Unit 1 Test Review Sheet: Structure of the Earth Please review the
advertisement

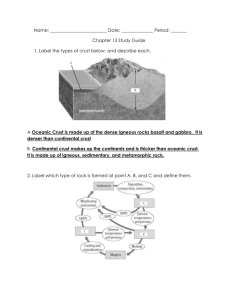
Unit 1 Test Review Sheet: Structure of the Earth Please review the following concepts for your unit test. You will have a skills test which you will be identifying and classifying different rocks and minerals on Wednesday, September 10th. Your written test will be Friday, September 12th. Reviews for the test will be Monday & Tuesday morning starting at 7am, or Tuesday and Wednesday after school starting at 2:45pm. You may use one 4x6” notecard, front and back to handwrite any notes regarding any of the information we have learned this year. Measuring: (notes & blog) Vocabulary: mass, volume, density, temperature, triple beam balance, scale, graduated cylinder, beaker, thermometer, ruler, grams, meters, liters Demonstrate how to find the mass of an object Demonstrate how to find the volume of a cubic shape, liquid, and/or irregular shape Associate the correct SCIENCE units for mass, volume, density, and temperature (Ex: mass = grams…) Associate the correct type of measurement with what needs measuring o (Ex: meters is used when finding the distance or length of an object) Demonstrate how to convert one metric unit to another (KHDUDCM) Scientific Method: (pg 8 – 11, notes & blog) Vocabulary: dependent variable, independent variable, constant, control Determine the dependent variable and the independent variable for a given experiment Identify if a control group would be applicable in an experiment Identify possible constants that would be necessary in an experiment Determine if an experiment would be reliable based on: number of trials, number of variables, and subjects tested Layers of the Earth: (pg 124-131) Vocabulary: crust, mantle, outer core, inner core, convection currents, density Identify the main layers of the earth from a diagram (crust, mantle, outer core, inner core) Describe what happens to the density of the earth as you move from the crust to the core Explain what happens to the temperature inside the earth as one moves from the crust to the core What happens to the pressure as one moves from the crust to the core Which layers are the thinnest and largest? Explain the states of matter of the layers (S, L, G) Explain how scientists know the details from inside the earth Convection: (pg 132 – 135) Describe how density relates to convection currents Explain why does heat rises and cool sinks? Explain how convection currents relate to plate tectonics Plate Tectonics: (pg 141-147) Vocabulary: plate tectonics, divergent, convergent, transform, subduction zone, sea floor spreading Explain how convection currents (heat currents) influence the plate movement Compare and contrast the 3 types of plate boundaries Mineral Properties (pg 66-75) Vocabulary: mineral, inorganic, color, streak, luster, density, hardness, Moh’s Hardness scale, cleavage, fracture, fluorescence Explain how to tell if something is or is not a mineral (SNIFC) (pg. 66-67) Identify minerals based on characteristics of: Color, Streak, Luster, Density, Hardness, Crystal Systems, Cleavage & fracture, Special Properties Be able to know how to find each of the previous characteristics and what it is Rock Types (pg 94-96, Igneous 98-101, Sed 102-109 Met 110-112) Vocabulary: igneous, intrusive, extrusive, magma, lava, sediment, deposition, sedimentation, cementation, sedimentary, metamorphic, foliated, non-foliated Compare how rocks and minerals are related (what makes up the other?) Identify samples of rocks as igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic and describe how they are formed. Describe the formation of intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks and use the characteristics of igneous rocks to determine if a given rock is igneous. Describe the formation of sedimentary rocks and use the characteristics of sedimentary rocks to determine if a given rock is sedimentary. Describe the formation of metamorphic rocks and use the characteristics such as foliated and non-foliated to determine if a rock is metamorphic. Rock Cycle (pg 114-115) Diagram multiple paths through the rock cycle and explain how the changes from one rock type to another occur.