confined. Decomposes at 210°C evolving highly toxic nitrous fumes Cool with copious water spray. Flood where necessary. Ventilate well. 4/2000 Substances & Synonyms Barium Formula Properties Emergency Action – Fire/Spillage Avoid any personal contact. Ba Solid: toxic. Reacts violently with water, halogens, oxygen acids and ammonia. Flammable in powder form. Barium Nitrate (nitrobarite) Ba(NO3)2 White crystals: nonflammable, toxic, oxidising agent. When heated gives off oxygen and highly toxic nitrous fumes. Explosive if contaminated with organic material. Avoid any person contact. Flush away spillage with copious water spray. Beware hazard on drying out. Barium Peroxide) (barium binoxide, barium dioxide) BaO2 Grey-white powder: toxic, oxidising. Reacts violently with water to produce heat. Oxygen liberated on heating to high temperatures. Avoid any personal contact with solid. Beware explosion risk on heating or on contamination with combustible materials. Boric Acid (boracic acid, orthoboric acid) H2BO3 Powder or crystals: noncombustible, toxic, irritating. Cadmium Cd Crystals: Flammable in powder form. Fumes toxic, fatal dose can be inhaled without immediate discomfort. Reacts vigorously with oxidising agents. Calcium Ca Metal: Reacts violently with water to produce hydrogen. Non-toxic. Avoid any personal contact. Cover spillage with dry sand. Calcium Carbide CaC2 Grey crystals: nonflammable. Reacts violently with water to produce acetylene gas, heat and corrosive solid. Beware explosion risk if water enters punctured containers. Calcium Chlorate Ca(ClO3)22H2O White to yellow crystals. Oxidising. When heated above 100°C decomposes to liberate volumes of oxygen. Explosive if contaminated with combustible material or when subjected to shock. Beware explosion risk on heating or shock. Calcium Cyanamide (calcium carbinide, lime nitrogen) CaCN2 Calcium Hypochlorite (bleaching powder, calcium oxychloride) Ca(ClO)2 4/2000 Colourless crystals: Reacts with heat or water to produce acetylene and ammonia. Irritant by contact. White powder, granules or pellets. Dangerous oxidising material. Heat evolves oxygen. Non-flammable. Evolves chlorine with acids. Irritant, toxic. Flood with copious water spray. Substances & Synonyms Calcium Hydroxide (calcium hydrate, slaked lime, hydrate lime). Camphor (2camphonone, gum camphor, laurel camphor) Formula Ca(OH)2 C10H10O Powder: non-flammable, skin irritant. Caustic. Reacts with acids to produce heat Crystals. Vapour given off when heated, toxic flammable. Explosive range 0,6 to 3,5 % in air. Emergency Action – Fire/Spillage Dilute and flush away spillage with copious water spray. Avoid personal contact. White flakes or powder. Flammable, burning slowly giving off black smoke. Cellulose Acetate (C.A.) Chloride of Lime (bleaching powder) Properties CaCl(ClO).4H2) Chromates (chromium compounds) White powder: Oxidising agent, corrosive. Explosive decomposition when heated – reacts with combustible material, acids or water to liberate chlorine. Dilute and flush away spillage with copious water spray. Keep containers cool with water spray. Toxic. When heated decomposes to liberate oxygen. Avoid any personnel contact with solid or fumes. Dilute and flush away spillage with copious water spray. Beware explosion risk on heating of containers. Chromic Acid (chromium trioxide, chromic anhydride) CrO3 Purple – red crystals. Oxidising material. Reaction with organic materials causes ignition. Severe irritant. Containers may explode when heated. Flood with copious water spray. Diethanolamine (DEA, Di(2-hydroxyethyl)-amine (HOCH2CH2)2NH Colourless crystals. Flammable poison. Melts at 28°C to form viscous liquid which smells of ammonia. Reacts with oxidising materials. Avoid personal contact. Dilute spillage with copious water spray. Hydroquinone (quinol, hydroquinol, paradihydroxybenzene) C6H4(OH)2 Crystals: toxic, combustible, irritant. Can react with oxidising materials. Beware explosion risk on ignition of released vapour if heated. Lithium Li Metal: Flammable, toxic. Vapour given off when heated, toxic. Reacts violently with water, acids and oxidisers. Avoid any personal contact with solid and/or fumes. Cover spillage with dry sand. Beware explosion risk. 4/2000 Substances & Synonyms