Microsoft Word - SC 7th Gd Science Pacing_2012
advertisement

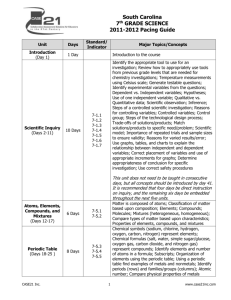
Blackville-Hilda Jr. High 7 Grade Science Pacing Guide th Unit Days Introduction (Day 1) 1 Day Scientific Inquiry (Days 2-11) Atoms, Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures (Days 12-17) 10 Days 6 Days Standard/ Indicator Major Topics/Concepts Introduction to the course 7-1.1 7-1.2 7-1.3 7-1.4 7-1.5 7-1.6 7-1.7 7-5.1 7-5.2 Identify the appropriate tool to use for an investigation; Review how to appropriately use tools from previous grade levels that are needed for chemistry investigations; Temperature measurements using Celsius scale; Generate testable questions; Identify experimental variables from the questions; Dependent vs. Independent variables; Hypotheses; Use of one independent variable; Qualitative vs. Quantitative data; Scientific observation; Inference; Steps of a controlled scientific investigation; Reasons for controlling variables; Controlled variables; Control group; Steps of the technological design process; Trade-offs of solutions/products; Match solutions/products to specific need/problem; Scientific model; Importance of repeated trials and sample sizes to ensure validity; Reasons for varied results/error; Use graphs, tables, and charts to explain the relationship between independent and dependent variables; Correct placement of variables and use of appropriate increments for graphs; Determine appropriateness of conclusion for specific investigation; Use correct safety procedures This unit does not need to be taught in consecutive days, but all concepts should be introduced by day 41. It is recommended that four days be direct instruction on inquiry, and the remaining six days be embedded throughout the next five units. Matter is composed of atoms; Classification of matter based upon composition; Elements; Compounds; Molecules; Mixtures (heterogeneous, homogeneous); Compare types of matter based upon characteristics; Properties of elements, compounds, and mixtures Blackville-Hilda Jr. 8th Grade Science Pacing Guide Revise 2013-2014 Periodic Table (Days 18-25 ) 8 Days 7-5.3 7-5.4 7-5.5 Chemical symbols (sodium, chlorine, hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen) represent elements; Chemical formulas (salt, water, simple sugar/glucose, oxygen gas, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen gas) represent compounds; Identify elements and number of atoms in a formula; Subscripts; Organization of elements using the periodic table; Using a periodic table find examples of metals and nonmetals; Identify periods (rows) and families/groups (columns); Atomic number; Compare physical properties of metals Unit Days Standard/ Indicator Major Topics/Concepts (luster, conductors, malleable, ductile, high density) and nonmetals (dull, nonconductors, brittle); Identify objects as metals or nonmetals Chemical Equations and Conservation of Matter (Days 26-31) 6 Days Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes (Days 32-37) 6 Days Acids and Bases (Days 38-41) 4 Days Days 42-43 7-5.7 7-5.8 Identify reactants and products in chemical equations; Explain how chemical equations illustrate the Law of Conservation of matter; Balanced chemical equations; Coefficients Physical properties (melting point, boiling point, density, color); Chemical properties (ability to burn, ability to rust); Classify properties as physical or chemical; Physical vs. Chemical changes; Physical 7-5.9 7-5.10 changes (change in state, change in size or shape); Sublimation; Evidence of chemical changes (color change, temperature change, precipitate, gas formation) Distinguish between acids, bases, and neutral solutions; pH scale; use of pH indicators (litmus paper, 7-5.6 phenolphthalein, pH paper); Identify solutions as acids or bases based on properties of solutions Review/Benchmark (covering content through day 41/standards 1 and 5) Blackville-Hilda Jr. 8th Grade