Environmental Science Name: Waste Goal: The student will name
advertisement

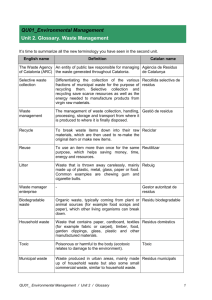
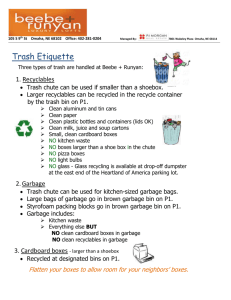
Environmental Science Name: ______________________________ Waste Goal: The student will name one characteristic that makes a material biodegradable and identify two types of solid waste. Vocabulary: 1. Solid waste 2. Biodegradable 3. Municipal solid waste Chapter 12.1: Solid Waste • You have lunch, throw away the garbage…but what happens to it after you ‘toss it away’? • It is picked up by a collection service and taken to a______________________ where it will be dumped with thousands of ___________________ of other trash and then covered with a thin layer of ________________________ at the end of the day • What happens when it is __________________, or ___________________ runs down into the landfill, dissolving harmful _____________________________ (paint thinner, nail polish remover) and that seeps into the groundwater? The Generation of Waste Imagine multiplying the waste ____________________ problems associated with your trash plus all the _____________________ everyone else throws away in a day; most is used once and then thrown away US generates more than __________billion metric tons of solid waste (any discarded ______________ material) in a year; this _____________________________ junk mail to coffee grounds to cars _______________ generated by Americans has ______________________________ since the 1960’s Space and Waste Many ______________ are running out of space to dispose of the amounts of trash people are producing Ex: In 1987, a huge barge full of trash _______________ up and down the East Coast for more than 5 months in search of a place to ___________________ the garbage; it contained____________ tons of garbage; eventually, it returned to Islip, New York, burned the garbage and finally buried ___________ tons of ash Population and Waste Thousands of years ago, hunter-gatherers had a ________________________ population and most of the ____________________ created was animal and vegetable matter (biodegradable material); larger amounts of land per person and disposal of _____________________ was easier Earth’s _______________________ and the waste we produce is getting larger; amount of land available per person is becoming ___________________________; therefore, it is getting harder to find space to dispose of all the waste we are creating Not All Wastes are Equal • The amount of waste is a concern; however, the ________________ of waste are just as important • ____________ basic kinds: ______________________________ (can be broken down by living things) and _________________________________________________ (cannot be broken down) • Examples of biodegradable products: plant and animal matter, newspaper, paper bags, cotton fibers, leather; examples of non-biodegradable waste are materials created by _____________________ chemicals to form compounds – polyester, nylon, plastic Plastic Problems ___________________________ illustrate how non-biodegradable materials can cause problems. Made from _________________________ or natural gas; these consists mostly of _____________ and hydrogen (same elements which make up most molecules in living things); however, in plastics, when put together in molecular chains, are _____________ found in nature. Microorganisms have evolved the ability to __________________ down nearly all biological molecules, but have yet to develop a way to break down the ________________________ structure of most plastics Some plastics we throw away may __________________________ and last for hundreds of years. Types of Solid Waste • Most of what we throw away on a day-to-day basis is called _________________________ solid waste • However, __________% of the other solid waste comes from manufacturing and mining; 6% is considered __________________________________ Municipal Solid Waste About __________% of the total solid waste in the US is made up of municipal solid waste (produced by __________________________ and _________________________________ 210 million metric tons of municipal waste produced per yr. in US; enough waste to ___________ a convoy of garbage trucks that would stretch around the Earth ____________ times! Growing _______________________ than manufacturing and mining waste Solid Waste from Manufacturing, Mining and Agriculture Waste from manufacturing, mining and agriculture make up the __________________ of the total solid waste produced in the US, about ________________% of the total Includes items like: scrap metal, plastics, paper, sludge and ash Consumers do ___________________ directly produce manufacturing waste but the indirectly contribute to it by ____________________________ products that have been manufactured Mining waste consists of ___________________ and ______________________________ that are left over from excavation and processing; left exposed in large heaps, dumped in oceans or rivers, or _____________________________ of by refilling and landscaping abandoned mines Agricultural waste makes up ____________% of the total solid waste; includes crop waste and manure Agricultural waste is ___________________________________, can be broken down and then returned to the soil; however, with the ________________________ use of fertilizers and pesticides, agricultural waste is becoming more ______________________________ to dispose of (harmful to the soil) Lesson Reflection: Assessment: 1. Explain what makes a material biodegradable. 2. Compare municipal solid waste and manufacturing solid waste. Active Reading: Solid Waste Lesson Extension (Technology/Application/Connection to Real World): Modifying Packaging to be Eco-Friendly: Construct a model of eco-friendly packaging for an existing commercial product. YouTube Video – Away: A Story of Trash (26 min)