Magnesium Formula Properties Emergency Action – Fire/Spillage Beware disturbing dust to form dust cloud. Use special powders to extinguish. Mg Metal: Flammable. When burning reacts explosively with water producing hydrogen. Dust explosive in air. Reacts violently with oxidisers. Melamine (2, 4, 6Triamino-s-triazine, cyanurotriamide) C3N3(NH2)3 Crystals: Decomposes on heating liberating cyanide fumes. Flush with copious water spray Naphthalene (moth balls, white tar, tar camphor). C10H8 Flammable, toxic. Reacts with oxidisers. Melts at 80°C. Avoid any personal contact with liquid spillage, danger of scalds. Copious water spray will solidify liquid spillage. Nicotine Sulphate (C10H14N2)H2SO4 White crystals, powerful poison. Soluble in water, combustible. Avoid any personal contact With solid or fumes. Nitrocellulose (nitrocotton, gun cotton, cellulose nitrate) C12H14(ONO2)6O4 Powder or cotton – like solid. FP 4,4°C. Dangerous when exposed to heat or oxidisers. Containers when heated or dropped may detonate with rupture of drum and violent flame. Cool containers with water spray. Octylphenol (diisobutyl phenol) C6H4(C8H17)OH Flakes, flammable. Vapour: heavier than air, highly toxic, irritating. Contain spillage with dry sand, earth. Decontaminate. Members of this group of chemicals may be pastes, powders or liquids. All are hazardous and can burn with explosive violence. May explode if subject to heat, shock, friction or acids. Avoid any personal contact. Beware explosion risk on heating of containers. Keep cool with water spray applied to containers from a distance. Do not move heated containers until they have cooled. White crystalline mass. Flammable, poison, corrosive. Vapour: very dangerous to eyes. Soluble in water; heavier than air. Vapour given off when heated. Dilute and flush away spillage with copious water spray. Grey-black solid. Decomposes when heated giving off toxic, flammable heavier than air, phenol and formaldehyde fumes. Dust is explosive in air. Beware explosion risk on ignition of dust or release of fumes of decomposition. Organic Peroxides Phenol (carbolic acid, phenic acid, phenylic acid) Phenol Formaldehyde (resin) 4/2000 C6H5OH Substances & Synonyms Phosphorus (Red) Formula P4 Phosphorus (yellow or white) P4 Phosphorus Pentachloride (phosphoric chloride, phosphoric perchloride) Properties Powder: flammable, toxic. Vapour given off when heated, toxic, heavier than air. Products of combustion highly toxic. Emergency Action – Fire/Spillage Avoid any personal contact. Cover spillage with wet sand. Flammable toxic. Reacts with air, spontaneously flammable at 30°C. Products of combustion highly toxic. Avoid any personal contact with solid. Cover contaminated areas with wet sand or earth. Solid phosphorus should be put under a water seal. PCl5 Flammable, corrosive. Reacts with water to produce hydrochloric acid and phosphoric acid. Decomposes when heated to produce highly toxic chloride fumes. Beware explosion risk on ignition of released vapour. Copious flooding. Phosphorus Pentasulphide (phosphorus sulphide, phosphorus persulphide, thiophosphoric anhydride) P2S5 Flammable, toxic. Reacts violently with water or acids to produce H2S. Decomposes when heated to liberate highly toxic fumes of sulphur and phosphorus oxides. Reacts with oxidisers. Avoid any personal contact with solid and/or fumes. Use dry powder or sand. Potassium K Soft metal: flammable, corrosive, poison. Transported molten in this state reacts violently with air to produce hydrogen, the heat being sufficient to result in ignition. Cold metal also reacts with water. When heated gives off highly toxic fumes. Cover spillage with dry sand. Beware explosion risk on contact with moisture. Potassium Cyanide KCN White crystalline solid: nonflammable, highly toxic. Reacts with heat, moisture or acids to produce volumes of highly flammable, toxic, lighter than air gas. Avoid any personal contact. Cover spillage with dry sand pending decontamination. Do not allow spillage to enter drains. Special powders. Potassium Ferrocyanide (yellow potassium prussiate) K4Fe(CN)63H2O Crystals or powder. Toxic. Decomposed by heat or acids to liberate cyanide fumes. Avoid any personal contact. Potassium Nitrate (nitre, saltpetre) KNO3 Crystals or powder: powerful oxidising agent. Decomposes on heating liberating oxygen and toxic fumes. If molten violent vaporisation if water is applied. Explosive if heated and confined or shocked. Flush away spillage with copious water spray. Beware hazard of contaminated combustibles on drying out. Beware explosion risk on heating. 