General Chemistry Final test 2009.12.10. Point Max Name: 32p In
advertisement
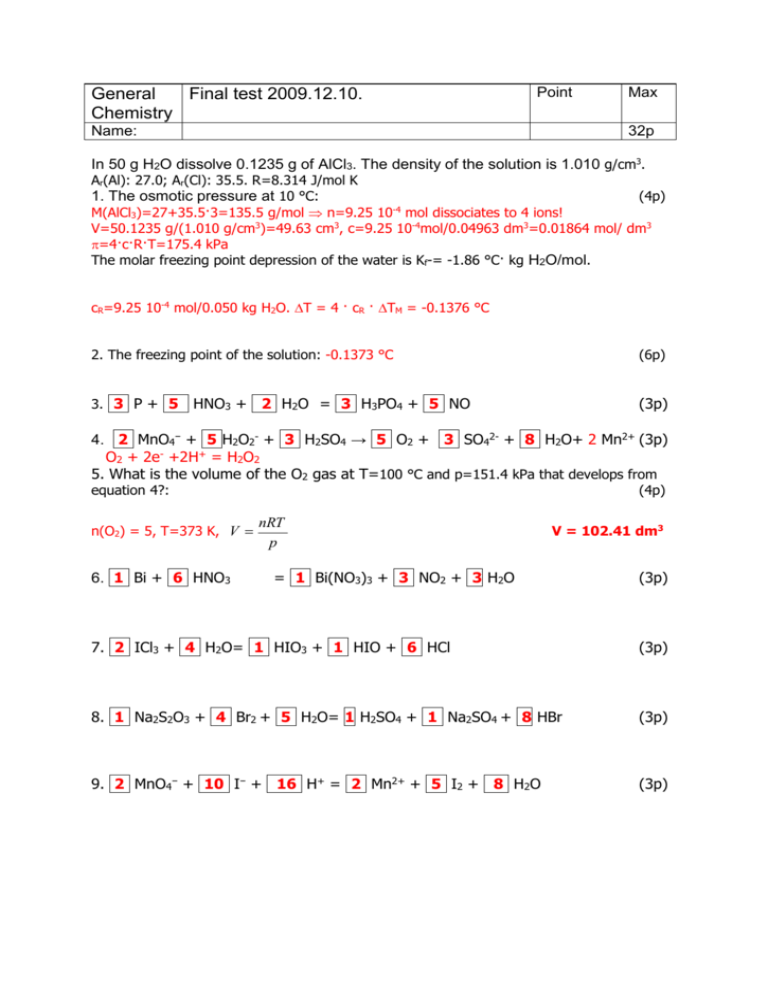
General Final test 2009.12.10. Chemistry Point Name: Max 32p In 50 g H2O dissolve 0.1235 g of AlCl3. The density of the solution is 1.010 g/cm3. Ar(Al): 27.0; Ar(Cl): 35.5. R=8.314 J/mol K 1. The osmotic pressure at 10 °C: (4p) -4 M(AlCl3)=27+35.5·3=135.5 g/mol n=9.25 10 mol dissociates to 4 ions! V=50.1235 g/(1.010 g/cm3)=49.63 cm3, c=9.25 10-4mol/0.04963 dm3=0.01864 mol/ dm3 =4·c·R·T=175.4 kPa The molar freezing point depression of the water is Kf-= -1.86 °C· kg H2O/mol. cR=9.25 10-4 mol/0.050 kg H2O. T = 4 · cR · TM = -0.1376 °C 2. The freezing point of the solution: -0.1373 °C (6p) 3. 3 P + 5 (3p) HNO3 + 2 H2O = 3 H3PO4 + 5 NO 4. 2 MnO4− + 5 H2O2- + 3 H2SO4 → 5 O2 + 3 SO42- + 8 H2O+ 2 Mn2+ (3p) O2 + 2e- +2H+ = H2O2 5. What is the volume of the O2 gas at T=100 °C and p=151.4 kPa that develops from equation 4?: n(O2) = 5, T=373 K, V 6. 1 Bi + 6 HNO3 (4p) nRT p V = 102.41 dm3 = 1 Bi(NO3)3 + 3 NO2 + 3 H2O (3p) 7. 2 ICl3 + 4 H2O= 1 HIO3 + 1 HIO + 6 HCl (3p) 8. 1 Na2S2O3 + 4 Br2 + 5 H2O= 1 H2SO4 + 1 Na2SO4 + 8 HBr (3p) 9. 2 MnO4− + 10 I− + 16 H+ = 2 Mn2+ + 5 I2 + 8 H2O (3p) Point General Final test 2009.12.10. Chemistry Name: Max 32p Name the following compounds (1p for each, total 10 points): 10. MnO4− permanganate anion 11. Na2S2O3 sodium thiosulphate 12. Bi(NO3)3 bismuth nitrate 13. HIO hypoiodous acic 14. HIO3 iodic acic 15. ICl3 iodine trichloride 16. H3PO4 phosphoric acide 17. H2O2 hydrogen peroxide (dihydrogen dioxide) 18. K2S4O6 potassium tetrathionate 19. CaSO3 calcium sulfite Reaction: N2O4 (g) 2 NO2 (g). Ar(N): 14; Ar(O): 16. Volume = 0.5 dm3, T= 80 °C, the initial mass of the N2O4 is 5.6 g. We wait for the dissociation equilibrium and in the equilibrium we measure the total pressure of 400 kPa Calculate equilibrium constant with mols (Kn), with concentrations (Kc), and with pressure (Kp), the degree of dissociation (), the volume %, and the average molar mass. M(N2O4)=92, M(NO2)=46. initial: ni(N2O4)=0.06087 mol, (5.6 g/92 g/mol) final (in equilibrium): ntotal=pV/(RT)= 0.06815 mol N2O4 2 NO2 