exam review spring 2013
advertisement

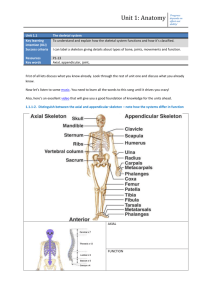
PSE4U Final Exam Review – June 2013 Introduction What is the anatomical position Directional terms Identify the three basic planes of motion, understand movements within planes Identify the three axes of motion, understand movements through the axis Movement Terminology Skeletal System Functions, skeletal changes Anatomy of a Long Bone Five classifications of Bones Bone disorders (arthritis, osteoporosis) Joints and Articulations: types of joints (3), types of synovial joints (6), characteristics of synovial joints (6) Define the following joint related structures: ligaments, tendons, cartilage, menisci Injuries to joints and treatment Joint disorders (dislocations, separations, tendonitis) Muscular System Types of muscle & function Muscle Movements, function & how to strengthen Motor Units, Skeletal Muscle anatomy and physiology Definitions: Origin, Insertion and antagonistic pairs Types of muscle contractions Muscle Contraction, Sliding Filament Theory Effects of resistance training Diagrams Anatomical Planes Anatomical Axis Directional Terms Movement Terms Bone Types Bones & Major landmarks Anatomy of the long bone Fracture Types Muscles of the body Physiology of muscle (layers and anatomy) Joint types and anatomy Energy Systems Cardiovascular System Heart Respiratory System Lung Volumes Energy Systems; Nutrition and Training Principles The energy systems Training Principles Training Methods Nutrition: Macronutrients & Micronutrients, Food guide & labels Growth, Motor Learning, Psychology of Sport, Coaching Principles & Biomechanics Growth: Chronological, skeletal and developmental age Human Morphology Four stages of Physical Development Piaget’s Four stages of Cognitive Development Motor Learning: Cognitive, associative & autonomous learning Factors Affecting Skill Development Feedback Open Loop vs. Closed Loop Skill Analysis & Phases of a skill Coaching Principles: Coaching Biomechanics: Biomechanical models & lever classification Newton’s Three Laws of Motion and their applications Principles of Biomechanics Cardiovascular and Respiratory system Blood pressure (Systole vs. Diastole) Vessels and venous return Blood composition Target Heart Rate Cardiac output and what affects it, response to exercise Blood Flow distribution Effects of training on CV system & Adaptations with endurance training Function of respiratory system and how we breath Internal Vs External Respiration Ventilation Lung volumes Rules governing gas movement and diffusion How is O2 and CO2 transported (pg 124 - 125) Why and Where does O2 and CO2 move into/out of the tissues/blood a – v O2 difference Cardio/Respiratory diseases VO2 and VO2 Max & limitations