4/2000 Substances & Synonyms Potassium Permanganate Formula Properties Emergency Action – Fire/Spillage Use B.A. at all times. Flush away spillage with copious water spray. Beware hazard of contaminated combustibles on drying out. Beware explosion risk on heating. KMnO4 Purple crystals: powerful oxidising agent, strongly irritant. Decomposes violently when heated liberating oxygen. Sodium (natrium) Na Silver-white solid: corrosive, flammable, poison. Reacts violently with water to produce hydrogen and caustic soda, the heat being sufficient to result in ignition of the hydrogen. When burning gives off toxic fumes. Contain spillage with dry sand. Evacuate area and decontaminate. Contact with moisture will result in ignition. Sodium Hydrosulphite (sodium hyposulphite, sodium dithionite) Na2S2O4 Flakes or powder. Decomposes when heated giving off volumes of toxic non-flammable, heavier than air gases. Heats on contact with air or moisture and may ignite combustibles. Strong reducing agent. Avoid any personal contact. Cover/contain spillage with dry sand, cement, salt, bicarbonate of soda. Do not allow spillage to enter drains. Beware explosion risk on heating of containers. Sodium Nitrate (soda niter, nitratine) NaNO3 Crystals. Powerful oxidising agent. Decomposes on heating liberating oxygen and toxic fumes. Explosive if heated and confined, or when shocked. Flush away spillage with copious water spray. Beware hazard of contaminated combustibles on drying out. Beware explosion risk on heating. Sodium Peroxide (sodium dioxide, sodium superoxide, sodium binoxide) Na2O2 White-powder: powerful oxidising agent, highly toxic. Reacts violently with water to produce oxygen and caustic soda. Decomposes on heating liberating oxygen. Explosive if contaminated with organic material. Avoid any personal contact. Beware explosion risk on heating or contact with organic material. Special powders. Strontium Nitrate Sr(NO2)2 White powder: powerful oxidising agent. Decomposes on heating liberating oxygen and toxic fumes. Explosive if heated and confined. Flush away spillage with copious water spray. Beware hazard of contaminated combustibles on drying out. Sulphur (brimstone, flowers of sulphur, sulphur flour) S Crystals or powder, combustible. Reacts violently with oxidising agents. Products of combustion highly toxic. Beware explosion risk on ignition of airborne dust. Flush with copious water spray. 4/2000 Substances & Synonyms Titanium Formula Ti Triisopropanolamine N(C3H6OH)3 Properties Powder or granular form, flammable (even if wet). May be ignited by spark. When dry burns without flame. When burning reacts explosively with water. Burns in N2 or CO2. Crystalline solid: flammable vapour: heavier than air flammable, toxic. Avoid any personal contact. Protect containers from heat with water spray. Dilute spillage and flush with copious water spray. Avoid personal contact. Dilute and flush with copious water spray. Zinc Hydrosulphite (zinc dithionite) (ZnS2O4) White solid: toxic. When burning or in contact with acids produces toxic, heavier than air gas. Self heats in contact with moisture. Decomposes on being heated to emit highly toxic fumes. Zirconium Zr Scales or powder: flammable and explosive in dust form. Ignites spontaneously in air or on contact with oxidising materials. Burning zirconium decomposes water. References: Hazardous Loads – Institution of Fire Engineers Hazardous Properties of Industrial Materials – N Irving Sax Condensed Chemical Dictionary Published by Fire Protection Association of Southern Africa (Incorporated Association not for Gain) (Reg. No. 73/00022/08) P O Box 15467 Impala Park 1472 4/2000 Emergency Action – Fire/spillage Beware explosion risk from dust in air mixture. Small spillage may be covered with dry salt or dry sand. Don’t strike sparks from tools during application. Avoid water and gaseous extinguishers. Beware explosion risk on ignition of dust. Special powders.