Science Pacing Guide Revise 2013-2014 Scientific Inquiry (Days 44-54) 11 Days 7-1.1 7-1.2 7-1.3 7-1.4 7-1.5 7-1.6 7-1.7 Procedures for proper use of a compound microscope; Parts of microscope (eyepiece, coarse adjustment knob/focus, fine adjustment knob/focus, objective lenses, stage, stage clips, diaphragm, light source, arm, base); Safe use of microscope; Generate testable questions; Identify experimental variables from the questions; Dependent vs. Independent variables; Hypotheses; Use of one independent variable; Qualitative vs. Quantitative data; Scientific observation; Inference; Steps of a controlled scientific investigation; Reasons for controlling variables; Controlled variables; Control group; Steps of the technological design process; Trade-offs of solutions/products; Match solutions/products to specific need/problem; Scientific model; Importance of repeated trials and sample sizes to ensure validity; Reasons for varied results/error; Use graphs, tables, and charts to explain the relationship between independent and dependent variables; Correct placement of variables and use of appropriate increments for graphs; Determine appropriateness of conclusion for specific investigation; Use correct safety procedures Eleven days are allowed to provide time for inquiry concepts to be embedded and reinforced through actual experimentation during the next four units. Unit Days Standard/ Indicator Comparing Plant and Animal Cells (Days 55-62) 8 Days 7-2.1 7-2.2 Bacteria, Protists, and Viruses (Days 63-67) 5 Days 7-2.3 Major Topics/Concepts Structures and functions of cell structures (cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuole, chloroplasts, mitochondria, cell wall); Organelles; Diffusion; Osmosis; DNA; Chlorophyll; Cellulose; Distinguish between plant and animal cells Classification of bacteria in Kingdom Monera; Types of bacteria (spiral, bacillus, coccus); Classification of protists in Kingdom Protista; Similarities and differences among protists; Compare food gathering and locomotion of euglena, paramecium, and amoeba; Flagella; Cilia; Pseudopodia Introduce basic structure and characteristics of viruses to build knowledge base for 7-3.4. This information will not be assessed. Blackville-Hilda Jr. 8th Grade Science Pacing Guide Revise 2013-2014 Cell Processes (Days 68-71) 4 Days 7-2.4 Genes and Heredity (Days 72-84) 13 Days 7-2.5 7-2.6 7-2.7 Review/Benchmark (covering content from day 44-84/Standards 1 and 2) Days 85-86 Scientific Inquiry (Days 87-92) Functions and impact of processes on survival of the cell; Photosynthesis; Respiration; Mitosis; Waste elimination; Photosynthesis vs. Respiration Passing genetic information (DNA) from parents to offspring; Genes; Chromosomes; Inherited traits; Genotype vs. Phenotype; Dominant vs. Recessive traits; Heredity; Sex cells (sperm, egg); Allele; Use Punnett squares for monohybrid crosses; Purebred; Hybrid; Determine ratio or probability of trait inheritance using Punnett squares; Inherited vs. Acquired traits; Environmental factors (temperature, nutrients, injuries, disease, sun exposure, living conditions) and how they influence physical characteristics of organisms 6 Days 7-1.1 7-1.2 7-1.3 7-1.4 7-1.5 7-1.6 7-1.7 Same description as the previous sections for Scientific Inquiry Six days are allowed to provide time for inquiry concepts to be embedded and reinforced through actual experimentation during the next six units. Overview of structural organization (cells tissues organs systems organism); Cells (blood, bone, nerve/neurons); Tissues (nerve, muscle, epithelial, connective); Organs (heart, lungs, stomach); Systems (skeletal, muscular, integumentary, respiratory, circulatory, digestive, excretory, nervous, endocrine, immune, reproductive); Identify/recognize major organs and functions of the skeletal, muscular, and integumentary systems and explain how these systems interact in the human body Human Body Organization, Support, and