3. ALC., ETH., ALD., KET.
advertisement

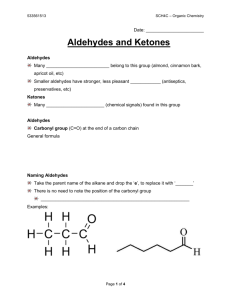
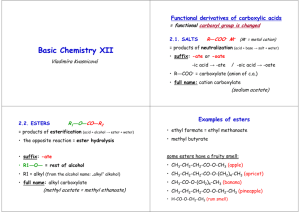
ALCOHOLS *Alcohols are the homologous series that contain the OH, hydroxyl, functional group. Alcohols are essentially water molecules with substituted _______________ groups. The difference between NaOH and alcohols is that NaOH is ionic and dissociates into Na+(aq) and OH-(aq) ions, whereas C-OH is covalent and does not dissociate – it’s a molecule. Water Generic Formula of an Alcohol “R” = an alkyl group n Name 1 Specific Example of an Alcohol Alkyl group = Molecular Formula Condensed structural formula 2 3 4 5 6 Primary (1°), Secondary (2°) and Tertiary (3°) Alcohols Examples: 1° alcohol e.g. butan-1-ol 2° alcohol e.g. butan-2-ol 3° alcohol e.g. 2-methylpropan-2-ol ETHERS Water Generic Formula of an Ether Specific Example of an Ether “R” = an alkyl group ; R’ = another alkyl group Alkyl group (left)= Alkyl group (right) = Naming Ethers *Ethers are named by adding _______ to the __________ hydrocarbon group and joining it to the alkane name of the _______________ hydrocarbon group. Name #1 (IUPAC) Drawing of Compound methoxymethane ethoxyethane ethoxypropane propoxybutane ALDEHYDES AND KETONES *Aldehydes and ketones are characterized by the presence of the same functional group – _____________. The carbonyl functional group consists of a carbon atom double bonded to an ____________ atom. What distinguishes aldehydes and ketones from one another structurally is the ______________ of the carbonyl group. *In aldehydes, the carbonyl group is located at the end (or beginning) of the carbon chain, and will therefore be bonded to at least one ____________ atom. *In ketones, the carbonyl group occurs in the interior of the carbon chain, and will therefore be bonded to two __________ groups. Naming Aldehydes *When naming aldehydes, add ________to the prefix of the parent alkane. Examples: methanal(formaldehyde) ethanal (acetaldehyde) propanal butanal Q. Why is it not necessary to write a number in front of any aldehyde? Naming Ketones *When naming ketones, add ________to the prefix of the parent alkane. Examples: propanone (acetone) butanone *pentan-2-one pentan-3-one