IR/Raman imaging in vitro
advertisement

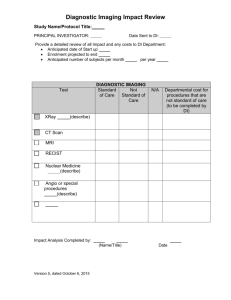
IR/Raman imaging in vitro for investigation of cell/fiber interaction Yao Seydou Université de Bordeaux, CNRS UMR 5248 CBMN, 14 Allée Geoffroy St-Hillaire, 33600 Pessac, France Abstract: Amphiboles caused cohorts of deaths in exposed workers, leading to some of the largest class actions in the industry. Once inhaled, these inorganic fibers are thought to be both chemically and morphologically toxic, and their biopersistence in lungs over decades lead to progressive pathologies, mesothelioma and asbestosis. However, this exceptionally long chronicity for human pathologies suggests that chemical toxicity is certainly low, making that morphological parameters could be more relevant in the pathology. Here, we developed a 3D Raman/optical imaging methodology in vitro to characterize both morphological and chemical parameters of cell/fiber interactions. We determined that lung cells could vesiculate amphiboles with length below 5 µm (figure 1) or could embed those not exceeding 15 µm in their fibrous extracellular matrix. Lung cells can thus develop defense strategies for handling the biopersistence of inorganic species, which may thus have major impact for biosafety issues related to nanomaterials. We also propose to use ATR-FTIR imaging of live cells for analyzing the interface formed by lung cell ECM and amphiboles when fibers have length between 5 and 15 µm. The methodology for in vitro FTIR imaging will be presented with analytical performances obtained on a new ATR objective designed for this purpose. The analytical potential of this multimodal vibrational spectroscopy imaging resource will be discussed. Figure: A) Visible image the target of cell B) combined image of the cell (in blue), the fiber (in white) and a vesicle (in red); z=1.5µm C) Spectra of each component from (B): cell spectrum in blue, fiber spectrum in black and the vesicle spectrum in red. Integration values (a.u., average ± standard deviation) from the lipids and asbestos fiber spectral region for each class of spectra are above the colored arrow. The red box corresponds to the Raman microscopy area of interest.