unit 4 outcomes
advertisement

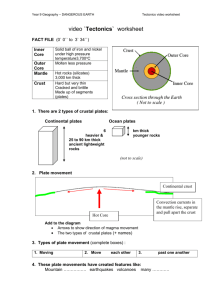
Grade 7 – Unit 4 Outcomes and Study Guide 2015 • classify minerals based on their physical properties - define mineral - list and describe properties of minerals, including: (i) colour (ii) streak (iii) lustre (iv) hardness (v) cleavage (vi) fracture • classify rocks based on their characteristics and method of formation - define rock - define igneous rock and describe their formation - differentiate between magma and lava - differentiate between intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks using examples, including: (i) granite (intrusive) magma (ii) basalt (extrusive) lava - define sedimentary rocks and describe their formation - list and show examples of sedimentary rocks, including: (i) shale (small particles) (ii) sandstone (medium particles) (iii) conglomerate (large particles) (iv) limestone (plant and animal particles) - define metamorphic rock - describe the formation of metamorphic rocks - list examples of metamorphic rocks and their parent rock, including: (i) slate from shale (ii) marble from limestone (iii) quartzite from sandstone (iv) gneiss from granite • identify questions to investigate arising from the study of the rock cycle - sketch and label a diagram of the rock cycle - recognize the relationship between various types of rocks (igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic) • describe the characteristics of Earth’s crust and some of the technologies which have allowed scientists to study geological features in and on the Earth’s crust - sketch and label a model of Earth’s layered interior, including: (i) inner core (ii) outer core (iii) mantle (iv) crust - describe the composition of each layer - recognize that Earth’s crust is broken into plates and movement occurs where plate margins meet (plate tectonics) • describe how plate tectonic theory has evolved in light of new geological evidence - identify Alfred Wegener as the person responsible for proposing the continental drift theory - describe the continental drift theory and the evidence supporting it, including evidence from: (i) continental fit (paleogeographic) (ii) fossils (biological) (iii) rock layers (geological) (iv) climate (meteorological) - identify the technological advances that have provided evidence to support the current theory of plate tectonics, including: (i) sonar (ii) magnetometers (iii) deep sea drilling - identify types of plate boundaries, including: (i) divergent (pulling apart) (ii) convergent (pushing together) (iii) transform (sliding past) - identify convection currents in the Earth as a possible explanation of the driving force mechanism behind plate tectonics • examine some of the catastrophic events that occur on or near Earth’s surface, including: (i) earthquakes (ii) volcanic eruptions - define earthquake - explain why earthquakes occur using the concept of plate tectonics - define volcano - identify how and where volcanoes form. Include (i) areas where plates converge (ii) areas where plates diverge (iii) areas where plates are thin (hot spots) • explain the processes of mountain formation - define folding and faulting - explain how mountains are formed using the theory of plate tectonics, including: (i) folding (ii) faulting (iii) volcanic eruption - describe the geologic time scale in terms of the four main eras and the major events that occurred in each, including: (i) Precambrian era – formation of the Earth and appearance of simple life forms (ii) Paleozoic era – appearance of more complex life forms (iii) Mesozoic era – appearance and extinction of dinosaurs (iv) Cenozoic era – appearance of humans