2nd_nine_weeks_exam_review_answers
advertisement

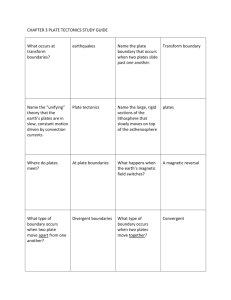
1. Who developed the theory that the continents were once joined? Alfred Wegener 2. Who proposed the theory of seafloor spreading? Harry Hess 3. Scientists have discovered alternating bands of magnetism in the rocks containing iron on the ocean floor. Explain why the magnetism in the rocks alternates. Earth’s magnetic field has continually reversed. The alignment of the iron atoms alternates depending on the polarity of Earth at the time the seafloor was created. 4. List the four evidences for continental drift. a. Puzzle-like fit of the continents b. Similar fossils have been found on different continents c. Remains of warm-weather plants in Arctic areas and glacial deposits in tropical areas suggest continents have moved. d. Similar rock structures are found on different continents. 5. Explain why Wegner’s ideas about continental drift were not accepted when he proposed the ideas in 1912. No one could explain how or why the continents had moved. 6. What is Pangaea? A large ancient landmass that was composed of all the continents joined together 7. What do the plates of the lithosphere float on? Describe the properties of this layer. the athenosphere – plastic-like, not rigid 8. What is the rigid layer made of the crust and upper mantle? the lithosphere 9. Discuss the two evidences of seafloor spreading. a. Youngest rocks are located at mid-ocean ridges. b. Reversals of Earth’s magnetic field are recorded by rocks in strips parallel to ridges. 10. Name the boundary when plates slide past one another. transform boundaries 11. Name the boundary when plates move apart from each other. Divergent boundary 12. How does a mid-ocean ridge form? Include the words “seafloor spreading” and “less dense” in your explanation. Less dense magma rises through cracks in the seafloor. This rising creates a ridge on the ocean floor. The seafloor spreads apart at the ridge, creating new seafloor. 13. Explain how the Himalayan Mountains were formed. Include the type of boundary and the names of the tectonic plates. (map on p. 285) Continental Collision between the Arabian and Eurasian Plate. 14. Where are the youngest rocks on the ocean floor found? Near the mid-ocean ridges 15. Give an example of a transform boundary. San Andreas fault 16. The Andes mountain range of South America was formed at what kind of plate boundary? convergent plate boundary – subduction zone 17. Give an example of a divergent plate boundary involving two oceanic plates. Mid-Atlantic ridge 18. Give an example of a divergent plate boundary involving two continental plates. Great Rift Valley of Africa 19. Plates that move towards one another are called? convergent plate boundary 20. What is a subduction zone? A more dense oceanic plate is forced under a less dense continental plate 21. Explain convection current. Hot less dense molten rock is forced upward, when it reaches the surface, it cools and sinks back into the Earth. (The entire cycle of heating, rising, cooling, and sinking) 22. What drives the plate motion on Earth? What is the source of this movement? Convection Current 23. On average, how much do the contintenal plates move in a year? 1 to 2 inches per year 24. Be able to use the map on page 285 to answer questions: What type of boundary occurs between the Nazca Plate and the South American Plate? Convergent, Subduction Zone What type of boundary occurs between the South American and the African Plate? Divergent – Mid Ocean Ridge 25. Compare and contrast epicenter and focus. Epicenter is the point on the Earth’s Surface above the earthquake and focus is the point below the Earth’s surface where the energy is released in the form of seismic waves. 26. Explain the elastic limit. Force causes rocks to bend and when the reach the elastic limit they break and cause an earthquake. 27. Which seismic waves are the most destructive? Surface 28. Which seismic waves are fastest? Slowest? Primary Surface 29. What is the difference between a seismogram and a seismograph? Seismogram is the paper reading and seismograph is the machine. 30. What is the plastic like layer of earth’s upper mantle. asthenosophere 31. Define the following words: focus, primary wave, surface wave, fault, mantle, crust, tsunami 32. What Type of fault is the San Andreas? Strike-slip fault 33. Define the following words: caldera, crater, tephra, volcano, vent, cinder cone volcano, shield volcano, composite volcano, hot spot 34. What determines if a volcanic eruption is violent or quiet? The amount of trapped gasses and silica. 35. What type of plate boundary tends to have volcanoes that are violent? Convergent 36. What determines the divisions of Geologic time? Fossils and Organisms 37. What is the longest subdivision in division in geologic time? Shortest? Eon Epoch 38. List examples of life-forms from the Cenozoic Era. Life forms living today 39. List examples of life-forms from the Precrambrian Era. Bacteria, sponges, jellyfish 40. Explain relative dating. Determining the order of events by examining the position of rocks 41. What are gaps in the rock layers? Unconformities 42. What does it mean if the same sequence of rocks is observed over a large area? a large deposit of rock formed over a large area 43. In a series of undisturbed rock layers where shale lies between sandstone below and limestone above, what is the oldest rock layer? The youngest? Oldest – sandstone Youngest – limestone 44. What is absolute dating? Dating that uses the properties of atoms in rocks and other objects to find their ages 45. Rock layers are correlated if they both contain the same ____. Fossils 46. (Fill in the blanks) With _____________ dating, a rock's exact age can be determined, whereas with ________________ dating, a rock's age is compared to the ages of other rocks. absolute, relative 47. A sample of a radioactive element has a mass of 40g. How much parent and daughter materials are in the sample after two half-lives? 10 grams parent 30 grams daughter How much parent and daughter materials are in the sample after three half-lives? 5 grams parent 35 grams daughter 48. A sample of a radioactive element has a mass of 60g. How much parent and daughter materials are in the sample after two half-lives? 15 grams parent 45 grams daughter How much parent and daughter materials are in the sample after three half-lives? 7.5 grams parent 52.5 grams daughter 49. If 12.5 percent of the parent material remains in a rock sample, how many half-lives have occurred? 3 half-lives 50. If 25 percent of the parent material remains in a rock sample, how many half-lives have occurred? 2 half-lives 51. Determine the percent of parent material that will be left after five half-lives. 6.25 divided by 2 = 3.125% 52. Determine how much parent material will be left after six half-lives. 3.125 vided by 2 = 1.5625% 53. Newton’s First Law of Motion 54. Newton’s Second Law of Motion 55. Newton’s Third Law of Motion 56. The gas in a rocket pushes down as the rocket ascends into the atmosphere. 3rd 57. Ian pushed a piano across the room with the correct amount of force. 2nd 58. Chris, a magician, pulled a tablecloth off the table from under the dishes which were on top of the tablecloth. 1st 59. A cannonball is shot from the barrel of a cannon and the cannon recoils 3rd 60. A book is sitting on a table. Assuming no friction, Zindi pushed it with the correct amount of force to make it move. 2nd 61. Alex's car stopped running. He needs to push it to get it started, however, he is not strong enough. Three of his girlfriends come over to help him and the car starts. 2nd 62. In space, a comet will keep going in the same direction forever until another force increases. (example - a planet's gravity) 1st