Freshman Unit Outlines
advertisement
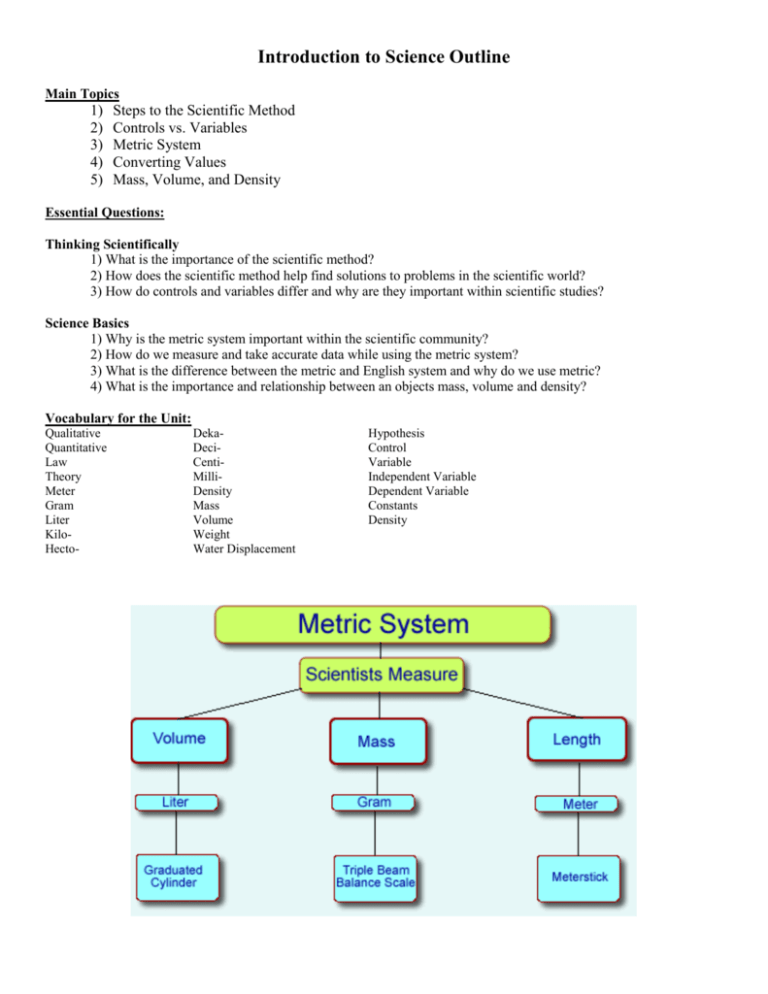
Introduction to Science Outline Main Topics 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Steps to the Scientific Method Controls vs. Variables Metric System Converting Values Mass, Volume, and Density Essential Questions: Thinking Scientifically 1) What is the importance of the scientific method? 2) How does the scientific method help find solutions to problems in the scientific world? 3) How do controls and variables differ and why are they important within scientific studies? Science Basics 1) Why is the metric system important within the scientific community? 2) How do we measure and take accurate data while using the metric system? 3) What is the difference between the metric and English system and why do we use metric? 4) What is the importance and relationship between an objects mass, volume and density? Vocabulary for the Unit: Qualitative Quantitative Law Theory Meter Gram Liter KiloHecto- DekaDeciCentiMilliDensity Mass Volume Weight Water Displacement Hypothesis Control Variable Independent Variable Dependent Variable Constants Density Physics Unit Outline Main Topics 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Distance, Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Forces Motion Energy Engineering Essential Questions: 1) What is the relationship between distance and displacement? 2) How does acceleration, velocity, and speed compare to each other and what are the different types of them? 3) What is a force and how are forces important in understanding the movement of matter in the universe? 4) What are Newton's three laws of motion and how are the important in understanding the universe? 5) What is energy and what forms does it come in? 6) How do engineers think and find answers to problems? Vocabulary for the Unit: Speed Momentum Friction Displacement Distance Acceleration Force Velocity Terminal Velocity Conservation of Momentum Centripetal Force Projectile Constant Speed Average Speed Instantaneous Speed Circular Motion Vertical Motion Horizontal Motion Newton's 1st Law of Motion Newton's 2nd Law of Motion Newton's 3rd Law of Motion Gravity Temperature Heat Convection Conduction Radiation Law of Conservation of Energy Chemical Energy Potential Energy Natural Energy Thermal Energy Mechanical Energy Electrical Energy Kinetic Energy Chemistry Unit Outline Main Topics 1) 2) 3) 4) Atomic Structure The Periodic Table Chemical Bonds Chemical Equations Essential Questions: 1) What makes up an atom and how do those subatomic particles relate to each other? 2) What is the current atomic structure model look like and how has it changed through the years? 3) How are the elements arranged on the periodic table and what is the importance to their arrangement? 4) What is the difference between the different groups and families on the periodic table? 5) How do elements form bonds and what are the two different types of chemical bonds? 6) What is the importance of chemical equations and how they are written? Vocabulary for the Unit: Atomic Number Atomic Mass Ionic Bond Covalent Bond Compound Malleable Polar Molecule Physical Change Atom Catalysts Alkaline Metal Metalloids Neutron Electron Double Replacement Combination Valence Electrons Endothermic Ductile Chemical Change Luster Transition Metals Periods Synthesis Isotope Nucleus Inhibitors Exothermic Halogen Noble Gases Group/Family Decomposition Ion Average Atomic Mass Nonpolar Molecule Law of Conservation of Mass Alkaline Earth Metals Proton Single Replacement Formula Acids and Bases Unit Outline Main Topics 1) Acids, Bases and the pH scale 2) Neutralization Reactions 3) Acid Rain Essential Questions: 1. What is the general structure and arrangement of the pH scale? 2. How do acids and bases compare to each other as far as chemical and physical characteristics? 3. How do neutralization reactions take place and how are they important to the chemistry of acids and bases? 4. What are essential lab chemistry lab skills need to perform labs safely and accurately? 5. How do we use indicators to learn about unknown solutions? 6. What are some common acids and bases we could find at home? 7. What is acid rain, how does it form, and what are some destructive results of it? Vocabulary for the Unit: Acid Base Hydronium Hydroxide Bitter Sour Strength Concentration Neutral Ionization Electrolyte Indicator pH Scale Neutralization Corrosive Ionization Acid Rain Ions Gas Laws and Liquids Unit Outline Main Topics 1) 2) 3) 4) Charles, Boyles and Gay-Lussac’s Laws Pressure and Pascal’s Gas Properties Osmosis, Buoyancy and Bernoulli’s Principle Essential Questions: 1) How does Charles, Boyles and Gay-Lusaac's laws compare and contrast to each other when it comes to pressure, volume and temperature of the gases at play? 2) What is the importance and how do we use the PV=nRT formula to the understand the movement of matter and gases? 3) How do gases and liquids behave when it comes to basic properties like diffusion, osmosis and concentration gradients? Vocabulary for the Unit: Pressure Pascals Diffusion Osmosis Weight Displacement Boyle’s Law Concentration Gradient Buoyant Force Charles’s Law Semipermeable Membrane Archimedes Principle Gay-Lussac’s Law Bernoulli’s Principle