Protection (Days 93-101) 9 Days Unit Days Standard/ Indicator 5 days 7-3.2 7-3.3 Identify/recognize major organs and functions of the respiratory and circulatory systems and explain how these systems interact in the human body 5 Days 7-3.2 7-3.3 Identify/recognize major organs and functions of the digestive and excretory systems and explain how these systems interact in the human body Respiratory and Circulatory Systems (Days 102-106) Digestive and Excretory Systems (Days 107-111) 7-3.1 7-3.2 7-3.3 Major Topics/Concepts Blackville-Hilda Jr. 8th Grade Science Pacing Guide Revise 2013-2014 Nervous System (Days 112-114) Infectious and Noninfectious Diseases (Days 115-122) Days 123-125 Identify/recognize major organs and functions of the 3 Days nervous system and explain how it interacts with other systems in the human body Effects of disease on major organs and systems; Cause, characteristics, and impact of infectious diseases (colds, influenza, athlete’s foot, AIDS, Strep throat); 8 Days 7-3.4 Pathogens; Immune system; Cause, characteristics, and impact of noninfectious diseases (diabetes, Parkinson’s, skin cancer, asthma) Review/Benchmark (covering content from day 87-122/Standards 1 and 3) 7-3.2 7-3.3 Ecosystem Organization and Energy Flow (Days 126-133) 8 Days 7-4.1 7-4.2 Natural Hazards (Days 134-138) 5 Days 7-4.3 Soil Quality (Days 139-144) 6 Days 7-4.4 Water (Days 145-150) 6 Days 7-4.5 Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources (Days 151-155) 5 Days 7-4.6 Unit Days Standard/ Indicator Characteristics of levels of organization in the living world (organism population community ecosystem biome); Habitat; Niche; Energy roles/trophic levels (producer, consumer, decomposer); Energy flow through food chains and food webs; Energy pyramids Ways natural hazards, changes in populations, and limiting factors impact the environment and lead to competition; Natural hazards (landslides, wildfires, floods); Population changes (immigration, emigration, births, deaths) impact on population density; Limiting factors (climate, food, water, space, shelter); Carrying capacity Soil as a valuable abiotic factor; Properties of soil that determine soil quality (soil profile, composition, pH, texture, particle size, permeability); Horizons; Humus; Sand; Loam; Sandy clay loam; Silt loam; Clay; Gravel Location of water (surface, ground); How water moves; Water as a valuable abiotic factor; Runoff; Zone of aeration; Zone of saturation; Water table; Aquifers; watershed/drainage basin; Divide; Importance of groundwater and surface-water to ecosystems and human activities; Floodplain; Delta Natural resources; Renewable resources (air, water, soil, trees, animals, solar energy); Nonrenewable resources (fossil fuels- coal, oil and natural gas); Depletion of natural resources and the importance of conservation measures; Human involvement in conservation of natural resources (reducing, reusing, recycling, protecting) Major Topics/Concepts Blackville-Hilda Jr. 8th Grade Science Pacing Guide Revise 2013-2014 Days 156-160 Days 161-165 Days 165-180 Review/Benchmark (covering content from day 126-155/Standard 1(in context of ecology) and standard 4 OR Districts may opt for a Comprehensive Benchmark (covering all content) and determine their own final testing window PASS Testing Review/Enrichment/Special Projects There will be four non-cumulative unit benchmarks with inquiry items (standard 1) included in each benchmark: • Chemical Nature of Matter: Indicators 7-1.1-1.7, 7-5.1-5.10 • Cells and Heredity: Indicators 7-1.1-1.7, 7-2.1-2.7 • Human Body Systems and Disease: Indicators 7-1.1-1.7, 7-3.1-3.4 • Ecology: Indicators 7-1.1-1.7, 7-4.1-4.6 These unit benchmarks can be given in any sequence if pacing differs from suggested CASE pacing. The comprehensive benchmark option is a cumulative assessment that tests all standards. Blackville-Hilda Jr. 8th Grade Science Pacing Guide Revise 2013-2014