TENTATIVE SYLLABUS for first nine weeks Exponents and
advertisement

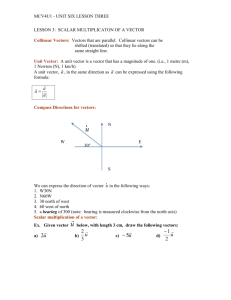
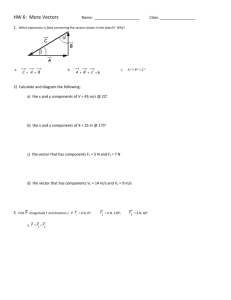
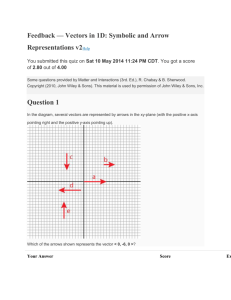
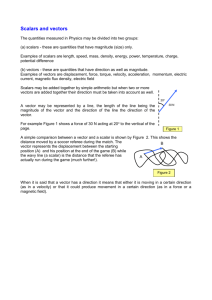
TENTATIVE SYLLABUS for first nine weeks Exponents and logarithms first 2 weeks ▪ Change of base ▪ Laws of Exponents; laws of logarithms ▪ Graph exponential and logarithmic functions ▪ Solve both exponential and logarithmic functions. Complex numbers next: 3 weeks ▪ real part, imaginary part, conjugate, modulus and argument ▪ Cartesian form z=a + ib (2-D vectors) ▪ Modulus-argument form (polar form) ▪ Sums, products and quotients of complex numbers ▪ De Moivre’s theorem ▪ Powers and roots of a complex number ▪ Conjugate roots of polynomial equations with real coefficients Mathematical Induction: a week ▪ Proof by mathematical induction (Process of induction and principle od induction) ▪ Indirect proof ▪ Forming conjectures to be proved by mathematical induction Vectors and planes, Solution of system of linear equations 5 weeks Solution of Linear Equations ▪Unique solution ▪No solution ▪Infinity of solutions ▪Find solution(s), if any exist, of a set of linear equations using matrix techniques. ▪Write solution(s) as a point, line, or plane. Vectors in Two and Three Dimensions ▪Graph vectors in 2 and 3 dimensions. ▪Represent vectors using vector notation. Components of a Vector ▪Identify the components of a vector. Addition and Multiplication of Vectors ▪Add vectors. ▪Multiply vectors by a scalar. ▪Graph the resultant vector. Length of Vector ▪Calculate the length (magnitude) of a vector. ▪Write down the unit vector for a given vector. Scalar Products and Projections ▪Calculate the scalar product. ▪Find the angle between 2 vectors using scalar product formula. ▪Prove orthogonality. Vector Products ▪Calculate the vector product of 2 vectors. ▪Find a 3rd vector that is perpendicular to 2 other vectors. Geometric Application of the Vector Product ▪Use of the formula involving vector product, magnitudes, and sine of the angle. Algebra of Scalar and Vector Products . ▪Show that two vectors are orthogonal. ▪Use the formula magnitude of cross product equals the product of the squared magnitudes minus the square of the dot product. Lines and Planes ▪Express equations of lines and planes in parametric, cartesian, and normal form. Intersections of: ▪Two lines ▪Line with a plane ▪Two planes ▪Three planes Distances in Three Dimensions ▪Write expressions and calculate the distance between 2 objects (points, lines, or planes) in 3-d.