Bellwork # 14 Diffusion and Osmosis
advertisement

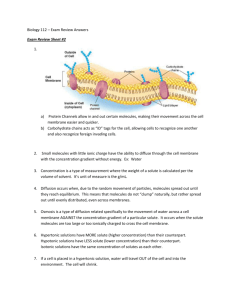
Bellwork # 14 Diffusion and Osmosis Molecules dissolved in a _1___________ are in constant random motion. One result of this motion is that dissolved molecules become _2__________ distributed throughout the solution. This tendency of molecules to spread out is an example of _3___________. For example, what will happen if we add a lump of sugar into a beaker full of water? A lump of sugar is composed of many individual sugar molecules and, even as a solid lump, the individual sugar molecules is in _4__________. When the lump of sugar is dropped into the water, it begins to _5___________. Individual sugar molecules move randomly and constantly from the area where they are common to the area where they are scarce. This type of motion when molecules move from areas of _6__________ concentration to areas of _7___________ concentration is called _8__________. Diffusion continues until all the sugar molecules become _9_____________ dispersed throughout the beaker. The rate of diffusion is affected by temperature, size of molecules, and the steepness of the concentration gradient. This is one of the processes whereby materials are _10___________ between a cell and its environment. Diffusion is the net movement of molecules down a concentration gradient. This process allows small molecules such as oxygen and carbon dioxide to cross the _11_______________. Bigger molecules such as _12_____________ and proteins cannot freely cross the lipid membrane. _13______________ molecules are small enough to pass through the membrane freely. This special case of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules across a membrane is called _14___________. If a molecule such as sucrose is added to one side of the plasma membrane, it will not be able to diffuse across the membrane because is it too _15___________. Sucrose will interact with water thereby reducing the number of free water molecules on that side of the membrane. With fewer free water molecules on the side with sucrose, there is now a net movement of _16 __________ molecules, down the concentration gradient to the side with the sucrose molecules. Because more water molecules are moving into this area than are leaving, the water level will _17____________ on the side with sucrose. If the osmotic concentrations of two solutions are equal, the solutions are _18__________. However, when the solutions have unequal osmotic concentrations, the solution with the higher concentration of solutes is _19____________ and the solution with the lower concentration of solutes is _20_______________. _______________________________________________ WORD BANK__________________________________________________ a. motion b. evenly (x2) c. higher e. sugars f. dissolve g. diffusion (x2) h. rise i. hypertonic j. isotonic k. hypotonic l. exchanged m. lower n. water (x2) o. osmosis p. plasma membrane q. large d. solution