Initial 0.06087 mol 0 mol Reaction −x mol + 2x mol Equilibrium 0.06087 −x mol 2x mol ntotal=0.06087 −x+2x = 0.06815 mol thus x=0.00728 mol. mol%(N2O4)= (0.06087 −0.00728 ) /0.06815 *100=78.64% = volume %(N2O4), # N2O4 NO2 K# n 0.05359 mol 0.01456 mol 0.01456 2 Kn c p 0.05359/0.5 M 0.7864·400=314.5 kPa 0.01456/0.5 M 0.2136 400=85.5 kPa 0.05359 3.956 10 3 2*Kn = Kc = 7.912 10-3 (85.5/101.325)2/ (314.5/101.325)=0.23 20. Kn = 3.956 10-3 (4p) 21. Kc = 7.912 10-3 (4p) 22. Kp = 0.23 (4p) 23. = x/0.06087 * 100% =11.96 % (4p) 24. volume % = 78.64 N2O4 (g) 25. average molar mass: 82.17 g/mol 21.36 NO2 (g) (4p) (2p) Point General Final test 2009.12.10. Chemistry Max Name: 36p 2+ Calculate the following non standard electrode potentials if °(Cu/Cu )= +0,340 V: 26. Metal Cu in 0.005 M CuSO4 solution: (Cu/Cu2+)= °(Cu/Cu2+)- a 0.0591 log red 2 a ox (4p) 0.0591V =+0.340 V+ log(0.005)= 0.272 V 2 27. Metal Cu in saturated Cu3(PO4)2 solution: (6p) Ksp[Cu3(PO4)2]= 1.08 x 10−13 Ksp=(3S)3·(2S)2=108·S5=1.08·10−13 S=1.00·10−3 M [Cu2+]=3S=3.0·10−3 M 0.059V log(3.0·10−3) = +0.266 V 2 28. Metal Fe in saturated Fe(OH)2 solution at pH=11.0, °(Fe/Fe2+)= -0,440 V: (6p) (Cu/Cu2+)=+0.340 V+ Ksp[Fe(OH)2]= 5.0·x 10−15 pH = 11.00 pOH = 3.00 [OH−] = 10−3 Ksp = [Fe2+]·[OH−]2 [Fe2+] = 5·10−15/(10−3)2 = 5.0·10−9 M (3p) 0.059V log(5.0·10−9) = 2 29. Hydrogen electrode in pH 7 solution: -0.686 V (H2/2H+)=°(H2/2H+)+0.059 V·lg[H+]=0.000 V + 0.059 V·(−pH) = −0.414 V (Fe/Fe2+)=-0.440 V+ (6p) 30. Hydrogen electrode in 0.02 M weak acid solution, the electrode potential is = -0.168 V. What is the value of Ks(weak acid): (8p) Ks = [H+]2/(c-[H+]) where -0.168 = -0.0592*pH 0.0592 log [H+] = -0.168 0.168 [H+] = 10 01 H 10 0.0592 =1.453 10-3 Ks = 1.138 10-4 31. Connect the electrodes in 29. and 30. What is the cell potential? Which electrode is the cathode and which electrode is the anode? How the cell potential will change in time as we use the cell? (6p) Ecell = E30-E29 = 0.2464 V Cathode E30 (more positive) reduction is going on Anode E29 (less positive) oxidation The cell potential will decrease to zero as the concentrations (activities) equalize in time (the salt bridge