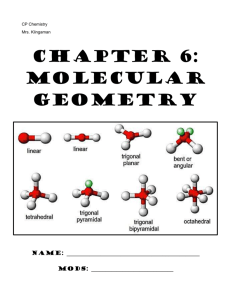
Molecular Geometry
advertisement

Honors Chemistry Mrs. Klingaman Chapter 9: Molecular GEOMETRY Name: _______________________________________________ Mods: _____________________________ Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry 1. VSEPR theory enables us to predict the shape (molecular geometry) of molecules based on the representative Lewis structure for each molecule. VSEPR stands for: V- _________________________ P- _________________________ S- _________________________ R- _________________________ E- _________________________ 2. VSEPR theory predicts the _________________________ of molecules based on the fact that there is ____________________________ between the valence electrons surrounding the central atom of molecule. a. Bonding electrons pairs (single/double/triple bonds) take up space in a molecule and repel one another b. Nonbonding electron pairs also take up space in a molecule and repel electrons __________________ strongly than bonding electron pairs c. As a result of this repulsion, the atoms in a molecule space themselves out ____________________________________ from one another as possible. *** VSEPR “The best arrangement of a given number of electron domains is the one that minimizes the repulsions among them.” 3. Fill in the table below: Name & Formula Lewis structure # atoms bonded to central # nonbonding electron pairs around central # of domains around central ABN type* Molecular Shape Methane CH4 Ammonia NH3 Water H2O * Write the ABN formula for each of these molecules. A= central atom, B= number of attached atoms, N= Number of nonbonding electron pairs. Use this notation to determine the shape of each molecule and fill in your answer in the table. 4. Molecular Polarity: We know (from chapter 8) that polar _______________ result from having a significant difference in the electronegativity of the 2 bonding atoms When it comes to an entire molecule being polar, we consider both the polarity of the ____________ within the molecule as well as its 3D ______________ a. Molecules are either considered polar or nonpolar A polar molecule is one which can visually be split in half to reflect one half of the molecule that is more negative and one half that is more positive b. Keys for finding Molecular Polarity: Molecules that are three dimensionally symmetrical are often considered _______________________ When the molecule is symmetrical, any polar bonds that may exist can cancel out with one another Molecules that are three dimensionally asymmetrical (not the same on all sides) are often considered ____________________________. Asymmetrical molecules are typically polar because their polar bonds cannot cancel, thus one side of the molecule ends up being slightly more negative than the other side, allowing the molecules to be “split” into two different poles! Many times, a molecule with __________________________ electron pairs on the central atom will end up being polar due to asymmetry. 5. Based on molecular shape and 3D symmetry, predict if the molecules below are polar or nonpolar: Methane = ______________________________ Ammonia = ______________________________ Water = _____________________________ Now You Try: Molecule Lewis Dot Structure # of Atoms Bonded to Central # of Nonbonding e– Pairs # of domains around central ABN type Molecular Shape ClO3– CHO– Based on molecular shape and symmetry, circle the correct polarity of each molecule: ClO3– : polar or nonpolar CHO– : polar or nonpolar The chart at the front of this packet lists possible shapes of molecules, based on their Lewis structure and ABN type. Be comfortable with interpreting this information…like you just did! The website below is excellent for visualizing the 3D orientation of each different molecular geometry or for building example molecules Online Simulator: http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/molecule-shapes VSEPR – Predicting Molecular Shapes Directions: Fill in the table below by drawing the Lewis Structure of the molecule and determining its ABN type and molecular shape Molecule CCl4 CO2 ClF3 XeBr2 Lewis Dot Structure # of atoms bonded to central # of nonbonding e– pairs on central # of domains around central ABN Type Molecular Shape Molecule IBr5 PH5 NO2– SCl6 XeF4 Lewis Dot Structure # of atoms bonded to central # of nonbonding e– pairs on central # of domains around central ABN Type Molecular Shape Molecule HCN CHBr3 HCl O3 I3– Lewis Dot Structure # of atoms bonded to central # of nonbonding e– pairs on central # of domains around central ABN Type Molecular Shape