File 5. kud inside earth
advertisement

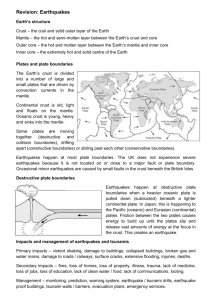
“Know – Understand – Do” Organizer Course: Science Grade(s): 6th Topic: Inside the Earth Unit School/District: /Glynn County ______________________________________________________________________________ Which Standards are students learning in this unit? S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formed. a. Compare and contrast the Earth’s crust, mantle, and core including temperature, density, and composition. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates move constantly and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geological features including oceans (composition, currents, and tides). S6E3. Students will recognize the significant role of water in earth processes. c. Describe the location and subsurface topography of the world’s oceans By the end of this unit, students will be able to……. Know The earth is layered with a lithosphere (crust and uppermost mantle), convecting mantle, and a dense metallic core. Understand The earth is layered with a partly molten, metallic core; a mantle that though solid, is hot enough to flow; and a colder, rigid lithosphere. Do Label the four layers of the earth. The definition of density and composition. Lithospheric plates on the scales of continents and oceans constantly move. Compare and contrast each layer in terms of its temperature, density, and composition. Each layer differs in composition, density, and temperature. Temperature and density increases as depth increases. The composition of the earth changes with depth and layers. The crust is the upper part of the rigid lithosphere and is of different composition under land as opposed to the ocean floor. Convection cell in the mantle is causing the lithospheric plates to move. Major geological events, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building, result from these plate motions. Some changes in the earth’s surface are abrupt (such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions) while other changes Investigate and analyze different models of the Earth. Compare and contrast basalt (oceanic crust) and granite (continental crust) rocks and determine their densities. Design and construct a model of interior of the earth. Label the layers. Write a summary or create a presentation using the information found through different websites and include Below the rigid lithosphere, the mantle consists of hot rock of tar-like consistency, which slowly moves or flows. The outer core is molten and the inner core is a dense solid. The lithosphere is divided into separate plates which move very slowly in response to the mantle. Heat from the mantle and core creates convection currents. This plate movement causes major geologic events such as volcanoes, earthquakes, and mountain formation. At the edges or boundaries of the plates, the earth's crust is in motion. The theory of plate tectonics connects the evidence for the formation, movement, and destruction of the plates. At divergent plate boundaries such as the mid-Atlantic ridge, new ocean floor is created. At convergent plate boundaries known as subduction zones, a trench and deep earthquakes mark the zone where a slab of oceanic lithosphere descends into the mantle, and volcanoes and mountain ranges form on adjacent land. Location of the ring of fire. When continental crust meets continental crust at a happen very slowly (such as uplift and wearing down of mountains). information about the density, composition, and temperature of each of the Earth’s layers. Moving plates cause major changes in a world map over tens of millions of years. Explain why we have not been able to explore the earth’s layers by drilling through the crust. Pangaea was the most recent of a succession of supercontinents that have formed and broken up over time. The mantle is solid but capable of flow (like hot asphalt or fudge). Only under special conditions (at hot spots and along plate boundaries) does the mantle or crust melt to make magma, which may then rise to the surface to make a volcanic eruption. Earthquakes represent sudden breaks in crust continuously stressed by plate movement. Gradually over time, the same movements result in major crustal features. Composition and currents of oceans can be impacted by physical processes such as weathering, erosion, and plate tectonic movements. Explain how the study of seismic waves helped scientists diagram the interior of the Earth. Design an original children’s storybook to explain the results of tectonic plate movements and its effects on earth. Identify the subsurface topography of the world’s oceans. Explain the connection between the effects of plate tectonics and the location of ocean floor topographic features. Use print and web sources to research the topography of the ocean floor. Identify location of the world’s oceans on a map. Draw or make clay model cross-section diagrams of ocean topographical features. Write a one page report about the conditions which formed the subsurface topography, and include information about the location, composition, and processes of formation for each topographic feature Research and write about a convergent boundary, a collision occurs, resulting in folds, faults, and high mountains. current event impacted by plate tectonic movement (recent volcano eruption, tsunami, or earthquake). Transform boundaries are where plates slide past each other. They connect other plate boundaries and are characterized by earthquakes and tsunamis. Answer reading comprehension questions about the author Jules Verne who wrote “Journey to the Center of the Earth”